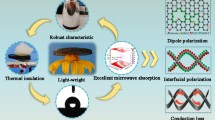
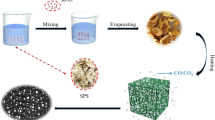
Abstract
Recently, biomass-derived three-dimensional (3D) porous carbon materials have been gaining more interest as promising microwave absorbers due to their low cost, vast availability, and sustainability. Here, a novel 3D interconnected porous magnetic carbon foams are in-situ synthesized via a combination of sol-gel and carbonization process with wheat straw as the carbon source and FeCl3·6H2O as the magnetic regulating agent. During the process of foams formation, the lignocelluloses from the steam-exploded wheat straw are converted into interconnected carbon sheet networks with hierarchical porous structures, and the precursor FeCl3·6H2O is converted into magnetic nanoparticles uniformly embedded in the porous carbon foams. The generated magnetic nanoparticles are benefit to enhance the interface polarization and magnetic loss ability to improve the efficient complementarities between the dielectric and magnetic loss, thus increasing the impedance matching. The obtained sample treated at 600 °C displays the best microwave absorption (MA) performance. It presents a minimal reflection loss (RL) of −43.6 dB at 7.1 GHz and the effective bandwidth (RL < −10 dB) is 3.3 GHz with the thickness of 4.7 mm. The 3D porous structure, multi-interfaces and the synergy of dielectric loss and magnetic loss make great contribution to the outstanding MA performance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, G. B.; Wu, H.; Liao, Q. L.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced microwave absorption performance of highly dispersed CoNi nanostructures arrayed on graphene. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 2689–2704.
Wang, H. G.; Meng, F. B.; Li, J. Y.; Li, T.; Chen, Z. J.; Luo, H. B.; Zhou, Z. W. Carbonized design of hierarchical porous carbon/Fe3O4@Fe derived from loofah sponge to achieve tunable high-performance microwave absorption. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 11801–11810.
Meng, F. B.; Wang, H. G.; Wei, W.; Chen, Z. J.; Li, T.; Li, C. Y.; Xuan, Y.; Zhou, Z. W. Generation of graphene-based aerogel microspheres for broadband and tunable high-performance microwave absorption by electrospinning-freeze drying process. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 2847–2861.
Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, B. H.; Liao, Q. L.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y. C.; Zhang, Y. Investigation on the broadband electromagnetic wave absorption properties and mechanism of Co3O4-nanosheets/reduced-graphene-oxide composite. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 980–990.
Liu, B.; Li, J. H.; Wang, L. F.; Ren, J. H.; Xu, Y. F. Ultralight graphene aerogel enhanced with transformed micro-structure led by polypyrrole nano-rods and its improved microwave absorption properties. Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 97, 141–150.
Meng, F. B.; Wang, H. G.; Huang, F.; Guo, Y. F.; Wang, Z. Y.; Hui, D.; Zhou, Z. W. Graphene-based microwave absorbing composites: A review and prospective. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2018, 137, 260–277.
Zhou, N.; An, Q. D.; Xiao, Z. Y.; Zhai, S. R.; Shi, Z. Solvothermal synthesis of three-dimensional, Fe2O3 NPs-embedded CNT/N-doped graphene composites with excellent microwave absorption performance. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 45156–45169.
Zhang, D. Q.; Jia, Y. X.; Cheng, J. Y.; Chen, S. M.; Chai, J. X.; Yang, X. Y.; Wu, Z. Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W. J.; Zhao, Z. L. et al. High-performance microwave absorption materials based on MoS2-graphene isomorphic hetero-structures. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 758, 62–71.
Feng, J.; Zong, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Long, G. K.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. H.; Zheng, X. L. Optimization of porous FeNi3/N-GN composites with superior microwave absorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 441–451.
Li, N.; Huang, G. W.; Li, Y. Q.; Xiao, H. M.; Feng, Q. P.; Hu, N.; Fu, S. Y. Enhanced microwave absorption performance of coated carbon nanotubes by optimizing the Fe3O4 nanocoating structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2973–2983.
Bhattacharya, P.; Das, C. K. In situ synthesis and characterization of CuFe10Al2O19/MWCNT nanocomposites for supercapacitor and microwave-absorbing applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 9594–9606.
Shu, R. W.; Li, W. J.; Zhou, X.; Tian, D. D.; Zhang, G. Y.; Gan, Y.; Shi, J. J.; He, J. Facile preparation and microwave absorption properties of RGO/MWCNTs/ZnFe2O4 hybrid nanocomposites. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 743, 163–174.
Han, M. K.; Yin, X. W.; Hou, Z. X.; Song, C. Q.; Li, X. L.; Zhang, L. T.; Cheng, L. F. Flexible and thermostable graphene/SiC nanowire foam composites with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 11803–11810.
Yang, Z. H.; Li, Z. W.; Yang, Y. H.; Xu, Z. C. J. Optimization of ZnxFe3−xO4 hollow spheres for enhanced microwave attenuation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21911–21915.
Li, Y. N.; Wu, T.; Jiang, K. D.; Tong, G. X.; Jin, K. Y.; Qian, N. X.; Zhao, L. H.; Lv, T. X. Mn2+ induced structure evolution and dual-frequency microwave absorption of MnxFe3−xO4 hollow/porous spherical chains made by a one-pot solvothermal approach. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 7119–7129.
Liu, W.; Pan, J. J.; Ji, G. B.; Liang, X. H.; Cheng, Y.; Quan, B.; Du, Y. W. Switching the electromagnetic properties of multicomponent porous carbon materials derived from bimetallic metal-organic frameworks: Effect of composition. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 3700–3709.
Zhang, H.; Hong, M.; Chen, P.; Xie, A. J.; Shen, Y. H. 3D and ternary rGO/MCNTs/Fe3O4 composite hydrogels: Synthesis, characterization and their electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 665, 381–387.
Deng, J.; Li, M. M.; Wang, Y. Biomass-derived carbon: Synthesis and applications in energy storage and conversion. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 4824–4854.
Jin, H.; Wang, X. M.; Gu, Z. R.; Fan, Q. H.; Luo, B. A facile method for preparing nitrogen-doped graphene and its application in supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 2015, 273, 1156–1162.
Perumal, A. B.; Sellamuthu, P. S.; Nambiar, R. B; Sadiku, E. R. Development of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan bio-nanocomposite films reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals isolated from rice straw. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 449, 591–602.
Zhou, X.; Zhou, X. L.; Tang, X. S.; Xu, Y. Process for calcium xylonate production as a concrete admixture derived from in-situ fermentation of wheat straw pre-hydrolysate. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 261, 288–293.
Littlewood, J.; Murphy, R. J.; Wang, L. Importance of policy support and feedstock prices on economic feasibility of bioethanol production from wheat straw in the UK. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2013, 17, 291–300.
Wang, L.; Littlewood, J.; Murphy, R. J. Environmental sustainability of bioethanol production from wheat straw in the UK. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2013, 28, 715–725.
Chen, M. J.; Zhang, X. Q.; Zhang, A. P.; Liu, C. F.; Sun, R. C. Direct preparation of green and renewable aerogel materials from crude bagasse. Cellulose 2016, 23, 1325–1334.
Zhong, C.; Wang, C. M.; Huang, F.; Jia, H. H.; Wei, P. Wheat straw cellulose dissolution and isolation by tetra-n-butylammonium hydroxide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 38–45.
Jiang, M.; Zhao, M. M.; Zhou, Z. W.; Huang, T.; Chen, X. L.; Wang, Y. Isolation of cellulose with ionic liquid from steam exploded rice straw. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 33, 734–738.
Wu, G. L.; Cheng, Y. H.; Yang, Z. H.; Jia, Z. R.; Wu, H. J.; Yang, L. J.; Li, H. L.; Guo, P. Z.; Lv, H. L. Design of carbon sphere/magnetic quantum dots with tunable phase compositions and boost dielectric loss behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 333, 519–528.
Du, Y. C.; Liu, W. W.; Qiang, R.; Wang, Y.; Han, X. J.; Ma, J.; Xu, P. Shell thickness-dependent microwave absorption of core-shell Fe3O4@C composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12997–3006.
Zhang, Y. N.; Liu, W.; Quan, B.; Ji, G. B.; Ma, J. N.; Li, D. R.; Meng, W. Achieving the interfacial polarization on C/Fe3C heterojunction structures for highly efficient lightweight microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 508, 462–468.
Wang, C.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, H. W.; Jin, C. D.; Sun, Q. F. Naturally three-dimensional laminated porous carbon network structured short nanochains bridging nanospheres for energy storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 15759–15770.
Fang, J. Y.; Shang, Y. S.; Chen, Z.; Wei, W.; Hu, Y.; Yue, X. G.; Jiang, Z. H. Rice husk-based hierarchically porous carbon and magnetic particles composites for highly efficient electromagnetic wave attenuation. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 4695–4705.
Lei, Y. L.; Chen, F.; Luo, Y. J.; Zhang, L. Three-dimensional magnetic graphene oxide foam/Fe3O4 nanocomposite as an efficient absorbent for Cr(VI) removal. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 4236–4245.
Jin, H; Nishiyama, Y.; Wada, M.; Kuga, S. Nanofibrillar cellulose aerogels. Colloids Surf. A: Phys. Eng. Aspects 2004, 240, 63–67.
Gan, S.; Zakaria, S.; Chia, C. H.; Chen, R. S.; Ellis, A. V.; Kaco, H. Highly porous regenerated cellulose hydrogel and aerogel prepared from hydrothermal synthesized cellulose carbamate. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0173743.
Wang, X. L.; Huang, X.; Chen, Z. R.; Liao, X. P.; Liu, C.; Shi, B. Ferromagnetic hierarchical carbon nanofiber bundles derived from natural collagen fibers: Truly lightweight and high-performance microwave absorption materials. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 10146–10153.
Yu, M.; Han, Y. Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L. J. Magnetic N-doped carbon aerogel from sodium carboxymethyl cellulose/collagen composite aerogel for dye adsorption and electrochemical supercapacitor. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 185–193.
Wang, Z. F.; Shen, B.; Zou, A. H.; He, N. Y. Synthesis of Pd/Fe3O4 nanoparticle-based catalyst for the cross-coupling of acrylic acid with iodobenzene. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 113, 27–34.
Wen, B.; Cao, M. S.; Hou, Z. L.; Song, W. L.; Zhang, L.; Lu, M. M.; Jin, H. B.; Fang, X. Y.; Wang, W. Z.; Yuan, J. Temperature dependent microwave attenuation behavior for carbon-nanotube/silica composites. Carbon 2013, 65, 124–139.
Feng, J.; Pu, F. Z.; Li, Z. X.; Li, X. H.; Hu, X. Y.; Bai, J. T. Interfacial interactions and synergistic effect of CoNi nanocrystals and nitrogen-doped graphene in a composite microwave absorber. Carbon 2016, 104, 214–225.
He, J. Z.; Wang, X. X.; Zhang, Y. L.; Cao, M. S. Small magnetic nanoparticles decorating reduced graphene oxides to tune the electromagnetic attenuation capacity. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 7130–7140.
Wang, L. N.; Jia, X. L.; Li, Y. F.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L. Q.; Liu, L. P.; Ren, X.; Yang, H. T. Synthesis and microwave absorption property of flexible magnetic film based on graphene oxide/carbon nanotubes and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 14940–14946.
Lv, H. L.; Liang, X. H.; Ji, G. B.; Zhang, H. Q.; Du, Y. W. Porous three-dimensional flower-like Co/CoO and its excellent electromagnetic absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9776–9783.
Hu, C. G.; Mou, Z. Y.; Lu, G. W.; Chen, N.; Dong, Z. L.; Hu, M. J.; Qu, L. T. 3D graphene-Fe3O4 nanocomposites with high-performance microwave absorption. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 13038–13043.
Wu, Z. C.; Tian, K.; Huang, T.; Hu, W.; Xie, F. F.; Wang, J. J.; Su, M. X.; Li, L. Hierarchically porous carbons derived from biomasses with excellent microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 11108–11115.
Cheng, Y.; Meng, W.; Li, Z. Y.; Zhao, H. Q.; Cao, J. M.; Du, Y. W.; Ji, G. B. Towards outstanding dielectric consumption derived from designing one-dimensional mesoporous MoO2/C hybrid heteronanowires. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 8981–8987.
Meng, F. B.; Wei, W.; Chen, X. N.; Xu, X. L.; Jiang, M.; Jun, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z. W. Design of porous C@Fe3O4 hybrid nanotubes with excellent microwave absorption. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 2510–2516.
Meng, F. B.; Wei, W.; Chen, J. J.; Chen, X. N.; Xu, X. L.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Z. W. Growth of Fe3O4 nanosheet arrays on graphene by a mussel-inspired polydopamine adhesive for remarkable enhancement in electromagnetic absorptions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 101121–101126.
Lu, M. M.; Cao, M. S.; Chen, Y. H.; Cao, W. Q.; Liu, J.; Shi, H. L.; Zhang, D. Q.; Wang, W. Z.; Yuan, J. Multiscale assembly of grape-like ferroferric oxide and carbon nanotubes: A smart absorber prototype varying temperature to tune intensities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19408–19415.
Jia, X. L.; Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, T. H.; Yang, F.; Dong, W. J.; Wang, G.; Yang, H. T.; Wei, F. Synthesis of lightweight and flexible composite aerogel of mesoporous iron oxide threaded by carbon nanotubes for microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 697, 138–146.
Yan, L. W.; Hong, C. Q.; Sun, B. Q.; Zhao, G. D.; Cheng, Y. H.; Dong, S.; Zhang, D. Y.; Zhang, X. H. In situ growth of core-sheath heterostructural SiC nanowire arrays on carbon fibers and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 6320–6331.
Liu, X. F.; Hao, C. C.; Jiang, H.; Zeng, M; Yu, R. H. Hierarchical NiCo2O4/Co3O4/NiO porous composite: A lightweight electromagnetic wave absorber with tunable absorbing performance. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 3770–3778.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51573149), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2682016CX069), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Sichuan Province (Nos. 2018GZ0132 and 2018GZ0427), and Sichuan Province Science and Technology Innovation Talent Project (No. 2017072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gou, G., Meng, F., Wang, H. et al. Wheat straw-derived magnetic carbon foams: In-situ preparation and tunable high-performance microwave absorption. Nano Res. 12, 1423–1429 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2376-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2376-x