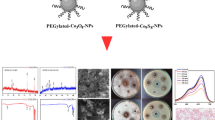
Abstract
Amyloid β-peptide (Aβ) aggregation is a critical step in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Inhibition of Aβ production, dissolution of existing aggregates and clearance of Aβ represent valid therapeutic strategies against AD. Herein, a novel platinum(II)-coordinated graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) nanosheet (g-C3N4@Pt) has been designed to covalently bind to Aβ and modulate the peptide’s aggregation and toxicity. Furthermore, g-C3N4@Pt nanosheets possess high photocatalytic activity and can oxygenate Aβ upon visible light irradiation, remarkably attenuating both the aggregation potency and neurotoxicity of Aβ. Due to its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and its good biocompatibility, g-C3N4@Pt nanosheet is a promising inhibitor of Aβ aggregation. This study may serve as a model for the engineering of novel multifunctional nanomaterials used for the treatment of AD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D. J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356.
Hamley, I. W. The amyloid beta peptide: A chemist’s perspective. Role in Alzheimer’s and fibrillization. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5147–5192.
Jakob-Roetne, R.; Jacobsen, H. Alzheimer’s disease: From pathology to therapeutic approaches. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3030–3059.
Gaggelli, E.; Kozlowski, H.; Valensin, D.; Valensin, G. Copper homeostasis and neurodegenerative disorders (Alzheimer’s, prion, and Parkinson's diseases and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis). Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1995–2044.
Takeda, S.; Sato, N.; Uchio-Yamada, K.; Sawada, K.; Kunieda, T.; Takeuchi, D.; Kurinami, H.; Shinohara, M.; Rakugi, H.; Morishita, R. Diabetes-accelerated memory dysfunction via cerebrovascular inflammation and Aβ deposition in an Alzheimer mouse model with diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7036–7041.
Jin, M.; Shepardson, N.; Yang, T.; Chen, G.; Walsh, D.; Selkoe, D. J. Soluble amyloid β-protein dimers isolated from Alzheimer cortex directly induce Tau hyperphosphorylation and neuritic degeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5819–5824.
De Felice, F. G.; Vieira, M. N. N.; Bomfim, T. R.; Decker, H.; Velasco, P. T.; Lambert, M. P.; Viola, K. L.; Zhao, W. Q.; Ferreira, S. T.; Klein, W. L. Protection of synapses against Alzheimer’s-linked toxins: Insulin signaling prevents the pathogenic binding of Abeta oligomers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1971–1976.
Ono, K.; Condron, M. M.; Teplow, D. B. Structureneurotoxicity relationships of amyloid β-protein oligomers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14745–14750.
Takahashi, T.; Mihara, H. Peptide and protein mimetics inhibiting amyloid β-peptide aggregation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1309–1318.
Frydman-Marom, A.; Rechter, M.; Shefler, I.; Bram, Y.; Shalev, D. E.; Gazit, E. Cognitive-performance recovery of Alzheimer's disease model mice by modulation of early soluble amyloidal assemblies. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 1981–1986.
Tjernberg, L. O.; Näslund, J.; Lindqvist, F.; Johansson, J.; Karlström, A. R.; Thyberg, J.; Terenius, L.; Nordstedt, C. Arrest of β-amyloid fibril formation by a pentapeptide ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8545–8548.
Ehrnhoefer, D. E.; Bieschke, J.; Boeddrich, A.; Herbst, M.; Masino, L.; Lurz, R.; Engemann, S.; Pastore, A.; Wanker, E. E. EGCG redirects amyloidogenic polypeptides into unstructured, off-pathway oligomers. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 558–566.
Matlack, K. E. S.; Tardiff, D. F.; Narayan, P.; Hamamichi, S.; Caldwell, K. A.; Caldwell, G. A.; Lindquist, S. Clioquinol promotes the degradation of metal-dependent amyloid-β (Aβ) oligomers to restore endocytosis and ameliorate Aβ toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4013–4018.
Barnham, K. J.; Kenche, V. B.; Ciccotosto, G. D.; Smith, D. P.; Tew, D. J.; Liu, X.; Perez, K.; Cranston, G. A.; Johanssen, T. J.; Volitakis, I. et al. Platinum-based inhibitors of amyloid-β as therapeutic agents for Alzheimer's disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6813–6818.
Hureau, C.; Faller, P. Platinoid complexes to target monomeric disordered peptides: A forthcoming solution against amyloid diseases? Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 4233–4237.
Scott, L. E.; Orvig, C. Medicinal inorganic chemistry approaches to passivation and removal of aberrant metal ions in disease. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4885–4910.
Cassagnes, L.-E.; Hervé, V.; Nepveu, F.; Hureau, C.; Faller, P.; Collin, F. The catalytically active copper-amyloid-beta state: Coordination site responsible for reactive oxygen species production. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11110–11113.
Lim, S.; Paterson, B. M.; Fodero-Tavoletti, M. T.; O’Keefe, G. J.; Cappai, R.; Barnham, K. J.; Villemagne, V. L.; Donnelly, P. S. A copper radiopharmaceutical for diagnostic imaging of Alzheimer’s disease: A bis(thiosemicarbazonato)copper(II) complex that binds to amyloid-β plaques. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 5437–5439.
Ma, G. L.; Huang, F.; Pu, X. W.; Jia, L. Y.; Jiang, T.; Li, L. Z.; Liu, Y. Z. Identification of [PtCl2(phen)] binding modes in amyloid-β peptide and the mechanism of aggregation inhibition. Chem.—Eur. J. 2011, 17, 11657–11666.
Kenche, V. B.; Hung, L. W.; Perez, K.; Volitakes, I.; Ciccotosto, G.; Kwok, J.; Critch, N.; Sherratt, N.; Cortes, M.; Lal, V. et al. Development of a platinum complex as an anti-amyloid agent for the therapy of Alzheimer's disease. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3374–3378.
Man, B. Y.-W.; Chan, H.-M.; Leung, C.-H.; Chan, D. S.-H.; Bai, L.-P.; Jiang, Z.-H.; Li, H.-W.; Ma, D.-L. Group 9 metal-based inhibitors of β-amyloid (1–40) fibrillation as potential therapeutic agents for Alzheimer's disease. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 917–921.
Cabaleiro-Lago, C.; Quinlan-Pluck, F.; Lynch, I.; Lindman, S.; Minogue, A. M.; Thulin, E.; Walsh, D. M.; Dawson, K. A.; Linse, S. Inhibition of amyloid β protein fibrillation by polymeric nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 15437–15443.
Yoo, S. I.; Yang, M.; Brender, J. R.; Subramanian, V.; Sun, K.; Joo, N. E.; Jeong, S.-H.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Kotov, N. A. Inhibition of amyloid peptide fibrillation by inorganic nanoparticles: Functional similarities with proteins. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5110–5115.
Mahmoudi, M.; Akhavan, O.; Ghavami, M.; Rezaeeef, F.; Ghiasi, S. M. A. Graphene oxide strongly inhibits amyloid beta fibrillation. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7322–7325.
Zheng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Liang, J.; Du, A. J.; Zhang, W. M.; Zhu, Z. H.; Smith, S. C.; Jaroniec, M. et al. Nanoporous graphitic-C3N4@carbon metal-free electrocatalysts for highly efficient oxygen reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 20116–20119.
Yan, S. C.; Li, Z. S.; Zou, Z. G. Photodegradation performance of g-C3N4 fabricated by directly heating melamine. Langmuir 2009, 25, 10397–10401.
Komatsu, T. Attempted chemical synthesis of graphite-like carbon nitride. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 799–801.
Zheng, Y.; Lin, L. H.; Wang, B.; Wang, X. C. Graphitic carbon nitride polymers toward sustainable photoredox catalysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 12868–12884.
Zhang, J. S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. C. Two-dimensional covalent carbon nitride nanosheets: Synthesis, functionalization, and applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 3092–3108.
Hou, Y.; Wen, Z. H.; Cui, S. M.; Guo, X. R.; Chen, J. H. Constructing 2D porous graphitic C3N4 nanosheets/ nitrogen-doped graphene/layered MoS2 ternary nanojunction with enhanced photoelectrochemical activity. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6291–6297.
Fang, Y.; Lv, Y. Y.; Che, R. C.; Wu, H. Y.; Zhang, X. H.; Gu, D.; Zheng, G. F.; Zhao, D. Y. Two-dimensional mesoporous carbon nanosheets and their derived graphene nanosheets: Synthesis and efficient lithium ion storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1524–1530.
Tian, J. Q.; Liu, Q.; Ge, C. J.; Xing, Z. C.; Asiri, A. M.; Al-Youbi, A. O.; Sun, X. P. Ultrathin graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets: A low-cost, green, and highly efficient electrocatalyst toward the reduction of hydrogen peroxide and its glucose biosensing application. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 8921–8924.
Wang, Q. B.; Wang, W.; Lei, J. P.; Xu, N.; Gao, F. L.; Ju, H. X. Fluorescence quenching of carbon nitride nanosheet through its interaction with DNA for versatile fluorescence sensing. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 12182–12188.
Zhang, X. D.; Xie, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J. J.; Pan, B. C.; Xie, Y. Enhanced photoresponsive ultrathin graphitic-phase C3N4 nanosheets for bioimaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 18–21.
Lee, E. Z.; Jun, Y. S.; Hong, W. H.; Thomas, A.; Jin, M. M. Cubic mesoporous graphitic carbon(IV) nitride: An all-in-one chemosensor for selective optical sensing of metal ions. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9706–9710.
Tang, Y. R.; Song, H. J.; Su, Y. Y.; Lv, Y. Turn-on persistent luminescence probe based on graphitic carbon nitride for imaging detection of biothiols in biological fluids. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11876–11884.
Li, M.; Zhao, C. Q.; Yang, X. J.; Ren, J. S.; Xu, C.; Qu, X. G. In situ monitoring Alzheimer's disease β-amyloid aggregation and screening of Aβ inhibitors using a perylene probe. Small 2013, 9, 52–55.
Klement, K.; Wieligmann, K.; Meinhardt, J.; Hortschansky, P.; Richter, W.; Fändrich, M. Effect of different salt ions on the propensity of aggregation and on the structure of Alzheimer’s abeta(1–40) amyloid fibrils. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 373, 1321–1333.
Wang, X. C.; Maeda, K.; Thomas, A.; Takanabe, K.; Xin, G.; Carlsson, J. M.; Domen, K.; Antonietti, M. A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 76–80.
Su, F. Z.; Mathew, S. C.; Lipner, G.; Fu, X. Z.; Antonietti, M.; Blechert, S.; Wang, X. C. mpg-C3N4-catalyzed selective oxidation of alcohols using O2 and visible light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 16299–16301.
Dong, F.; Wu, L. W.; Sun, Y. J.; Fu, M.; Wu, Z. B.; Lee, S. C. Efficient synthesis of polymeric g-C3N4 layered materials as novel efficient visible light driven photocatalysts. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 15171–15174.
Shalom, M.; Molinari, V.; Esposito, D.; Clavel, G.; Ressnig, D.; Giordano, C.; Antonietti, M. Sponge-like nickel and nickel nitride structures for catalytic applications. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1272–1276.
Geng, J.; Li, M.; Ren, J. S.; Wang, E. B.; Qu, X. G. Polyoxometalates as inhibitors of the aggregation of amyloid β peptides associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4184–4188.
Yu, H. J.; Li, M.; Liu, G. P.; Geng, J.; Wang, J. Z.; Ren, J. S.; Zhao, C. Q.; Qu, X. G. Metallosupramolecular complex targeting an α/β discordant stretch of amyloid β peptide. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 3145–3153.
Schlamadinger, D. E.; Kats, D. I.; Kim, J. E. Quenching of tryptophan fluorescence in unfolded cytochrome c: A biophysics experiment for physical chemistry students. J. Chem. Educ. 2010, 87, 961–964.
Puchalski, M. M.; Morra, M. J.; von Wandruszka, R. Assessment of inner filter effect corrections in fluorimetry. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1991, 340, 341–344.
Cheng, N. Y.; Tian, J. Q.; Liu, Q.; Ge, C. J.; Qusti, A. H.; Asiri, A. M.; Al-Youbi, A. O.; Sun, X. P. Au-nanoparticleloaded graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets: Green photocatalytic synthesis and application toward the degradation of organic pollutants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6815–6819.
Pei, W. B.; Wu, J. S.; Liu, J. L.; Ren, X. M.; Shen, L. J. Ion-pair complexes with strong near infrared absorbance: Syntheses, crystal structures and spectroscopic properties. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2010, 75, 191–197.
Tian, J. Q.; Liu, Q.; Asiri, A. M.; Al-Youbi, A. O.; Sun, X. P. Ultrathin graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet: A highly efficient fluorosensor for rapid, ultrasensitive detection of Cu2+. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5595–5599.
Li, M.; Xu, C.; Wu, L.; Ren, J. S.; Wang, E. B.; Qu, X. G. Self-assembled peptide-polyoxometalate hybrid nanospheres: Two in one enhances targeted inhibition of amyloid β-peptide aggregation associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Small 2013, 9, 3455–3461.
Mishra, R.; Bulic, B.; Sellin, D.; Jha, S.; Waldmann, H.; Winter, R. Small-molecule inhibitors of islet amyloid polypeptide fibril formation. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 4679–4682.
Li, M.; Yang, X. J.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, K. G.; Qu, X. G. Using graphene oxide high near-infrared absorbance for photothermal treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1722–1728.
Petkova, A. T.; Leapman, R. D.; Guo, Z. H.; Yau, W.-M.; Mattson, M. P.; Tycko, R. Self-propagating, molecular-level polymorphism in Alzheimer's beta-amyloid fibrils. Science 2005, 307, 262–265.
Balducci, C.; Beeg, M.; Stravalaci, M.; Bastone, A.; Sclip, A.; Biasini, E.; Tapella, L.; Colombo, L.; Manzoni, C.; Borsello, T. et al. Synthetic amyloid-β oligomers impair long-term memory independently of cellular prion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2295–2300.
Li, M.; Xu, C.; Ren, J. S.; Wang, E. B.; Qu, X. G. Photodegradation of β-sheet amyloid fibrils associated with Alzheimer’s disease by using polyoxometalates as photocatalysts. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 11394–11396.
Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Inhibition of metalinduced amyloid aggregation using light-responsive magnetic nanoparticle prochelator conjugates. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 868–873.
Rastogi, R. P.; Singh, S. P.; Häder, D.-P.; Sinha, R. P. Detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by the oxidantsensing probe 2',7'-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate in the cyanobacterium Anabaena variabilis PCC 7937. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 397, 603–607.
Ahmed, M. H.; Keyesa, T. E.; Byrne, J. A. The photocatalytic inactivation effect of Ag-TiO2 on β-amyloid peptide (1–42). J. Photoch. Photobio. A: Chem. 2013, 254, 1–11.
Pramanik, D.; Ghosh, C.; Dey, S. G. Heme-Cu bound Aβ peptides: Spectroscopic characterization, reactivity, and relevance to Alzheimer's disease. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15545–15552.
Taniguchi, A.; Sasaki, D.; Shiohara, A.; Iwatsubo, T.; Tomita, T.; Sohma, Y.; Kanai, M. Attenuation of the aggregation and neurotoxicity of amyloid-β peptides by catalytic photooxygenation. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1382–1385.
D’Angelo, B.; Santucci, S.; Benedetti, E.; Di Loreto, S.; Phani, R.; Falone, S.; Amicarelli, F.; Cerù, M.; Cimini, A. Cerium oxide nanoparticles trigger neuronal survival in a human Alzheimer disease model by modulating BDNF pathway. Curr. Nanosci. 2009, 5, 167–176.
Li, M.; Shi, P.; Xu, C.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Cerium oxide caged metal chelator: Anti-aggregation and anti-oxidation integrated H2O2-responsive controlled drug release for potential Alzheimer's disease treatment. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 2536–2542.
Harris, M. E.; Hensley, K.; Butterfield, D. A.; Leedle, R. A.; Carney, J. M. Direct evidence of oxidative injury produced by the Alzheimer's β-amyloid peptide (1–40) in cultured hippocampal neurons. Exp. Neurol. 1995, 131, 193–202.
Miranda, S.; Opazo, C.; Larrondo, L. F.; Muñoz, F. J.; Ruiz, F.; Leighton, F.; Inestrosa, N. C. The role of oxidative stress in the toxicity induced by amyloid beta-peptide in Alzheimer's disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2000, 62, 633–648.
Liu, Y. L.; Ai, K. L.; Liu, J. H.; Yuan, Q. H.; He, Y. Y.; Lu, L. H. A high-performance ytterbium-based nanoparticulate contrast agent for in vivo X-ray computed tomography imaging. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1437–1442.
Liu, Z.; Pu, F.; Huang, S.; Yuan, Q. H.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Long-circulating Gd2O3:Yb3+, Er3+ up-conversion nanoprobes as high-performance contrast agents for multi-modality imaging. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1712–1721.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Guan, Y., Chen, Z. et al. Platinum-coordinated graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet used for targeted inhibition of amyloid β-peptide aggregation. Nano Res. 9, 2411–2423 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1127-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1127-5