Abstract
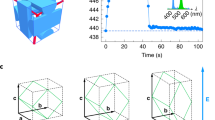
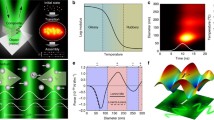
We demonstrate the fabrication of magnetically assembled one-dimensional chain-like photonic nanostructures with significantly high photonic stability. The key lies in the use of agarose hydrogel to prevent coagulation of the magnetic assemblies. When exposed to an external magnetic field, negatively charged Fe3O4@SiO2 particles can effectively assemble in the hydrogel matrix into one-dimensional chains with internal periodicity and display a fast, fully reversible, and tunable photonic response to the changes in the external field. The steric hindrance and the hydrogen bonding from the agarose network effectively limit the migration of the Fe3O4@SiO2 particles and their chain-like assemblies. As a result, the system shows remarkable stability in photonic response under external magnetic fields of large gradients, something which has previously been a challenge. The ability to stabilize the magnetic particle assemblies over a long period represents a major stride toward practical applications of such field-responsive photonic materials.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ge, J.; Yin, Y. Responsive photonic crystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1492.
Matsubara, K.; Watanabe, M.; Takeoka, Y. A thermally adjustable multicolor photochromic hydrogel. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1688.
Maurer, M. K.; Lednev, I. K.; Asher, S. A. Photoswitchable spirobenzopyran-based photochemically controlled photonic crystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1401.
Ge, J.; Hu, Y.; Yin, Y. Highly tunable superparamagnetic colloidal photonic crystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7428.
Ge, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Huynh, T.; Yin, Y. Self-assembly and field-responsive optical diffractions of superparamagnetic colloids. Langmuir 2008, 24, 3671.
Ge, J.; Yin, Y. Magnetically responsive colloidal photonic crystals. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 5041.
Ge, J.; Yin, Y. Magnetically tunable colloidal photonic structures in alkanol solutions. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3485.
Hu, Y.; He, L.; Yin, Y. Charge stabilization of superparamagnetic colloids for high performance responsive photonic structures. Small 2012, 8, 3795.
Hu, Y.; He, L.; Yin, Y. Magnetically responsive photonic nanochains. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3747.
Xu, X.; Friedman, G.; Humfeld, K. D.; Majetich, S. A.; Asher, S. A. Synthesis and utilization of monodisperse superparamagnetic colloidal particles for magnetically controllable photonic crystals. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 1249.
Wang, M.; He, L.; Yin, Y. Magnetic field guided colloidal assembly. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 110.
Zhang, Q.; Janner, M.; He, L.; Wang, M.; Hu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yin, Y. Photonic labyrinths: Two-dimensional dynamic magnetic assembly and in situ solidification. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 1770.
Malik, V.; Petukhov, A. V.; He, L.; Yin, Y.; Schmidt, M. Colloidal crystallization and structural changes in suspensions of silica/magnetite core-shell nanoparticles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14777.
Haque, M. A.; Kurokawa, T.; Kamita, G.; Yue, Y.; Gong, J. P. Rapid and reversible tuning of structural color of a hydrogel over the entire visible spectrum by mechanical stimulation. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 5200.
Asher, S. A.; Holtz, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, Z. Self-assembly motif for creating submicron periodic materials. polymerized crystalline colloidal arrays. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 4997.
Foulger, S. H.; Jiang, P.; Ying, Y.; Lattam, A. C.; Smith, D. W.; Ballato, J. Photonic bandgap composites. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 1898.
Arott, S.; Fulmer, A.; Scott, W. E. The agarose double helix and its function in agarose gel structure. J. Mol. Biol. 1974, 90, 269.
Brody, J. R.; Kern, S. E. History and principles of conductive media for standard DNA electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 333, 1.
Djabourov, M.; Clark, A. H.; Rowlands, D. W.; Ross-Murphy, S. B. Small-angle x-ray scattering characterization of agarose sols and gels. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 180.
Labropoulos, K. C.; Niesz, D. E.; Danforth, S. C.; Kevrekidis, P. G. Dynamic rheology of agar gels: Theory and experiments. Part I. Development of a rheological model. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 50, 393.
Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Tora, I.; Ide, M.; Lu, J.; Davis, R.; Green, D.; Landers, J. Rapid, cost-effective DNA quantification via a visually-detectable aggregation of superparamagnetic silica-magnetite nanoparticles. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 755.
Pernodet, N.; Maaloum, M.; Tinland, B. Pore size of agarose gels by atomic force microscopy. Electrophoresis 1997, 18, 55.
Maaloum, M.; Pernodet, N.; Tinland, B. Agarose gel structure using atomic force microscopy: Gel concentration and ionic strength effects. Electrophoresis 1998, 19, 1606.
Xiong, J.; Narayanan, J.; Liu, X.; Chong, T.; Chen, S.; Chung, T. Topology evolution and gelation mechanism of agarose gel. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 5638.
Ge, J.; Hu, Y.; Biasini, M.; Beyermann, W. P.; Yin, Y. Superparamagnetic magnetite colloidal nanocrystal clusters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4342.
Hu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Goebl, J.; Zhang, T.; Yin, Y. Control over the permeation of silica nanoshells by surface-protected etching with water. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 11836.
Workshop on Marine Algae Biotechnology: Summary Report; National Academy Press, 1986.
Narayanan, J.; Xiong, J.; Liu, X. Determination of agarose gel pore size: Absorbance measurements vis a vis other techniques. JPCS 2006, 28, 83.
Griess, G. A.; Guiseley, K. B.; Serwer, P. The relationship of agarose gel structure to the sieving of spheres during agarose gel electrophoresis. Biophys. J. 1993, 65, 138.
Johnson, E. M.; Berk, D. A.; Jain, R. K.; Deen, W. M. Hindered diffusion in agarose gels: Test of effective medium model. Biophys. J. 1996, 70, 1017.
Xia, Y.; Gates, B.; Yin, Y.; Lu, Y. Monodispersed colloidal spheres: Old materials with new applications. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 693.
Phillips, R. J.; Deen, W. M.; Brady, J. F. Hindered transport in fibrous membranes and gels: Effect of solute size and fiber configuration. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 1990, 139, 363.
Yamakov, V.; Milchev, A. Diffusion of a polymer chain in porous media. Phys. Rev. E: Stat., Nonlinear, Soft Matter Phys. 1997, 55, 1704.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., He, L., Han, X. et al. Magnetically responsive photonic films with high tunability and stability. Nano Res. 8, 611–620 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0732-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0732-z