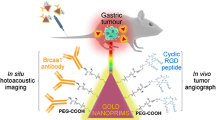
Abstract
By binding molecular probes that target tumor cells, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) with superior characteristics have shown great potential in tumor molecular imaging studies. The non-invasive, high-resolution, and three-dimensional imaging of the targeted AuNPs within the tumor is desirable for both diagnosis and therapy. In this study, gold nanoflowers (AuNFs) are presented as a novel contrast agent for photoacoustic tomography (PAT). By binding to folic acid, the molecular probe, the tail-vein injected AuNFs concentrated within the tumor site in mice; this was clearly visualized by three-dimensional (3D) PAT imaging. In addition, toxicity assay proved that AuNFs were harmless to living cells and animals. Our results demonstrate that AuNFs have great potential in tumor molecular imaging.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loo, C.; Lin, A.; Hirsch, L.; Lee, M. H.; Barton, J.; Halas, N. J.; West, J.; Drezek, R. Nanoshell-enabled photonics-based imaging and therapy of cancer. Technol. Cancer. Res. T. 2004, 3, 33–40.
Xu, M. H.; Wang, L. V. Photoacoustic imaging in biomedicine. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 77, 41101–41122.
Oraevsky, A.; Karabutov, A. Optoacoustic Tomography. In Biomedical Photonics Handbook. T. Vo-Dinh, Ed.; CRC; Boca Raton, FL, 2003; pp 34–31.
Li, C. H.; Wang, L. V. Photoacoustic tomography and sensing in biomedicine. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 54, R59–97.
Beard, P. Biomedical photoacoustic imaging. Interface Focus 2011, 1, 602–631.
Wang, L. H. V.; Hu, S. Photoacoustic tomography: In vivo imaging from organelles to organs. Science 2012, 335, 1458–1462.
Lu, W.; Huang, Q.; Geng, K. B.; Wen, X. X.; Zhou, M.; Guzatov, D.; Brecht, P.; Su, R.; Oraevsky, A.; Wang, L. V. et al. Photoacoustic imaging of living mouse brain vasculature using hollow gold nanospheres. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2617–2626.
Nie, L. M.; Wang, S. J.; Wang, X. Y.; Rong, P. F.; Bhirde, A.; Ma, Y.; Liu, G.; Huang, P.; Lu, G. M.; Chen, X. Y. In vivo volumetric photoacoustic molecular angiography and therapeutic monitoring with targeted plasmonic nanostars. Small 2014, 10, 1585–1593.
Wang, Y. W.; Xie, X. Y.; Wang, X. D.; Ku, G.; Gill, K. L.; O’Neal, D. P.; Stoica, G.; Wang, L. V. Photoacoustic tomography of a nanoshell contrast agent in the in vivo rat brain. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1689–1692.
Eghtedari, M.; Oraevsky, A.; Copland, J. A.; Kotov, N. A.; Conjusteau, A.; Motamedi, M. High sensitivity of in vivo detection of gold nanorods using a laser optoacoustic imaging system. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1914–1918.
Agarwal, A.; Huang, S. W.; O’Donnell, M.; Day, K. C.; Day, M.; Kotov, N.; Ashkenazi, S. Targeted gold nanorod contrast agent for prostate cancer detection by photoacoustic imaging. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 064701.
Yang, X. M.; Skrabalak, S. E.; Li, Z.-Y.; Xia, Y. N.; Wang, L. V. Photoacoustic tomography of a rat cerebral cortex in vivo with au nanocages as an optical contrast agent. Nano. Lett. 2007, 7, 3798–3802.
Song, K. H.; Kim, C. H.; Cobley, C. M.; Xia, Y. N.; Wang, L. V. Near-infrared gold nanocages as a new class of tracers for photoacoustic sentinel lymph node mapping on a rat model. Nano. Lett. 2009, 9, 183–188.
Chen, P. J.; Hu, S.-H.; Fan, C.-T.; Li, M.-L.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chen, S.-Y.; Liu, D.-M. A novel multifunctional nanoplatform with enhanced anti-cancer and photoacoustic imaging modalities using gold-nanorod-filled silica nanobeads. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 892–894.
Kim, C.; Song, H.-M.; Cai, X.; Yao, J. J.; Wei, A.; Wang, L. V. In vivo photoacoustic mapping of lymphatic systems with plasmon-resonant nanostars. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2841–2844.
Jiang, Y. Y.; Wu, X.-J.; Li, Q.; Li, J. J.; Xu, D. S. Facile synthesis of gold nanoflowers with high surface-enhanced Raman scattering activity. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 385601.
Ye, S. Q.; Yang, J. Y.; Xi, J. Z.; Ren, Q. S.; Li, C. H. Studying murine hindlimb ischemia by photoacoustic microscopy. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2012, 10, 121701.
Kumar, M.; Singh, G.; Arora, V.; Mewar, S.; Sharma, U.; Jagannathan, N. R.; Sapra, S.; Dinda, A. K.; Kharbanda, S.; Singh, H. Cellular interaction of folic acid conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and its use as contrast agent for targeted magnetic imaging of tumor cells. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2012, 7, 3503–3516.
Hainfeld, J. F.; Slatkin, D. N.; Smilowitz, H. M. The use of gold nanoparticles to enhance radiotherapy in mice. Phys. Med. Biol. 2004, 49, N309–315.
BALB/c Nude Mouse Hematology [online]. http:// www.criver.com/files/pdfs/rms/balbc-nude/rm_rm_r_balbc_nude_mouse_clinical_pathology_data.aspx (accessed Dec. 9th, 2014)
Song, K. H.; Stein, E. W.; Margenthaler, J. A.; Wang, L. V. Noninvasive photoacoustic identification of sentinel lymph nodes containing methylene blue in vivo in a rat model. J. Biomed. Opt. 2008, 13, 054033–054036.
Ko, H.; Singamaneni, S.; Tsukruk, V. V. Nanostructured surfaces and assemblies as SERS media. Small 2008, 4, 1576–1599.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1485-7.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Deng, Z., Yang, D. et al. Gold nanoflowers for 3D volumetric molecular imaging of tumors by photoacoustic tomography. Nano Res. 8, 2152–2161 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0688-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0688-4