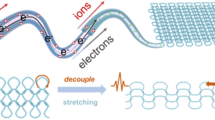
Abstract
In this study, we combined silver nanowires with cupro fabrics using a dipping-drying method to prepare electrically conductive fabrics. The silver nanowires were first adhered to and then absorbed by microfibers to form electrically conductive fibers. They also filled the gaps and spaces between the microfibers, and were stacked or piled together to form networks with high electrical conductivity. The electrically conductive fabric had low resistance and good stretchability, e.g., 0.0047–0.0091 Ω in the strain range of 0–190%. They also exhibited stable electrical conductivity, as well as excellent flexibility, which remained even when the fabric was stretched, shrunk, or bent. The results show that the electrically conductive fabric can be used as a smart textile, especially in fields associated with weaving, clothing, food products, lifestyle products, medicine, biology, electronics, aviation, and military equipment and accessories.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu, J. L.; Meng, H. P.; Li, G. Q.; Ibekwe, S. I. A review of stimuli-responsive polymers for smart textile applications. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 053001.
Castano, L. M.; Flatau, A. B. Smart fabric sensors and e-textile technologies: a review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 053001.
Akerfeldt, M.; Straat, M.; Walkenstrom, P. Electrically conductive textile coating with a PEDOT-PSS dispersion and a polyurethane binder. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 618–627.
Bashir, T.; Skrifvars, M.; Persson, N. K. Production of highly conductive textile viscose yarns by chemical vapor deposition technique: a route to continuous process. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 214–2221.
Anderson, E. B.; Ingildeev, D.; Hermanutz, F.; Muller, A.; Schweizer, M.; Buchmeiser, M. R. Synthesis and dry-spinning fibers of sulfinyl-based poly(p-phenylene vinylene) (ppv) for semi-conductive textile applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 11851–11860.
Yang, K.; Torah, R.; Wei, Y.; Beeby, S.; Tudor, J. Waterproof and durable screen printed silver conductive tracks on textiles. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 2023–2031.
Maity, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Singh, B.; Singh, A. P. Polypyrrole based electro-conductive textiles for heat generation. J. Text. Institu. 2014, 105, 887–893.
Hu, L. B.; Pasta, M.; La Mantia, F.; Cui, L. F.; Jeong, S.; Deshazer, H. D.; Choi, J. W.; Han, S. M.; Cui, Y. Stretchable, porous, and conductive energy textiles. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 708–714.
Lim, Z. H.; Chia, Z. X.; Kevin, M.; Wong, A. S. W.; Ho, G. W. A facile approach towards ZnO nanorods conductive textile for room temperature multifunctional sensors. Sensor Actuat. B 2010, 151, 121–126.
Nateghi, M. R.; Dehghan, S.; Shateri-Khalilabad, M. A facile route for fabrication of conductive hydrophobic textile materials using N-octyl/N-perfluorohexyl substituted polypyrrole. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2013, 62, 648–652.
Zhao, Y. P.; Cai, Z. S.; Fu, X. L.; Song, B. Z.; Zhu, H. Y. Electrochemical deposition and characterization of copper crystals on polyaniline/poly(ethylene terephthalate) conductive textiles. Synthetic Met. 2013, 175, 1–8.
Yamashita, T.; Khumpuang, S.; Miyake, K.; Itoh, T. Characterization of contact structure for woven electronic textile using conductive polymer micro-cantilever array. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 2014, 97, 48–53.
Perumalraj, R.; Anilkumar, A.; Devi, A. S. N.; Saranya, B.; Deepa, P.; Karthika, R.; Maheshwari, N. Silver-filled electrically conductive epoxy and silver nitrate-plated textile composite materials for EMC. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2011, 30, 203–215.
Ramachandran, T.; Vigneswaran, C. Design and development of copper core conductive fabrics for smart textiles. J. Ind. Text. 2009, 39, 81–93.
Kim, B. C.; Innis, P. C.; Wallace, G. G.; Low, C. T. J.; Walsh, F. C.; Cho, W. J.; Yu, K. H. Electrically conductive coatings of nickel and polypyrrole/poly(2-methoxyaniline-5-sulfonic acid) on nylon Lycra (R) textiles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 1296–1301.
Lee, H. M.; Choi, S.-Y.; Jung, A.; Ko, S. H. Highly conductive aluminum textile and paper for flexible and wearable electronics. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2013, 52, 7718–7723.
Ko, Y. H.; Kim, M. S.; Park, W.; Yu, J. S. Well-integrated ZnO nanorod arrays on conductive textiles by electrochemical synthesis and their physical properties. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 28.
Nilsson, E.; Oxfall, H.; Wandelt, W.; Rychwalski, R.; Hagstrom, B. Melt spinning of conductive textile fibers with hybridized graphite nanoplatelets and carbon black filler. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 2579–2587.
Khumpuang, S.; Miyake, K.; Itoh, T. Characterization of a SWNT-reinforced conductive polymer and patterning technique for applications of electronic textile. Sensor Actuat. A 2011, 169, 378–382.
Xue, C.-H.; Chen, J.; Yin, W.; Jia, S.-T.; Ma, J.-Z. Superhydrophobic conductive textiles with antibacterial property by coating fibers with silver nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 2468–2472.
Paul, G.; Torah, R.; Yang, K.; Beeby, S.; Tudor, J. An investigation into the durability of screen-printed conductive tracks on textiles. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2014, 25, 025006.
Paul, G.; Torah, R.; Beeby, S.; Tudor, J. The development of screen printed conductive networks on textiles for biopotential monitoring applications. Sensor Actuat. A 2014, 206, 35–41.
Wang, Y. D.; Lu, N.; Wang, W. T.; Liu, L. X.; Feng, L.; Zeng, Z. F.; Li, H. B.; Xu, W. Q.; Wu, Z. J.; Hu, W.; Lu, Y. Q.; Chi, L. F. Highly effective and reproducible surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates based on Ag pyramidal arrays. Nano Res. 2013, 6, 159–166.
Preston, C.; Xu, Y. L.; Han, X. G.; Munday, J. N.; Hu, L. B. Optical haze of transparent and conductive silver nanowire films. Nano Res. 2013, 6, 461–468.
Araki, T.; Jiu, J. T.; Nogi, M.; Koga, H.; Nagao, S.; Sugahara, T.; Suganuma, K. Low haze transparent electrodes and highly conducting air dried films with ultra-long silver nanowires synthesized by one-step polyol method. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 236–245.
Tokuno, T.; Nogi, M.; Karakawa, M.; Jiu, J. T.; Nge, T. T.; Aso, Y.; Suganuma, K. Fabrication of silver nanowire transparent electrodes at room temperature. Nano Res. 2011, 4, 1215–1222.
Jiu, J. T.; Nogi, M.; Sugahara, T.; Tokuno, T.; Araki, T.; Komoda, N.; Suganuma, K.; Uchida, H.; Shinozaki, K. Strongly adhesive and flexible transparent silver nanowire conductive films fabricated with a high-intensity pulsed light technique. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 23561–23567.
Cui, H.-W.; Fan, Q.; Li, D.-S. Novel flexible electrically conductive adhesives from functional epoxy, flexibilizers, micro-silver flakes and nano-silver spheres for electronic package. Polym. Int. 2013, 62, 1644–1651.
Cui, H.-W.; Jiu, J.-T.; Nagao, S.; Sugahara, T.; Suganuma, K.; Uchida, H.; Schroder, K. A. Ultra-fast photonic curing electrically conductive adhesives fabricated from vinyl ester resin and silver flakes for printed electronics. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 15914–15922.
Hu, L. B.; Pasta, M.; La Mantia, F.; Cui, L. F.; Jeong, S.; Deshazer, H. D.; Choi, J. W.; Han, S. M.; Cui, Y. Stretchable, porous, and conductive energy textiles. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 708–714.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, HW., Suganuma, K. & Uchida, H. Highly stretchable, electrically conductive textiles fabricated from silver nanowires and cupro fabrics using a simple dipping-drying method. Nano Res. 8, 1604–1614 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0649-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0649-y