Abstract
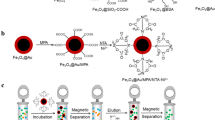
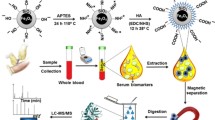
A new process to produce magnetite partially coated with strawberry-like gold nanoparticles in aqueous media is reported. The fast response to magnetic fields and optical properties of gold nanoparticle-based colloidal systems are the two main advantages of this new Fe@Au nanomaterial. These advantages allow for the use of this new colloidal nanomaterial for various purposes in proteomics and biomedicine, as proteins can bind to the surface, and the surface can also be functionalized. As proof-of-concept, the new Fe@Au nanoparticles have been assessed in biomarker discovery as a tool for pre-concentration and separation of proteins from complex proteomes. To this end, sera from healthy people were compared with sera from patients diagnosed with multiple myeloma. The application of this new Fe@Au nanomaterial combined with mass spectrometry has allowed for the identification of 53 proteins, and it has also shown that the heat shock protein HSP75 and the plasma protease C1 inhibitor are potential biomarkers for diagnostics and control of multiple myeloma progression.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Umut, E.; Pineider, E.; Arosio, P.; Sangregorio, C.; Corti, M.; Tabak, F.; Lascialfari, A.; Ghigna, P. Magnetic, optical and relaxometry properties of organically coated gold-magnetite (Au-Fe3O4) by hybrid nanoparticles for potential use in biomedical applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324 2373–2379.
Malaki, H.; Simchi, A.; Imani, M.; Costa, B. F. O. Size-controlled synthesis of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and their surface coating by gold for biomedical applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 3997–4005.
Gallo, J.; Long, N. J.; Aboagye, E. O. Magnetic nanoparticles as contrast agents in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7816–7833.
Harivardhan Reddy, L.; Arias, J. L.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Magnetic nanoparticles: Design and characterization, toxicity and biocompatiblity, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5818–5878.
Ling, D. S.; Hyeon, T. Chemical design of biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles for medical applications. Small 2013, 9, 1450–1466.
Ho, D.; Sun, X. L.; Sun, S. H. Monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles of theranostic applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 875–882.
Zhang, S.; Qi, Y. Y.; Yang, H.; Gong, M. F.; Zhang, D.; Zou, L. G. Optimization of the composition of bimetallic core/shell Fe2O3/Au nanoparticles for MRI/CT dual-mode imaging. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 2023.
Lou, L.; Yu, K.; Zhang, Z. L.; Huang. R.; Zhu, J. Z.; Wang, Y. T.; Zhu, Z. Q. Dual-mode protein detection based on Fe3O4-Au hybrid nanoparticles. Nano Res. 2014, 5, 272–282.
Zhao, T.; Chen, K. M.; Gu, H. C. Investigations on the interactions of proteins with polyampholyte-coated magnetite nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 14129–14135.
Jiang, H. R.; Zeng, X.; He, N. Y.; Deng, Y.; Lu, G. M.; Li, K. Preparation and biomedical applications of gold-coated magnetic nanocomposites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 1617–1625.
Magni, F.; Van der Burgt, Y. E. M.; Chinello C.; Mainini, V.; Gianazza, E.; Squeo, V.; Deelder, A. M.; Kienle, M. G. Biomarkers discovery by peptide and protein profiling in biological fluids based on functionalized magnetic beads purification and mass spectrometry. Blood Transfus. 2010, 8, s92–s97.
Fernández-Costa, C.; Reboiro-Jato, M.; Fdez-Riverola, F.; Ruiz-Romero, C.; Blanco, F.J.; Capelo-Martínez, J. L. Sequential depletion coupled to C18 sequential extraction as a rapid tool for human serum multiple profiling. Talanta 2014, 125, 189–195.
Fernández-Costa, C.; Calamia, V.; Fernandez-Puente, P.; Mateos, J.; Rocha, B.; Lourido, L.; Capelo, J. L.; Ruiz-Romero, C.; Blanco, F. J. Haptoglobin chains as potential biomarkers in serum of osteoarthritis disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, S65–S66.
López-Cortés, R.; Oliveira, E.; Núñez, C.; Lodeiro, C.; de la Cadena, M. P.; Fdez-Riverola, F.; López-Fernández, H.; Reboiro-Jato, M.; Glez-Peña, D.; Capelo, J. L.et al. Fast humam serum profiling through chemical depletion coupled to gold nanoparticle-assisted protein separation. Talanta 2012, 100, 239–245.
Goloudina, A. R.; Demidov, O. N.; Garrido, C. Inhibition of HSP70: A challenging anti-cancer strategy. Cancer Lett. 2012, 325, 117–124.
Afanasyeva, E. A.; Komarova, E. Y.; Laurson, L.-G.; Barhran, F.; Margulis, B. A.; Guzhova, L. V. Drug-induced Myc-mediated apoptosis of cancer cells is inhibited by stress protein HSP70. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 2615–2621.
Matokanovic, M.; Barisic, K.; Filipovic-Grcic, J.; Maysinger, D. HSP70 silencing with siRNA in nanocarriers enhances cancer cell death induced by the inhibitor HSP90. Eur. J. Pharma. Sci. 2013, 50, 149–158.
Turkevich J. Colloidal gold. Part I. Gold Bull. 1985, 18, 86–91.
Turkevich J. Colloidal gold. Part II. Gold Bull. 1985, 18, 125–131
Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P. C.; Hillier, J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday. Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75.
Vergés, M. A.; Costo, R.; Roca, A.G.; Marco, J. F.; Goya, G.F.: Serna, C. J.; Morales, M. P. Uniform and water stable magnetite nanoparticles with diameters around the monodomain-multidomain limit. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 134003–134010.
Caruso, F.; Lichtenfeld, H.; Giersig, M.; Möhwald, H. Electrostatic self-assembly of silica nanoparticle-polyelectrolyte multilayers on polystyrene latex particles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 8523–8524.
Caruso, F.; Caruso, R. A.; Möhwald, H. Nanoengineering of inorganic and hybrid hollow spheres by solloidal templating. Science 1998, 282, 1111–1114.
Caruso, F.; Caruso, R.A.; Mohwald, H. Production of hollow microspheres from nanostructured composite particles. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 3309–3314.
Caruso, F. Hollow capsule processing through colloidal templating and self-assembly. Chem.-Eur. J. 2000, 6, 413–419.
Warder, S. E.; Tucker, L. A.; Strelitzer, T. J.; McKeegan, E. M.; Meuth, J. L.; Jung, P. M.; Saraf, A.; Singh, B.; Lai-Zhang, J.; Gagne, G. et al. Reducing agent-mediated precipitation of high-abundance plasma proteins. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 387, 184–193.
Fernández, C.; Santos, H. M.; Ruíz-Romero, C.; Blanco, F. J.; Capelo-Martínez, J. L. A comparison of depletion versus equalization for reducing high-abundance proteins in human serum. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 2966–2974.
Candiano, G.; Bruschi, M.; Musante, L.; Santucci. L.; Ghiggeri, G. M.; Carnemolla, B.; Orecchia. P.; Zardi, L.; Righetti. P. G. Blue silver: A very sensitive colloidal Coomassie G-250 staining for proteome analysis. Electrophoresis 2004, 25, 1327–1333.
Oliveira, E.; Araújo. J.E.; Gómez-Meire, S.; Lodeiro, C.; Perez-Melon, C.; Iglesias-Lamas, E.; Otero-Glez, A.; Capelo, J. L.; Santos, H. M. Proteomics analysis of the peritoneal dialysate effluent reveals the presence of calcium-regulation proteins and acute inflammatory response. Clin. Proteomics 2014, 11, 17.
Bataille, R.; Harousseau, J. L. Multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1657–1664.
Elinav, E.; Nowarski, R.; Thaiss, C. A.; Hu, B.; Jin, C. C.; Flavell R.A. Inflammation-induced cancer: Crosstalk between tumours, immune cells and microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 759–771.
Zhang, L.; Fok, J. H. L.; Davies, F. E. Heat Shock proteins in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1132–1148.
Didelot, C.; Lanneau, D.; Brunet, M.; Joly, A.-L.; Thonel, A. D.; Chiosis, G.; Garrido, C. Anti-cancer therapeutic approaches based on intracellular and extracellular heat shock proteins. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 2839–2847.
Ciocca, D. R.; Calderwood, S. K.; Heat shock proteins in cancer: Diagnostic, prognostic, predictive and treatment implications. Cell Stress Chaperones 2005, 10, 86–103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Araújo, J.E., Lodeiro, C., Capelo, J.L. et al. Novel nanocomposites based on a strawberry-like gold- coated magnetite (Fe@Au) for protein separation in multiple myeloma serum samples. Nano Res. 8, 1189–1198 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0599-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0599-4