Abstract
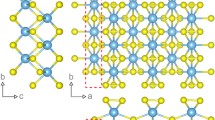
The progressive stacking of chalcogenide single layers gives rise to two-dimensional semiconducting materials with tunable properties that can be exploited for new field-effect transistors and photonic devices. Yet the properties of some members of the chalcogenide family remain unexplored. Indium selenide (InSe) is attractive for applications due to its direct bandgap in the near infrared, controllable p- and n-type doping and high chemical stability. Here, we reveal the lattice dynamics, optical and electronic properties of atomically thin InSe flakes prepared by micromechanical cleavage. Raman active modes stiffen or soften in the flakes depending on which electronic bonds are excited. A progressive blue-shift of the photoluminescence peaks is observed for decreasing flake thickness (as large as 0.2 eV for three single layers). First-principles calculations predict an even larger increase in the bandgap, 0.40 eV, for three single layers, and as much as 1.1 eV for a single layer. These results are promising from the point of view of the versatility of this material for optoelectronic applications at the nanometer scale and compatible with Si and III-V technologies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu, G.; Yu, K.; Wen, Z.; Chen, J. Semiconducting graphene: converting graphene from semimetal to semiconductor. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1353–1368.
Wang, F.; Liu, G.; Rothwell, S.; Nevius, M.; Tejeda, A.; Taleb-Ibrahimi, A.; Feldman, L. C.; Cohen, P. I.; Conrad, E. H. Wide-gap semiconducting graphene from Nitrogen-seeded SiC. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 4827–4832.
Novoselov, K. S.; Geim, A. K.; Morozov, S. V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S. V.; Grigorieva, I. V.; Firsov, A. A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669.
Wang, Y.; Brar, V. W.; Shytov, A. V.; Wu, Q.; Regan, W.; Tsai, H.-Z.; Zettl, A.; Levitov, L. S.; Crommie, M. F. Mapping Dirac quasiparticles near a single Coulomb impurity on graphene. Nat. Phys. 2012, 8, 653–657.
Wang, Q. H.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kis, A.; Coleman, J. N.; Strano, M. S. Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 699–712.
Geim, A. K.; Grigorieva, I. V. Van der Waals heterostructures. Nature 2013, 499, 419–425.
Ayari, A.; Cobas, E.,; Ogundadegbe, O.; Fuhrer, M. S. Realization and electrical characterization of ultrathin crystals of layered transition-metal dichalcogenides. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 014507.
Zhang, Y.; Ye, J.; Matsuhashi, Y.; Iwasa, Y. Ambipolar MoS2 thin flake transistors. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 1136–1140.
Fang, H.; Chuang, S.; Chang, T. C.; Takei, K.; Takahashi, T.; Javey, A. High-performance single layered WSe2 p-FETs with chemically doped contacts. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3788–3792.
Braga D.; Gutiérrez Lezama, I.; Berger, H.; Morpurgo, A. F. Quantitative determination of the band gap of WS2 with ambipolar ionic liquid-gated transistors. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5218–5223.
Hwang, W. S.; Remskar, M.; Yan, R.; Protasenko, V.; Tahy, K.; Chae, S. D.; Zhao, P.; Konar, A.; Xing, H.; Seabaugh, A.; et al. Transistors with chemically synthesized layered semiconductor WS2 exhibiting 105 room temperature modulation and ambipolar behavior. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 013107.
Liu, K. K.; Zhang, W.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chang, M.-T.; Su, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-S.; Li, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Growth of large-area and highly crystalline MoS2 thin layers on insulating substrates. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 1538–1544.
Elias, A. L.; Perea-López, N.; Castro-Beltrán, A.; Berkdemir, A.; Lv, R.; Feng, S.; Long, A. D.; Hayashi, T.; Kim, Y. A.; Endo, M.; et al. Controlled synthesis and transfer of large-area WS2 sheets: From single layer to few layers. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5235–5242.
Mak; K. F.; He, K.; Shan, J.; Heinz, T. F. Control of valley polarization in monolayer MoS2 by optical helicity. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 494–498.
Zeng, H.; Dai, J.; Yao, W.; Xiao, D.; Cui, X. Valley polarization in MoS2 monolayers by optical pumping. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 490–493.
Cao, T.; Wang, G.; Han, W.; Ye, H.; Zhu, C.; Shi, J.; Niu, Q.; Tan, P.; Wang, E.; Liu, B.; et al. Valley-selective circular dichroism of monolayer molybdenum disulphide. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 887.
Mak, K. F.; Lee, C.; Hone, J.; Shan, J.; Heinz, T. F. Atomically thin MoS2: A new direct-gap semiconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 136805.
Tongay, S.; Zhou, J.; Ataca, C.; Lo, K.; Matthews, T. S.; Li, J.; Grossman, J. C.; Wu, J. Thermally driven crossover from indirect toward direct bandgap in 2D semiconductors: MoSe2 versus MoS2. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5576–5580.
Zhao, W.; Ghorannevis, Z.; Chu, L.; Toh, M.; Kloc, C.; Tan, P.-H.; Eda, G. Evolution of electronic structure in atomically thin sheets of WS2 and WSe2. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 791–797.
Lopez-Sanchez, O.; Lembke, D.; Kayci, M.; Radenovic, A.; Kis, A. Ultrasensitive photodetectors based on monolayer MoS2. Nat. Nanotechol. 2013, 8, 497–501.
Baugher, B. W. H.; Churchill, H. O. H.; Yang, Y.; Jarillo-Herrero, P. Optoelectronic devices based on electrically tunable p-n diodes in a monolayer dichalcogenide. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 262–267.
Gauthier, M.; Polian, A.; Besson, J. M.; Chevy, A. Optical properties of gallium selenide under high pressure. Phys. Rev. B 1989, 40, 3837–3854.
Bringuier, E.; Bourdon, A.; Piccioli, N.; Chevy, A. Optical second-harmonic generation in lossy media: Application to GaSe and InSe. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 49, 16971–16982.
Segura, A.; Bouvier, J.; Andrés, M. V.; Manjón, F. J.; Muñoz, V. Strong optical nonlinearities in gallium and indium selenides related to inter-valence-band transitions induced by light pulses. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 56, 4075–4084.
Ferrer-Roca, Ch.; Bouvier, J.; Segura, A.; Andrés, M. V.; Muñoz, V. Light-induced transmission nonlinearities in gallium selenide. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 3780–3785.
Camassel, J.; Merle, P.; Mathieu, H.; Chevy, A. Excitonic absorption edge of indium selenide. Phys. Rev. B 1978, 17, 4718–4725.
Manjón, F. J.; Errandonea, D.; Segura, A.; Muñoz, V.; Tobías, G.; Ordejón, P.; Canadell, E. Experimental and theoretical study of band structure of InSe and In1−x GaxSe (x < 0.2) under high pressure. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 63, 125330.
Errandonea, D.; Segura, A.; Manjón, F. J.; Chevy, A.; Machado, E.; Tobias, G.; Ordejón, P.; Canadell, E. Crystal symmetry and pressure effects on the valence band structure of Γ-InSe and ɛ-GaSe: Transport measurements and electronic structure calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 125206.
Sánchez-Royo, J. F.; Segura, A.; Lang, O.; Schaar, E.; Pettenkofer, C.; Jaegermann, W.; Roa, L.; Chevy, A. Optical and photovoltaic properties of indium selenide thin films prepared by van der Waals epitaxy. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 2818–2823.
Julien, C.; Balkanski, M. Thin-film growth and structure for solid-state batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1991, 48–49, 1–11.
Martinez-Pastor, J.; Segura, A.; Valdes, J. L.; Chevy, A. Electrical and photovoltaic properties of indium-tin-oxide/p-InSe/Au solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 62, 1477–1483.
Rybkovskiy, D. V.; Arutyunyan, N. R.; Orekhov, A. S.; Gromchenko, I. A.; Vorobiev, I. V.; Osadchy, A. V.; Salaev, E. Yu.; Baykara, T. K.; Allakhverdiev, K. R.; Obraztsova, E. D. Size-induced effects in gallium selenide electronic structure: The influence of interlayer interactions. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 085314.
Hu, P.A.; Wen, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, P.; Xiao, K. Synthesis of few-layer GaSe nanosheets for high performance photodetectors. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5988–5994.
Lei, S.; Ge, L.; Najmaei, S.; George, A.; Kappera, R.; Lou, J.; Chhowalla, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Gupta, G.; Vajtai, R.; Mohite, A. D.; Ajayan, P. M. Evolution of the electronic band structure and efficient photo-detection in atomic layers of InSe. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1263–1272.
Late, D. J.; Liu, B.; Luo, J.; Yan, A.; Ramakrishna Matte, H. S. S.; Grayson, M.; Rao, C. N. R.; Dravid, V. P. GaS and GaSe ultrathin layer transistors. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3549–3554.
Mudd, G. W.; Svatek, S. A.; Ren, T.; Patanè, A.; Makarovsky, O.; Eaves, L.; Beton, P. H.; Kovalyuk, Z. D.; Lashkarev, G. V.; Kudrynskyi, Z. R.; et al. Tuning the bandgap of exfoliated InSe nanosheets by quantum confinement. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5714–5718.
Rigoult, J.; Rimsky, A.; Kuhn, A. Refinement of the 3R Γ-indium monoselenide structure type. Acta Cryst. B 1980, 36, 916–918.
Faradev, F. E.; Gasanly, N. M.; Mavrin, B. N.; Melnik, N. N. Raman scattering in some III–VI layer single crystals. Phys. Stat. Sol. (b) 1978, 85, 381–386.
Kuroda N.; Nishina, Y. Resonant Raman scattering at higher M0 exciton edge in layer compound InSe. Solid State Commun. 1978, 28, 439–443.
Millot, M.; Broto, J.-M.; George, S.; González, J.; Segura, A. Electronic structure of indium selenide probed by magnetoabsorption spectroscopy under high pressure. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 205211.
Mulliken, R. S. Electronic population analysis on LCAO-MO molecular wave functions. I. J. Chem. Phys. 1955, 23, 1833–1840.
Mulliken, R. S. Electronic population analysis on LCAO-MO molecular wave functions. II. J. Chem. Phys. 1955, 23, 1841–1846.
Arenal, R.; Ferrari, A. C.; Reich, S.; Wirtz, L.; Mevellec, J.-Y.; Lefrant, S.; Rubio, A.; Loiseau, A. Raman spectroscopy of single-wall boron nitride nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1812–1816.
Splendiani, A.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Kim, J.; Chim, C.-Y.; Galli, G.; Wang, F. Emerging photoluminescence in monolayer MoS2. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1271–1275.
Zeng, H.; Liu, G.-B.; Dai, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, B.; He, R.; Xie, L.; Xu, S.; Chen, X.; Yao, W.; Cui, X. Optical signature of symmetry variations and spin-valley coupling in atomically thin tungsten dichalcogenides. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1608.
Riera, J.; Segura, A.; Chevy, A. Photoluminescence in silicon-doped n-indium selenide. Phys. Stat. solidi (a) 1994, 142, 265–274.
Ferrer-Roca, Ch.; Segura, A.; Andrés, M. V.; Pellicer, J.; Muñoz, V. Investigation of nitrogen-related acceptor centers in indium selenide by means of photoluminescence: Determination of the hole effective mass. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 55, 6981–6987.
Segura, A.; Guesdon, J. P.; Besson, J. M.; Chevy, A. Photoconductivity and photovoltaic effect in indium selenide. J. Appl. Phys. 1983, 54, 876–888.
Ramasubramaniam, A. Large excitonic effects in monolayers of molybdenum and tungsten dichalcogenides. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 115409.
Manjón, F. J.; Segura, A.; Muñoz-Sanjosé, V.; Tobías, G.; Ordejón, P.; Canadell, E. Band structure of indium selenide investigated by intrinsic photoluminescence under high pressure. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 125201.
Martinez-Pastor, J.; Segura, A.; Julien, C.; Chevy, A. Shallow-donor impurities in indium selenide investigated by means of far-infrared spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 46, 4607–4616.
Davies, J. H. The Physics of Low-dimensional Semiconductors: An Introduction. Cambridge University Press: New York, 1997.
Dvorak, M.; Wei, S.-H.; Wu, Z. Origin of the variation of exciton binding energy in semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 016402.
Youn, D.-H.; Yu, Y.-J.; Choi, H.; Kim, S.-H.; Choi, S.-Y.; Choi, C.-G. Graphene transparent electrode for enhanced optical power and thermal stability in GaN light-emitting diodes. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 075202.
Lee, M. S.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; Choi, K.-H.; Kim, H.-K.; Kim, D.-G.; Lee, D.-Y.; Nam, S.; Park, J.-U. High-performance, transparent, and stretchable electrodes using graphene-metal nanowire hybrid structures. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2814–2821.
Shigetomi, S.; Ikari, T. Electrical and optical properties of n- and p-InSe doped with Sn and As. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 2301–2303.
Micocci, G.; Tepore, A.; Rella, R.; Siciliano, P. Investigation of deep levels in Zn-doped InSe single crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 71, 2274–2279.
Sánchez-Royo, J. F.; Pellicer-Porres, J.; Segura, A.; Gilliland, S.-J.; Avila, J.; Asensio, M.-C.; Safonova, O.; Izquierdo, M.; Chevy, A. Buildup and structure of the InSe/Pt interface studied by angle-resolved photoemission and X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 155308.
Ning, J.; Xiao, G.; Wang, C.; Liu, B.; Zou, G.; Zou, B. Synthesis of doped zinc blende-phase InSe:M (M = Fe and Co) nanocrystals for diluted magnetic semiconductor nanomaterials. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2013, 15, 3734–3738.
Chevy, A. Improvement of growth parameters for Bridgman-grown InSe crystals. J. Cryst. Growth 1984, 67, 119–124.
Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B864–B871.
Kohn W.; Sham, L. J. Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, A1133–A1138.
Soler, J. M.; Artacho, E.; Gale, J. D.; García, A.; Junquera, J.; Ordejón, P.; Sánchez-Portal, D. The SIESTA method for ab initio order-N materials simulation. J. Phys: Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 2745–2779.
Artacho, E.; Anglada, E.; Diéguez, O.; Gale, J. D.; García, A.; Junquera, J.; Martin, R. M.; Ordejón, P.; Pruneda, J. M.; Sánchez-Portal, D.; et al. The SIESTA method; developments and applicability. J. Phys: Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 064208.
Sánchez-Portal, D.; Ordejón, P.; Canadell, E. Computing the properties of materials from first principles with SIESTA. Struct. Bond. 2004, 113, 103–170.
Perdew, J. P.; Zunger, A. Self-interaction correction to density-functional approximations for many-electron systems. Phys. Rev. B 1981, 23, 5048–5079.
Trouiller, N.; Martins, J. L. Efficient pseudopotentials for plane-wave calculations. Phys. Rev. B 1991, 43, 1993–2006.
Kleinman, L.; Bylander, D. M. Efficacious form for model pseudopotentials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 48, 1425–1428.
Louie, S. G.; Froyen, S.; Cohen, M. L. Nonlinear ionic pseudopotentials in spin-density-functional calculations. Phys. Rev. B 1982, 26, 1738–1742.
Artacho, E.; Sánchez-Portal, D.; Ordejón, P.; García, A.; Soler, J. M. Linear-scaling ab-initio calculations for large and complex systems. Phys. Stat. Solidi B 1999, 215, 809–817.
Monkhorst, H. J.; Pack, J. D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez-Royo, J.F., Muñoz-Matutano, G., Brotons-Gisbert, M. et al. Electronic structure, optical properties, and lattice dynamics in atomically thin indium selenide flakes. Nano Res. 7, 1556–1568 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0516-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0516-x