Abstract
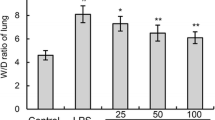
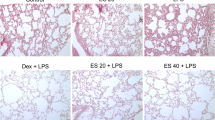
The aim of the present study was to assess the effects and mechanisms of Schisandrin B (SchB) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury (ALI). ALI was induced in mice by intratracheal instillation of LPS (1 mg/kg), and SchB (25, 50, and 75 mg/kg) was injected 1 h before LPS challenge by gavage. After 12 h, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) samples and lung tissues were collected. Histological studies demonstrated that SchB attenuated LPS-induced interstitial edema, hemorrhage, and infiltration of neutrophils in the lung tissue. SchB pretreatment at doses of 25, 50, and 75 mg/kg was shown to reduce LPS-induced lung wet-to-dry weight ratio and lung myeloperoxidase activity. In addition, pretreatment with SchB lowered the number of inflammatory cells and pro-inflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, and interleukin-6 in BALF. The mRNA and protein expression levels of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling-related molecules activated by P2X7 were investigated to determine the molecular mechanism of SchB. The findings presented here suggest that the protective mechanism of SchB may be attributed partly to the decreased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines through the inhibition of P2X7/NF-κB activation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bönig H, Packeisen J, Röhne B, Hempel L, Hannen M, Klein-Vehne A, Burdach S, Körholz D (1998) Interaction between interleukin 10 and interleukin 6 in human B-cell differentiation. Immunol Investig 27:267–280
Chang X, He H, Zhu L, Gao J, Wei T, Ma Z, Yan T (2015) Protective effect of apigenin on Freund’s complete adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats via inhibiting P2X7/NF-κB pathway. Chem Biol Interact 236:41–46
Chatterjee S, Das S (2015) P2X7 receptor as a key player in oxidative stress-driven cell fate in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015:172493
Chen N, Ko M (2010) Schisandrin B-induced glutathione antioxidant response and cardioprotection are mediated by reactive oxidant species production in rat hearts. Biol Pharm Bull 33:825–829
Cribbs SK, Martin GS (2009) Fluid balance and colloid osmotic pressure in acute respiratory failure: optimizing therapy. Expert Rev Respir Med 3:651–662
Eltom S, Stevenson CS, Rastrick J, Dale N, Raemdonck K, Wong S, Catley MC, Belvisi MG, Birrell MA (2011) P2X7 receptor and caspase 1activation are central to airway inflammation observed after exposure to tobacco smoke. PLoS One 6:e24097
Feng G, Jiang ZY, Sun B, Fu J, Li TZ (2015) Fisetin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via TLR4-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway in rats. Inflammation. doi:10.1007/s10753-015-0233-y
Gubert C, Fries GR, Pfaffenseller B, Ferrari P, Coutinho-Silva R, Morrone FB, Kapczinski F, Battastini AM (2014) Role of P2X7 receptor in an animal model of mania induced by d-amphetamine. Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-9031-z
Hughes JP, Hatcher JP, Chessell IP (2007) The role of P2X7 in pain and inflammation. Purinergic Signal 3:163–169
Jing W, Chunhua M, Shumin W (2015) Effects of acteoside on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in acute lung injury via regulation of NF-κB pathway in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 285:128–135
Li JW, Wu X (2015) Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate LPS-induced acute lung injury through KGF promoting alveolar fluid clearance of alveolar type II cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 19:2368–2378
Li W, Qiu X, Jiang H, Zhi Y, Fu J, Liu J (2015) Ulinastatin inhibits the inflammation of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice via regulation of AMPK/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2015.09.028
Liu Y, Xiao Y, Li Z (2011) P2X7 receptor positively regulates MyD88-dependent NF-κB activation. Cytokine 55:229–236
Lucattelli M, Cicko S, Müller T, Lommatzsch M, De Cunto CG, Cardini S, Sundas W, Grimm M, Zeiser R, Dürk T, Zissel G (2011) P2X7 receptor signaling in the pathogenesis of smoke-induced lung inflammation and emphysema. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 44:423–429
Lv XJ, Zhao LJ, Hao YQ, Su ZZ, Li JY, Du YW (2015) Schisandrin B inhibits the proliferation of human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells by inducing cycle arrest and apoptosis. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:6926–6936
Ma C, Zhu L, Wang J, He H, Chang X, Gao J, Shumin W, Yan T (2015) Anti-inflammatory effects of water extract of Taraxacum mongolicum hand.-Mazz on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in acute lung injury by suppressing PI3 K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 168:349–355
McInnes IB, Cruwys S, Bowers K, Braddock M (2014) Targeting the P2X7 receptor in rheumatoid arthritis: biological rationale for P2X7 antagonism. Clin Exp Rheumatol 32:878–882
Poroyko V, Meng F, Meliton A, Afonyushkin T, Ulanov A, Semenyuk E, Latif O, Tesic V, Birukova AA, Birukov KG (2015) Alterations of lung microbiota in a mouse model of LPS-induced lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 309:L76–L83
Thandavarayan RA, Giridharan VV, Arumugam S, Suzuki K, Ko KM, Krishnamurthy P, Watanabe K, Konishi T (2015) Schisandrin B prevents doxorubicin induced cardiac dysfunction by modulation of DNA damage, oxidative stress and inflammation through inhibition of MAPK/p53 signaling. PLoS One 10:e0119214
Vladimir L, Stephen AR, Alistair GR, Daniel EZ, Kathleen AK, Aaron EL, Matti N, Ilya S, Alan A (2009) Role of the transcription factor C/EBPδ in a regulatory circuit that discriminates between transient and persistent toll-like receptor 4-induced signals. Nat Immunol 10:437–443
Xing J, Yakubov B, Poroyko V, Birukova AA (2012) Opposite effects of ANP receptors in attenuation of LPS-induced endothelial permeability and lung injury. Microvasc Res 83:194–199
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in parts by grants from the Nanjing medical university, China. The authors gratefully acknowledge associate Professor Su Ning for her assistance in histopathological analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Zhiyong Cai and Jindi Liu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Z., Liu, J., Bian, H. et al. Suppression of P2X7/NF-κB pathways by Schisandrin B contributes to attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in acute lung injury. Arch. Pharm. Res. 39, 499–507 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0713-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0713-0