Abstract
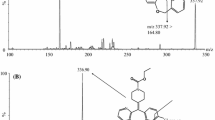
A highly sensitive bioanalytical method for the quantification of acacetin in human plasma was developed and comprehensively validated using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS). A minimal volume of human plasma sample (20 μL) was prepared by simple deproteinization with 80 μL of acetonitrile. Chromatographic separation was performed using Kinetex C18 column with an isocratic mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (20:80, v/v) containing 0.1 % formic acid at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min over a total run time of 2.0 min. Mass spectrometric detection was performed using multiple reaction-monitoring modes at the mass/charge transitions m/z 285.22 → 242.17 for acacetin and m/z 277.59 → 175.04 for chlorpropamide (internal standard). The calibration curve was linear over the range of 0.1–500 ng/mL with a lower limit of quantitation of 0.1 ng/mL. The coefficients of variation for both intra- and inter-day validation were less than 11.9 %, and the intra- and inter-day accuracy ranged from 96.8 to 108 %. Mean recovery of acacetin in human plasma was within the range of 91.5–95.6 %. This validated LC–MS/MS method was successfully applied to a human plasma protein binding study that indicated extensive and concentration-independent protein binding of acacetin in human plasma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhat TA, Nambiar D, Tailor D, Pal A, Agarwal R, Singh RP (2013) Acacetin inhibits in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis and downregulates Stat signaling and VEGF expression. Cancer Prev Res 6:1128–1139
Bian JH, Qian K, Xu X, Shen J (2006) Determination of acacetin in Xiangjuganmao Keli (no sweet) by HPLC. J Chin Med Mater 29:1233–1235
Bolandnazar S, Divsalar A, Valizadeh H, Khodaei A, Zakeri-Milani P (2013) Development and application of an HPLC method for erlotinib protein binding studies. Adv Pharm Bull 3:289–293
Bordbar A, Saboury A, Moosavi-Movahedi A (1996) The shapes of Scatchard plots for systems with two sets of binding sites. Biochem Educ 24:172–175
Chen WP, Yang ZG, Hu PF, Bao JP, Wu LD (2015) Acacetin inhibits expression of matrix metalloproteinases via a MAPK-dependent mechanism in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J Cell Mol Med 19:1910–1915
Chien ST, Lin SS, Wang CK, Lee YB, Chen KS, Fong Y, Shih YW (2011) Acacetin inhibits the invasion and migration of human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells by suppressing the p38alpha MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 350:135–148
Dai P, Zhu L, Luo F, Lu L, Li Q, Wang L, Wang Y, Wang X, Hu M, Liu Z (2015) Triple recycling processes impact systemic and local bioavailability of orally administered flavonoids. AAPS J 17:723–736
du Souich P, Verges J, Erill S (1993) Plasma protein binding and pharmacological response. Clin Pharmacokinet 24:435–440
Fan LH, Li X, Chen DY, Zhang N, Wang Y, Shan Y, Hu Y, Xu RA, Jin J, Ge RS (2015) Determination of acacetin in rat plasma by UPLC-MS/MS and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 986–987:18–22
Hu M (2007) Commentary: bioavailability of flavonoids and polyphenols: call to arms. Mol Pharm 4:803–806
Illamola SM, Labat L, Benaboud S, Tubiana R, Warszawski J, Treluyer JM, Hirt D (2014) Determination of total and unbound concentrations of lopinavir in plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and ultrafiltration methods. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 965:216–223
Mano Y, Kusano K (2015) A validated LC-MS/MS method of total and unbound lenvatinib quantification in human serum for protein binding studies by equilibrium dialysis. J Pharm Biomed Anal 114:82–87
Nielsen SE, Dragsted LO (1998) Column-switching high-performance liquid chromatographic assay for determination of apigenin and acacetin in human urine with ultraviolet absorbance detection. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 713:379–386
Shen H, Guo Q, Fang H, Wang Y, Jin M (2010a) Determination of quercetin, luteolin, apigenin and acacetin in Flos Chrysanthemi Indici by RP-HPLC. China J Chin Materia Medica 35:191–193
Shen KH, Hung SH, Yin LT, Huang CS, Chao CH, Liu CL, Shih YW (2010b) Acacetin, a flavonoid, inhibits the invasion and migration of human prostate cancer DU145 cells via inactivation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 333:279–291
Streit F, Shipkova M, Armstrong VW, Oellerich M (2004) Validation of a rapid and sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for free and total mycophenolic acid. Clin Chem 50:152–159
Valkama E, Salminen JP, Koricheva J, Pihlaja K (2004) Changes in leaf trichomes and epicuticular flavonoids during leaf development in three birch taxa. Ann Bot 94:233–242
Wang SF, Leng J, Xu YM, Feng ML (2013) Identification and determination of major constituents in a traditional Chinese medicine compound recipe Xiongdankaiming tablet using HPLC-PDA/ESI-MS(n) and HPLC-UV/ELSD. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 14:604–614
Watanabe K, Kanno S, Tomizawa A, Yomogida S, Ishikawa M (2012) Acacetin induces apoptosis in human T cell leukemia Jurkat cells via activation of a caspase cascade. Oncol Rep 27:204–209
Waters NJ, Jones R, Williams G, Sohal B (2008) Validation of a rapid equilibrium dialysis approach for the measurement of plasma protein binding. J Pharm Sci 97:4586–4595
Zeitlinger MA, Derendorf H, Mouton JW, Cars O, Craig WA, Andes D, Theuretzbacher U (2011) Protein binding: do we ever learn? Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:3067–3074
Zhao J, Dasmahapatra AK, Khan SI, Khan IA (2008) Anti-aromatase activity of the constituents from damiana (Turnera diffusa). J Ethnopharmacol 120:387–393
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIP) (No. 2009-0083533).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SB., Lee, T., Lee, H.S. et al. Development and validation of a highly sensitive LC–MS/MS method for the determination of acacetin in human plasma and its application to a protein binding study. Arch. Pharm. Res. 39, 213–220 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0697-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0697-1