Abstract
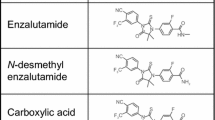
We characterized the pharmacokinetics of enzalutamide, a novel anti-prostate cancer drug, in rats after intravenous and oral administration in the dose range 0.5–5 mg/kg. Tissue distribution, liver microsomal stability, and plasma protein binding were also examined. After intravenous injection, systemic clearance, volumes of distribution at steady state (Vss), and half-life (T½) remained unaltered as a function of dose, with values in the ranges of 80.4–86.3 mL/h/kg, 1020–1250 mL/kg, and 9.13–10.6 h, respectively. Following oral administration, absolute oral bioavailability was 89.7 % and not dose-dependent. The recoveries of enzalutamide in urine and feces were 0.0620 and 2.04 %, respectively. Enzalutamide was distributed primarily in 10 tissues (brain, liver, kidneys, testis, heart, spleen, lungs, gut, muscle, and adipose) and tissue-to-plasma ratios of enzalutamide ranged from 0.406 (brain) to 10.2 (adipose tissue). Further, enzalutamide was stable in rat liver microsomes, and its plasma protein binding was 94.7 %. In conclusion, enzalutamide showed dose-independent pharmacokinetics at intravenous and oral doses of 0.5–5 mg/kg. Enzalutamide distributed primarily to 10 tissues and appeared to be eliminated primarily by metabolism.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astellas. 2012. Full prescribing information. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/203415lbl.pdf.
Astellas. 2014. Product monograph. http://www.cmsastellas.ca/uploads/pdf/Xtandi_PM_EN-Approved.pdf.
Crawford, E.D., M.A. Eisenberger, D.G. McLeod, J.T. Spaulding, R. Benson, F.A. Dorr, B.A. Blumenstein, M.A. Davis, and P.J. Goodman. 1989. A controlled trial of leuprolide with and without flutamide in prostatic carcinoma. The New England Journal of Medicine 321: 419–424.
Davies, B., and T. Morris. 1993. Physiological parameters in laboratory animals and humans. Pharmaceutical Research 10: 1093–1095.
El-Amm, J., N. Patel, A. Freeman, and J.B. Aragon-Ching. 2013. Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: critical review of enzalutamide. Clinical Medicine Insights: Oncology 7: 235–245.
FDA U. 2001. Guidance for industry, bioanalytical methods validation. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidancecomplianceregulatoryinformation/guidances/ucm070107.pdf.
Houston, J.B., and D.J. Carlile. 1997. Prediction of hepatic clearance from microsomes, hepatocytes, and liver slices. Drug Metabolism Reviews 29: 891–922.
Huggins C, Hodges CV. (2002). Studies on prostatic cancer. I. The effect of castration, of estrogen and of androgen injection on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. 1941. The Journal of Urology 167:948–51; discussion 52.
Kahl, P., L. Gullotti, L.C. Heukamp, S. Wolf, N. Friedrichs, R. Vorreuther, G. Solleder, P.J. Bastian, J. Ellinger, E. Metzger, et al. 2006. Androgen receptor coactivators lysine-specific histone demethylase 1 and four and a half LIM domain protein 2 predict risk of prostate cancer recurrence. Cancer Research 66: 11341–11347.
Koo, T.S., S.J. Kim, D.J. Ha, M. Baek, and H. Moon. 2011. Pharmacokinetics, brain distribution, and plasma protein binding of the antiepileptic drug lacosamide in rats. Archives of Pharmacal Research 34: 2059–2064.
Lee, K.R., Y.J. Chae, and T.S. Koo. 2011. Pharmacokinetics of lurasidone, a novel atypical anti-psychotic drug, in rats. Xenobiotica; The Fate of Foreign Compounds in Biological Systems 41: 1100–1107.
Metzger, E., M. Wissmann, N. Yin, J.M. Muller, R. Schneider, A.H. Peters, T. Gunther, R. Buettner, and R. Schule. 2005. LSD1 demethylates repressive histone marks to promote androgen-receptor-dependent transcription. Nature 437: 436–439.
Mullard, A. 2013. 2012 FDA drug approvals. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 12: 87–90.
Nguyen, T.V., M. Yao, and C.J. Pike. 2007. Flutamide and cyproterone acetate exert agonist effects: induction of androgen receptor-dependent neuroprotection. Endocrinology 148: 2936–2943.
Pang, K.S., and M. Rowland. 1977. Hepatic clearance of drugs. I. Theoretical considerations of a “well-stirred” model and a “parallel tube” model. Influence of hepatic blood flow, plasma and blood cell binding, and the hepatocellular enzymatic activity on hepatic drug clearance. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 5: 625–653.
Parkin, D.M., F. Bray, J. Ferlay, and P. Pisani. 2005. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 55: 74–108.
Peters, S.A. 2012. Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling and simulations: principles, methods, and applications in the pharmaceutical industry. Hoboken: Wiley.
Scher, H.I., T.M. Beer, C.S. Higano, A. Anand, M.E. Taplin, E. Efstathiou, D. Rathkopf, J. Shelkey, E.Y. Yu, J. Alumkal, et al. 2010. Antitumour activity of MDV3100 in castration-resistant prostate cancer: a phase 1-2 study. Lancet 375: 1437–1446.
Scher, H.I., K. Fizazi, F. Saad, M.E. Taplin, C.N. Sternberg, K. Miller, R. de Wit, P. Mulders, K.N. Chi, N.D. Shore, et al. 2012. Increased survival with enzalutamide in prostate cancer after chemotherapy. New England Journal of Medicine 367: 1187–1197.
Semenas, J., N. Dizeyi, and J.L. Persson. 2013. Enzalutamide as a second generation antiandrogen for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Drug Design Development and Therapy 7: 875–881.
Song, J.H., T.H. Kim, J.W. Jung, N. Kim, S.H. Ahn, S.O. Hwang, N.S. Kang, S.E. Yoo, and T.S. Koo. 2014. Quantitative determination of enzalutamide, an anti-prostate cancer drug, in rat plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. Biomedical Chromatography 28(8): 1112–1117.
Tran, C., S. Ouk, N.J. Clegg, Y. Chen, P.A. Watson, V. Arora, J. Wongvipat, P.M. Smith-Jones, D. Yoo, A. Kwon, et al. 2009. Development of a second-generation antiandrogen for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Science 324: 787–790.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the research fund of Chungnam National University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Tae-Heon Kim and Jong-Woo Jeong have been contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, TH., Jeong, JW., Song, JH. et al. Pharmacokinetics of enzalutamide, an anti-prostate cancer drug, in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 38, 2076–2082 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0592-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0592-9