Abstract
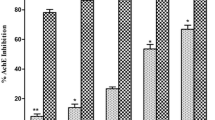
As part of our ongoing isolation of cholinesterase (ChE) inhibitors from natural marine sources, the bioactivity of the ethanolic extracts from 12 Korean seaweeds were screened for their inhibitory activities against acetylcholinesterase (AChE), butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), and total reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Eisenia bicyclis exhibited promising inhibitory properties against AChE, BChE and total ROS with inhibition percentages (%) of 68.01 ± 1.37, 95.72 ± 3.80, and 73.20 ± 1.82 at concentrations of 25 µg/mL, respectively. Among the different solvent–soluble fractions obtained from the ethanolic extract, the ethyl acetate (EtOAc) fraction was found to cause the most potent scavenging, or inhibitory activities, against 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), peroxynitrite (ONOO−) and total ROS with the respective IC50 values of 2.48 ± 0.01, 8.70 ± 0.06, and 0.81 ± 0.03 µg/mL. Likewise, the EtOAc fraction also exhibited potent inhibitory activities against AChE and BChE with IC50 values of 2.78 ± 0.07 and 3.48 ± 0.32 µg/mL, respectively. Silica gel column chromatography of the EtOAc fraction yielded a phlorotannin, 974-B, based on the comparison with reported 1H- and 13C-NMR spectroscopic data. 974-B showed strong scavenging/or inhibitory potential against DPPH, ONOO−, total ROS, AChE, and BChE with the respective IC50 values of 0.86 ± 0.02, 1.80 ± 0.01, 6.45 ± 0.04, 1.95 ± 0.01, and 3.26 ± 0.08 µM, respectively. These results indicate that the potential of E. bicyclis and its phlorotannin for use in the development of therapeutic or preventive agents of Alzheimer’s disease mainly through ChE inhibition and additional antioxidant capacities.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, B.R., H.E. Moon, H.R. Kim, H.A. Jung, and J.S. Choi. 2012. Neuroprotective effect of edible brown alga Eisenia bicyclis on amyloid beta peptide-induced toxicity in PC12 cells. Archives of Pharmacal Research 35: 1989–1998.
Airanthi, M.K., M. Hosokawa, and K. Miyashita. 2011. Comparative antioxidant activity of edible Japanese brown seaweeds. Journal of Food Science 76: 104–111.
Artan, M., Y. Li, F. Karadeniz, S.H. Lee, M.M. Kim, and S.K. Kim. 2008. Anti-HIV-1 activity of phloroglucinol derivative, 6,6′-bieckol, from Ecklonia cava. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry 16: 7921–7926.
Athukorala, Y., K.W. Lee, S.K. Kim, and Y.J. Jeon. 2007. Anticoagulant activity of marine green and brown algae collected from Jeju Island in Korea. Bioresource Technology 98: 1711–1716.
Atta-ur-Rahman, and M.I. Choudhary. 2001. Bioactive natural products as a potential source of new pharmacophores. A theory of memory. Pure and Applied Chemistry 73: 555–560.
Blois, M.S. 1958. Antioxidant determination by the use of a stable free radical. Nature 181: 1199–1200.
Butterfield, D.A., J. Drake, C. Pocernich, and A. Castegna. 2001. Evidence of oxidative damage in Alzheimer’s diseases brain: Central role for amyloid β-peptide. Trends in Molecular Medicine 7: 548–554.
Butterfield, D.A., T. Reed, S.F. Newman, and R. Sultana. 2007. Roles of amyloid β-peptide-associated oxidative stress and brain protein modifications in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s diseases and mild cognitive impairment. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 43: 658–677.
Cardona, F., C. Andrés-Lacueva, S. Tulipani, F.J. Tinahones, and M.I. Queipo-Ortuño. 2013. Benefits of polyphenols on gut microbiota and implications in human health. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 24: 1415–1422.
Cecchi, C., S. Latorraca, S. Sorbi, T. Iantomasi, F. Favilli, M.T. Vincenzini, and G. Liquri. 1999. Gluthatione level is altered in lymphoblasts from patients with familial Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience Letters 275: 152–154.
Cheng, D.H., H. Ren, and X.C. Tang. 1996. Huperzine A, a novel promising acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. NeuroReport 8: 97–101.
Choi, B.W., G. Ryu, S.H. Park, E.S. Kim, J. Shin, S.S. Roh, H.C. Shin, and B.H. Lee. 2007. Anticholinesterase activity of plastoquinones from Sargassum sagamianum: Lead compounds for Alzheimer’s diseases therapy. Phytotherapy Research 21: 423–426.
Ellman, G.L., K.D. Courtney, V.J. Andres, and R.M. Featherstone. 1961. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochemistry and Pharmacology 7: 88–95.
Ermakova, S., R. Men’shova, O. Vishchuk, S.M. Kim, B.H. Um, V. Isakov, and T. Zvyagintseva. 2013. Water-soluble polysaccharides from the brown alga Eisenia bicyclis: Structural characteristics and antitumor activity. Algal Research 2: 51–58.
Fallarero, A., J.J. Loikkanen, P.T. Männistö, O. Castañeda, and A. Vidal. 2003. Effects of aqueous extracts of Halimeda incrassata (Ellis) Lamouroux and Bryothamnion triquetrum (S.G.Gmelim) Howe on hydrogen peroxide and methyl mercury-induced oxidative stress in GT1–7 mouse hypothalamic immortalized cells. Phytomedicine 10: 39–47.
Greig, N.H., T. Utsuki, Q. Yu, X. Zhu, H.W. Holloway, T. Perry, B. Lee, D.K. Ingram, and D.K. Lahiri. 2001. A new therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s disease treatment: Attention to butyrylcholinesterase. Current Medical Research and Opinion 17: 159–165.
Heo, S.J., E.J. Park, K.W. Lee, and Y.J. Jeon. 2005. Antioxidant activities of enzymatic extracts from brown seaweeds. Bioresource Technology 96: 1613–1623.
Heo, S.J., J.Y. Hwang, J.I. Choi, J.S. Han, H.J. Kim, and Y.J. Jeon. 2009. Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol isolated from Ishige okamurae, a brown algae, a potent α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitor, alleviates postprandial hyperglycemia in diabetic mice. European Journal of Pharmacology 615: 252–256.
Houghton, P.J., J.M. Agbedahunsi, and A. Adegbulugbe. 2004. Choline esterase inhibitory properties of alkaloids from two Nigerian Crinum species. Phytochemistry 65: 2893–2896.
Jeong, E.S., Y.H. Yoon, and J.K. Kim. 2009. Contrasting correlation in the inhibition response of ADP-induced platelet aggregation and the anti-coagulant activities of algal fucoidans derived from Eisenia bicyclis and Un-daria pinnatifida sporophylls (Mekabu). Fisheries Aquatic Sciences 12: 194–202.
Jha, R., and S.I. Rizvi. 2009. Age-dependent decline in erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase activity: Correlation with oxidative stress. Biomedical Papers of the Medical Faculty of the University Palacký, Olomouc, Czechoslovakia 153: 195–198.
Jung, H.A., S.E. Jin, B.R. Ahn, C.M. Lee, and J.S. Choi. 2013. Anti-inflammatory activity of edible brown alga Eisenia bicyclis and its constituents fucosterol and phlorotannins in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Food and Chemical Toxicology 59: 199–206.
Jung, H.A., S.H. Oh, and J.S. Choi. 2010. Molecular docking studies of phlorotannins from Eisenia bicyclis with BACE1 inhibitory activity. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 20: 3211–3215.
Kang, K.A., K.H. Lee, S. Chae, R. Zhang, M.S. Jung, Y.M. Ham, J.S. Baik, N.H. Lee, and J.W. Hyun. 2006. Cytoprotective effect of phloroglucinol on oxidative stress induced cell damage via catalase activation. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 97: 609–620.
Khan, S.B., C.S. Kong, J.A. Kim, and S.K. Kim. 2010. Protective effect of Amphiroa dilatata on ROS induced oxidative damage and MMP expressions in HT1080 cells. Biotechnology Bioprocess Engineering 15: 191–198.
Kim, M.M., N. Rajapakse, and S.K. Kim. 2009. Anti-inflammatory effect of Ishige okamurae ethanolic extract via inhibition of NF-κB transcription factor in RAW 264.7 cells. Phytotherapy Research 23: 628–634.
Kong, C.S., J.A. Kim, N.Y. Yoon, and S.K. Kim. 2009. Induction of apoptosis by phloroglucinol derivative from Ecklonia cava in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Food and Chemical Toxicology 47: 1653–1658.
Kooy, N.W., J.A. Royall, H. Ischiropoulos, and J.S. Beckman. 1994. Peroxynitrite-mediated oxidation of dihydrorhodamine 123. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 16: 149–156.
Lahiri, D.K., J.T. Rogers, K. Sambamurti, and N.H. Greig. 2004. Rationale for the development of cholinesterase inhibitors as anti-Alzheimer agents. Current Pharmaceutical Design 10: 3111–3119.
Lebel, C.P., and S.C. Bondy. 1990. Sensitive and rapid quantitation of oxygen reactive species formation in rat synaptosomes. Neurochemistry International 17: 435–440.
Li, Y., S.H. Lee, Q.T. Le, M.M. Kim, and S.K. Kim. 2008. Anti-allergic effects of phlorotannins on histamine release via binding inhibition between IgE and Fc epsilonRI. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 56: 12073–12080.
Li, Y., Z.J. Qian, B. Ryu, S.H. Lee, M.M. Kim, and S.K. Kim. 2009. Chemical components and its antioxidant properties in vitro: an edible marine brown alga, Ecklonia cava. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry 17: 1963–1973.
Lim, C.S., D.Q. Jin, J.Y. Sung, J.H. Lee, H.G. Choi, I. Ha, and J.S. Han. 2006. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of the methanolic extract of Neorhodomela aculeate in hippocampal and microglial cells. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 29: 1212–1216.
Liu, J., J. Qiu, M. Wang, L. Wang, L. Su, J. Gao, Q. Gu, J. Xu, S.L. Huang, L.Q. Gu, Z.S. Huang, and D. Li. 2014. Synthesis and characterization of 1H-phenanthro[9,10-d] imidazole derivatives as multifunctional agents for treatment of Alzheimer’s diseases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1840: 2886–2903.
Luque-Contreras, D., K. Carvajal, D. Toral-Rios, D. Franco-Bocanegra, and V. Campos-Peña. 2014. Oxidative stress and metabolic syndrome: Cause or consequence of Alzheimer’s diseases? Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2014: 1–11.
Maeda, H., M. Hosokawa, T. Sashima, and K. Miyashita. 2007. Dietary combination of fucoxanthin and fish oil attenuates the weight gain of white adipose tissue and decreases blood glucose in obese/diabetic KK-Ay Mice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 55: 7701–7706.
Markesbery, W.R. 1997. Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer’s diseases. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 23: 134–147.
Melo, A., L. Monteiro, R.M. Lima, D.M. Oliveira, M.D. Cerqueira, and R.S. El-Bacha. 2011. Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases: Mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2011: 1–14.
Myung, C.S., H.C. Shin, H.Y. Bao, S.J. Yeo, B.H. Lee, and J.S. Kang. 2005. Improvement of memory by dieckol and phlorofucofuroeckol in ethanol-treated mice: Possible involvement of the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase. Archives of Pharmacal Research 28: 691–698.
Orhan, I., B. Sener, M.I. Choudhary, and A. Khalid. 2004. Acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of some Turkish medicinal plants. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 91: 57–60.
Pangestuti, R., and S.K. Kim. 2011. Neuroprotective effects of marine algae. Marine Drugs 9: 803–818.
Parihar, M.S., and T. Hemnani. 2004. Alzheimer’s diseases pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience 11: 456–467.
Rao, A.A., G.R. Sridhar, and U.N. Das. 2007. Elevated butyrylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase may predict the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer’s diseases. Medical Hypotheses 69: 1272–1276.
Roberson, E.D., and L. Mucke. 2006. 100 years and counting: Prospects for defeating Alzheimer’s disease. Science 314: 781–784.
Smith, C.D., J.M. Carney, P.E. Starke-Reed, C.N. Oliver, E.R. Stadtman, R.A. Floyd, and W.R. Markesbery. 1991. Excess brain protein oxidation and enzyme dysfunction in normal aging and in Alzheimer’s disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 88: 10540–10543.
Smith, M.A., C.A. Rottkamp, A. Nunomura, A.K. Raina, and G. Perry. 2000. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1502: 139–144.
Suganthy, N., P.S. Karutha, and D.K. Pandima. 2010. Neuroprotective effect of seaweeds inhabiting South Indian coastal area (Hare Island, Gulf of Mannar marine biosphere reserve): Cholinesterase inhibitory effect of Hypnea valentiae and Ulva reticulata. Neuroscience Letters 468: 216–219.
Tanzi, R.E., and L. Bertram. 2005. Twenty years of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid hypothesis: A genetic perspective. Cells 120: 545–555.
Thomas, N.V., and S.K. Kim. 2011. Potential pharmacological applications of polyphenolic derivatives from marine brown algae. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology 32: 325–335.
Torreilles, F., S. Salman-Tabcheh, M. Guérin, and J. Torreilles. 1999. Neurodegenerative disorders: The role of peroxynitrite. Brain Research Reviews 30: 153–163.
Uttara, M., A.V. Singh, P. Zamboni, and R.T. Mahajan. 2009. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: A review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Current Neuropharmacology 7: 65–74.
Valko, M., D. Leibfritz, J. Moncol, M.T. Cronin, M. Mazur, and J. Telser. 2007. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology 39: 44–84.
Wimo, A., B. Winblad, H. Aguero-Torres, and E. Von Strauss. 2003. The magnitude of dementia occurrence in the world. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders 17: 63–67.
Yoon, N.Y., H.Y. Chung, H.R. Kim, and J.S. Choi. 2008. Acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory activities of sterols and phlorotannins from Ecklonia stolonifera. Fisheris Science 74: 200–207.
Yoon, N.Y., S.H. Lee, K.B. Shim, C.W. Lim, M.H. Lee, H.A. Cho, and C. Xie. 2013. Quinone reductase induction activity of phlorotannins derived from Eisenia bicyclis in Hepa1c1c7 cells. Fisheries Aquatic Sciences 16: 1–5.
Yotsu-Yamashita, M., S. Kondo, S. Segawa, Y.C. Lin, H. Toyohara, H. Ito, K. Konoki, Y. Cho, and T. Uchida. 2013. Isolation and structural determination of two novel phlorotannins from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome Okamura, and their radical scavenging activities. Marine Drugs 11: 165–183.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), which is funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2012R1A1A2004035). We thank Aging Tissue Bank for providing research materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J.S., Haulader, S., Karki, S. et al. Acetyl- and butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitory activities of the edible brown alga Eisenia bicyclis . Arch. Pharm. Res. 38, 1477–1487 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0515-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0515-1