Abstract
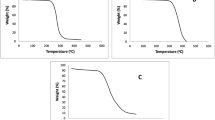
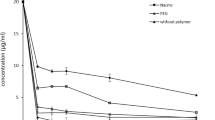
Clarithromycin (CAM) is known to be poorly water-soluble and acid-labile drug. Various alkalizers such as MgO, Na2CO3, Na2HPO4 and NaHCO3 were utilized to modulate the microenvironmental pH (pHM) and to improve the low stability and solubility of CAM in a crystalline-solid dispersion system (CSD). Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP K-30) and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) 4000-based CSDs containing alkalizers were prepared by cosolvent precipitation followed by evaporation process. The dried-CSDs mixed with microcrystalline cellulose, 2 % croscarmellose sodium, and 1 % magnesium stearate was then directly compressed into tablet. A dissolution test was carried out in 900 mL of pH 5.0 buffer solutions at 37 °C with a 50 rpm paddle speed. pHM, surface morphology, and structural behaviors were investigated. The dissolution rates of CAM in CSD containing alkalizers were improved. The drug in CSD remained crystalline as observed by differential scanning calorimetry and powder X-ray diffraction. Scanning electron microscopy revealed nearly identical images regardless of the sorts and amounts of carriers. PVP-based CSD tablet without alkalizer showed greater drug release, while HPMC-based CSD tablet without alkalizer retarded drug release due to its greater swelling capability. However, when the alkalizers were added in CSD tablet, the drug release was sharply increased. NaHCO3 induced the most rapid drug release while MgO retarded drug dissolution. Alkalizers in CSD also could maintain the pHM of the tablet above pH 5 under acidic conditions. The use of pH modifiers in CSDs could provide a useful method to improve the dissolution rate and stability of CAM via modulation of pHM without changing drug crystallinity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ching, A.L., C.V. Liew, L.W. Chan, and P.W.S. Heng. 2008. Modifying matrix micro-environmental pH to achieve sustained drug release from highly laminating alginate matrices. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Science 33: 361–370.
Chiou, W.L., and S. Riegelman. 1971. Pharmaceutical applications of solid dispersion systems. Journal of Pharmaceutical Science 60: 1281–1302.
Chun, M.-K., H. Sah, and H.-K. Choi. 2005. Preparation of mucoadhesive microspheres containing antimicrobial agents for eradication of H. pylori. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 297: 172–179.
Colombo, P., R. Bettini, P. Santi, and N.A. Peppas. 2000. Swellable matrices for controlled drug delivery: Gel-layer behaviour, mechanisms and optimal performance. Pharmaceutical Science & Technology Today 3: 198–204.
Conti, S., L. Maggi, L. Segale, E. Ochoa Machiste, U. Conte, P. Grenier, and G. Vergnault. 2007. Matrices containing NaCMC and HPMC: 2. Swelling and release mechanism study. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 333: 143–151.
Erah, P., A. Goddard, D. Barrett, P. Shaw, and R. Spiller. 1997. The stability of amoxycillin, clarithromycin and metronidazole in gastric juice: Relevance to the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 39: 5–12.
Ha, N.S., T.T.-D. Tran, P.H.-L. Tran, J.-B. Park, and B.-J. Lee. 2011. Dissolution-enhancing mechanism of alkalizers in poloxamer-based solid dispersions and physical mixtures containing poorly water-soluble valsartan. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 59: 844–850.
Jannin, V., E. Pochard, and O. Chambin. 2006. Influence of poloxamers on the dissolution performance and stability of controlled-release formulations containing Precirol® ATO 5. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 309: 6–15.
Kawabata, Y., K. Yamamoto, K. Debari, S. Onoue, and S. Yamada. 2010. Novel crystalline solid dispersion of tranilast with high photostability and improved oral bioavailability. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 39: 256–262.
Kawakami, E., S.K. Ogata, Á. Portorreal, A.M. Magni, M.L.E. Pardo, and F.R. Patrício. 2001. Triple therapy with clarithromycin, amoxicillin and omeprazole for Helicobacter pylori eradication in children and adolescents. Arquivos de Gastroenterologia 38: 203–206.
Kim, N.A., J.Y. Lim, K.H. Kim, D.G. Lim, E. Lee, E.-S. Park, and S.H. Jeong. 2014. Investigation of polymeric excipients for dutasteride solid dispersion and its physicochemical characterization. Archives of Pharmacal Research 37: 214–224.
Kranz, H., and T. Wagner. 2006. Effects of formulation and process variables on the release of a weakly basic drug from single unit extended release formulations. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 62: 70–76.
Lee, S.N., B.K. Poudel, T.H. Tran, N. Marasini, R. Pradhan, Y. Im Lee, D.W. Lee, J.S. Woo, H.-G. Choi, and C.S. Yong. 2013. A novel surface-attached carvedilol solid dispersion with enhanced solubility and dissolution. Archives of Pharmacal Research 36: 79–85.
Lin, C.-K., P.-I. Hsu, K.-H. Lai, G.-H. Lo, H.-H. Tseng, C.-C. Lo, N.-J. Peng, H.-C. Chen, H.-S. Jou, and W.-K. Huang. 2002. One-week quadruple therapy is an effective salvage regimen for Helicobacter pylori infection in patients after failure of standard triple therapy. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 34: 547–551.
Martin, L., C.G. Wilson, F. Koosha, L. Tetley, A.I. Gray, S. Senel, and I.F. Uchegbu. 2002. The release of model macromolecules may be controlled by the hydrophobicity of palmitoyl glycol chitosan hydrogels. Journal of Controlled Release 80: 87–100.
Nakagawa, Y., S. Itai, T. Yoshida, and T. Nagai. 1992. Physicochemical properties and stability in the acidic solution of a new macrolide antibiotic, clarithromycin, in comparison with erythromycin. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 40: 725–728.
Onoue, S., H. Sato, Y. Kawabata, T. Mizumoto, N. Hashimoto, and S. Yamada. 2009. In vitro and in vivo characterization on amorphous solid dispersion of cyclosporine A for inhalation therapy. Journal of Controlled Release 138: 16–23.
Rajinikanth, P., and B. Mishra. 2008. Floating in situ gelling system for stomach site-specific delivery of clarithromycin to eradicate H. pylori. Journal of Controlled Release 125: 33–41.
Siepe, S., B. Lueckel, A. Kramer, A. Ries, and R. Gurny. 2006. Strategies for the design of hydrophilic matrix tablets with controlled microenvironmental pH. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 316: 14–20.
Tran, H.T.T., J.B. Park, K.-H. Hong, H.-G. Choi, H.-K. Han, J. Lee, K.T. Oh, and B.-J. Lee. 2011a. Preparation and characterization of pH-independent sustained release tablet containing solid dispersion granules of a poorly water-soluble drug. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 415: 83–88.
Tran, P.H.-L., T.T.-D. Tran, K.-H. Lee, D.-J. Kim, and B.-J. Lee. 2010a. Dissolution-modulating mechanism of pH modifiers in solid dispersion containing weakly acidic or basic drugs with poor water solubility. Expert opinion on drug delivery 7: 647–661.
Tran, P.H.-L., T.T.-D. Tran, J.-B. Park, D.H. Min, H.-G. Choi, H.-K. Han, Y.-S. Rhee, and B.-J. Lee. 2011b. Investigation of physicochemical factors affecting the stability of a pH-modulated solid dispersion and a tablet during storage. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 414: 48–55.
Tran, P.H.-L., T.T.-D. Tran, J.B. Park, and B.-J. Lee. 2011c. Controlled release systems containing solid dispersions: Strategies and mechanisms. Pharmaceutical Research 28: 2353–2378.
Tran, P.H.-L., T.T.-D. Tran, S.A. Lee, V.H. Nho, S.-C. Chi, and B.-J. Lee. 2011d. Roles of MgO release from polyethylene glycol 6000-based solid dispersions on microenvironmental pH, enhanced dissolution and reduced gastrointestinal damage of telmisartan. Archives of Pharmacal Research 34: 747–755.
Tran, P.H.L., H.T.T. Tran, and B.-J. Lee. 2008. Modulation of microenvironmental pH and crystallinity of ionizable telmisartan using alkalizers in solid dispersions for controlled release. Journal of Controlled Release 129: 59–65.
Tran, T.T.-D., P.H.-L. Tran, H.-G. Choi, H.-K. Han, and B.-J. Lee. 2010b. The roles of acidifiers in solid dispersions and physical mixtures. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 384: 60–66.
Tran, T.T.-D., P.H.-L. Tran, and B.-J. Lee. 2009. Dissolution-modulating mechanism of alkalizers and polymers in a nanoemulsifying solid dispersion containing ionizable and poorly water-soluble drug. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 72: 83–90.
Tu, Y.-O., and A. Ouano. 1977. Model for the kinematics of polymer dissolution. IBM Journal of Research and Development 21: 131–142.
Turner, S., Ravishankar, J., Fassihi, R. 2005. Method for improving the bioavailability of orally delivered therapeutics. Google Patents US 20060068010 A1.
Umamaheshwari, R., S. Jain, and N. Jain. 2003. A new approach in gastroretentive drug delivery system using cholestyramine. Drug Delivery 10: 151–160.
Wan, L.S., P.W. Heng, and L. Wong. 1993. Relationship between swelling and drug release in a hydrophilic matrix. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy 19: 1201–1210.
Yonemochi, E., S. Kitahara, S. Maeda, S. Yamamura, T. Oguchi, and K. Yamamoto. 1999. Physicochemical properties of amorphous clarithromycin obtained by grinding and spray drying. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 7: 331–338.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (2013M3A9B5075841) and by a Grant from the Korean Health Technology R&D Project (A092018), Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea. We would like to thank KBSI for the use of SEM, PXRD, DSC and FTIR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, JB., Park, YJ., Kang, CY. et al. Modulation of microenvironmental pH and utilization of alkalizers in crystalline solid dispersion for enhanced solubility and stability of clarithromicin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 38, 839–848 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0471-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0471-9