Abstract
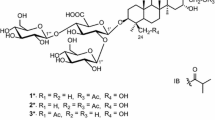
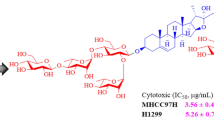
Seven steroidal saponins (1–7) and two xanthones (8, 9) were isolated from the rhizomes of Anemarrhena asphodeloides. Then in order to discover more analogues, which may possess good biological activity, the structural modifications of 2 and 9 were performed by acid hydrolysis and acetylation. Consequently, one novel steroidal saponin (2d, timosaponin BII-d), three compounds (2c, 2e and 2f) which were also the new products prepared by the diluted acid hydrolysis of 3 by our group previously, and four known compounds (2a, 2b, 9a and 9b) were obtained. The structures were elucidated by analyses of NMR and MS data. All the compounds were evaluated for their cytotoxicities against BEL-7402, HT-29, HeLa and MDA-MB-468 cell lines in vitro by Sulforhodamine protein coloration method. Compounds 1, 2, 2b, 4–6, 9a and 9b showed certain anti-proliferative activities against the four cell lines, in which compounds 2, 4 and 9b exhibited especially more potent activities. The structure–activity relationships of these compounds were simply discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharya, S.K., S. Ghosal, R.K. Chandhuri, and A.K. Sanyal. 1971. Canscora decussata (Gentianaceae) xanthones III: Pharmacological studies. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 61: 1838–1840.
Bian, J., S.S. Xu, and S. Huang. 1996. A study on the chemical constituents of Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bge. Journal of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University 13: 34–39.
Dong, J.X., and G.Y. Han. 1992. Studies on the active consitituents of Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bunge. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica 27: 26–32.
Hong, Y.F., G.Y. Han, and X.M. Guo. 1997. Isolation and structure determination of xanthone glycosides of anemarrhena asphodeloides. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica 32: 473–475.
Hu, Y.M., Z.L. Yu, and W.F. Fong. 2011. Stereoselective biotransformation of Timosaponin A-III by Saccharomyyces cerevisiae. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 21: 582–589.
Kang, L.P., B.P. Ma, T.J. Shi, J. Zhang, and C.Q. Xiong. 2006. Two new furostanol saponins from the rhizomes of Anemarrhena asphodeloides. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica 6: 527–532.
Lin, K.W., S.C. Fang, C.F. Hung, B.J. Shieh, S.C. Yang, C.M. Teng, and C.N. Lin. 2009. Synthesis, antiplatelet and vasorelaxing activities of xanthone derivatives. Archiv der Pharmazie 342: 19–26.
Liu, Z.Y., W.X. Jiang, B. Wu, and C.G. Huang. 2013. New saponins from timosaponin BIII by acid hydrolysis. Asian Journal of Chemistry 5: 2503–2505.
Ma, B.P., B.J. Wang, J.X. Dong, and X.Z. Yan. 1996. Studies on the furostanol saponins from Anemarrhena asphodeloides bunge. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica 4: 271–277.
Ma, B.P., B.J. Wang, J.X. Dong, X.Z. Yan, H.J. Zhang, and A.P. Tu. 1997. New spirostanol glycosides from Anemarrhena asphodeloides. Planta Medica 63: 376–379.
Nagumo, S., S. Kishi, T. Inoue, and M. Nagai. 1991. Saponins of Anemarrhena rhizoma. Yakugaku Zasshi 6: 306–310.
Niwa, A., O. Takeda, M. Ishimaru, Y. Nakamoto, and K. Yamasaki. 1988. Screening test for platelet aggregation inhibitor in natural products. The active principle of Anemarrhena rhizome. Yakugaku Zasshi 108: 555–561.
Nian, H., L.P. Qin, W.S. Chen, Q.Y. Zhang, L. Zheng, and L. Wang. 2006. Protective effect of steroidal saponins from rhizomes of Anemarrhena asphodeloides on ovariectomy-induced bone loss in rats. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 27: 728–734.
Pei, Y.H., H.M. Hua, Z.L. Li, and G. Chen. 2011. Application of nuclear magnetic resonance to the determination of the configuration of glycoside bond. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica 46: 127–131.
Takahashi, M., C. Komo, and H. Hikino. 1985. Isolation and hypoglycemic activity of anemarans A, B, C and D, glycans of Anemarrhena asphodeloides rhizomes. Planta Medica 51: 100–102.
Takeda, Y., H. Togashi, T. Matsuo, H. Shinzawa, Y. Takeda, and T. Takahashi. 2011. Growth inhibition and apoptosis of gastric cancer cell lines by Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bunge. Journal of Gastroenterology 36: 79–80.
Wu, B., Z.Y. Liu, M.S. Fan, Z.L. Sun, W.X. Jiang, and C.G. Huang. 2012. The structural elucidation of two new artificial steroidal saponins. Chinese Chemical Letters 23: 332–334.
Zhang, J.Y., Z.Y. Meng, M.Y. Zhang, D.S. Ma, S.X. Xu, and H. Kodama. 1999. Effect of six steroidal saponins isolated from Anemarrhena rhizome on platelet aggregation and hemolysis in human blood. Clinica Chimica Acta 289: 79–88.
Zhou, R.G., Z.X. Yang, J. Yang, J. Wang, B. Yang, and W. Zhang. 2011. Total synthesis of norathyriol. Applied Chemical Industry 9: 1516–1521.
Zhou, W.B., B. Feng, H.Z. Huang, P. Liu, H.S. Yu, Y. Zhao, Y.J. Qin, L.P. Kang, and B.P. Ma. 2010. Hydrolysis of timosaponin BII by the crude enzyme from Aspergillus niger AS 3.0739. Journal of Asian Natural Products Research 12: 955–961.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81274055).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Xu, C., Xue, R. et al. Cytotoxic activities of chemical constituents from rhizomes of Anemarrhena asphodeloides and their analogues. Arch. Pharm. Res. 38, 598–603 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0431-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0431-4