Abstract
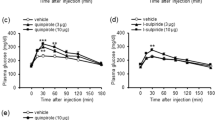
The blood glucose profiles were characterized after mice were forced into immobilization stress with various exposure durations. The blood glucose level was significantly enhanced by immobilization stress for 30 min or 1 h, respectively. On the other hand, the blood glucose level was not affected in the groups which were forced into immobilization stress for 2 or 4 h. We further examined the effect of yohimbine (an α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist) administered systemically or centrally in the immobilization stress model. Mice were pretreated intraperitoneally (i.p.; from 0.5 to 5 mg/kg), intracerebroventricularly (i.c.v.; from 1 to 10 µg/5 µl), or intrathecally (i.t.; from 1 to 10 µg/5 µl) with yohimbine for 10 min and then, forced into immobilization stress for 30 min. The blood glucose level was measured right after immobilization stress. We found that up-regulation of the blood glucose level induced by immobilization stress was abolished by i.p. pretreatment with yohimbine. And the immobilization stress-induced blood glucose level was not inhibited by i.c.v. or i.t. pretreatment with yohimbine at a lower dose (1 µg/5 µl). However, immobilization stress-induced blood glucose level was significantly inhibited by i.c.v. or i.t. pretreatment with yohimbine at higher doses (5 and 10 µg/5 µl). In addition, the i.p. (5 mg/kg), i.c.v. (10 µg/5 µl), or i.t. (10 µg/5 µl) pretreatment with yohimbine reduced hypothalamic glucose transporter 4 expression. The involvement of α2-adrenergic receptor in regulation of immobilization stress- induced blood glucose level was further confirmed by the i.p, i.c.v, or i.t pretreatment with idazoxan, another specific α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist. Finally, i.p., i.c.v., or i.t. pretreatment with yohimbine attenuated the blood glucose level in d-glucose-fed model. We suggest that α2-adrenergic receptors located at the peripheral, the brain and the spinal cord play important roles in the up-regulation of the blood glucose level in immobilization stress.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Zaher, A.O., I.T. Ahmed, and A.D. El-Koussi. 2001. The potential antidiabetic activity of some alpha-2 adrenoceptor antagonists. Pharmacological Research 44: 397–409.
Bialik, R.J., J.W. Smythe, and D.C. Roberts. 1998. Alpha 2-adrenergic receptors mediate the increase in blood glucose levels induced by epinephrine and brief footshock stress. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 12: 307–314.
Brant, A.M., T.J. Jess, G. Milligan, C.M. Brown, and G.W. Gould. 1993. Immunological analysis of glucose transporters expressed in different regions of the rat brain and central nervous system. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 192(3): 1297–1302.
Bundzikova, J., Z. Pirnik, D. Zelena, J.D. Mikkelsen, and A. Kiss. 2009. Alpha2-adrenergic impact on hypothalamic magnocellular oxytocinergic neurons in long evans and brattleboro rats: Effects of agonist and antagonists. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology 29: 1015–1023.
Chen, Y., E.A. Kramár, L.Y. Chen, A.H. Babayan, A.L. Andres, C.M. Gall, G. Lynch, and T.Z. Baram. 2012. Impairment of synaptic plasticity by the stress mediator CRH involves selective destruction of thin dendritic spines via RhoA signaling. Molecular Psychiatry 18(4): 485–496.
Corrodi, H., K. Fuxe, P. Lidbrink, and L. Olson. 1971. Minor tranquilizers, stress and central catecholamine neurons. Brain Research 29: 1–16.
Das, V.A., F. Chathu, and C.S. Paulos. 2006. Decreased alpha2-adrenergic receptor in the brain stem and pancreatic islets during pancreatic regeneration in weanling rats. Life Science 79: 1507–1513.
DeTurck, K.H., and W.H. Vogel. 1982. Effects of acute ethanol on plasma and brain catecholamine levels in stressed and unstressed rats: Evidence for an ethanol-stress interaction. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 223: 348–354.
Fagerholm, V., M. Haaparanta, and M. Scheinin. 2011. α2-Adrenoceptor regulation of blood glucose homeostasis. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology 108: 365–370.
Fagerholm, V., J. Rokka, L. Nyman, J. Sallinen, J. Tiihonen, E. Tupala, M. Haaparanta, and J. Hietala. 2008. Autoradiographic characterization of alpha(2C)-adrenoceptors in the human striatum. Synapse 62(7): 508–515.
Gądek-Michalska, A., J. Tadeusz, P. Rachwalska, J. Spyrka, and J. Bugajski. 2011. Effect of prior stress on interleukin-1β and HPA axis responses to acute stress. Pharmacological Reports 63: 1393–1403.
Jansen, A.S., X.V. Nguyen, V. Karpitskiy, T.C. Mettenleiter, and A.D. Loewy. 1995. Central command neurons of the sympathetic nervous system: Basis of the fight-or-flight response. Science 270: 644–646.
Kalantaridou, S.N., E. Zoumakis, A. Makrigiannakis, L.G. Lavasidis, T. Vrekoussis, and G.P. Chrousos. 2010. Corticotropin-releasing hormone, stress and human reproduction: An update. Journal of Reproductive Immunology 85: 33–39.
Haley, T.J., and W.G. Mccormick. 1957. Pharmacological effects produced by intracerebral injection of drugs in the conscious mouse. British journal of pharmacology and chemotherapy 12: 12–15.
Hsu, W.H. 1988. Yohimbine increases plasma insulin concentrations and reverses xylazine-induced hypoinsulinemia in dogs. American Journal of Veterinary Research 49: 242–244.
Hylden, J.L., and G.L. Wilcox. 1981. Intrathecal substance P elicits a caudally-directed biting and scratching behavior in mice. Brain Research 217: 212–215.
Laychock, S.G., and S. Bilgin. 1987. Alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of pancreatic islet glucose utilization is mediated by an inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. FEBS Letters 218: 7–10.
Melia, K.R., A.E. Ryabinin, R. Schroeder, F.E. Bloom, and M.C. Wilson. 1994. Induction and habituation of immediate early gene expression in rat brain by acute and repeated restraint stress. The Journal of Neuroscience 14: 5929–5938.
Miki, T., B. Liss, K. Minami, T. Shiuchi, A. Saraya, Y. Kashima, M. Horiuchi, F. Ashcroft, Y. Minokoshi, J. Roeper, and S. Seino. 2001. ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the hypothalamus are essential for the maintenance of glucose homeostasis. Nature Neuroscience 4(5): 507–512.
Nakadate, T., T. Nakaki, T. Muraki, and R. Kato. 1980. Regulation of plasma insulin level by alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. European Journal of Pharmacology 65: 421–424.
Niddam, R., I. Angel, S. Bidet, and S.Z. Langer. 1990. Pharmacological characterization of alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtype involved in the release of insulin from isolated rat pancreatic islets. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 254: 883–887.
Pan, Y.Z., D.P. Li, and H.L. Pan. 2002. Inhibition of glutamatergic synaptic input to spinal lamina II(o) neurons by presynaptic alpha(2)-adrenergic receptors. Journal of Neurophysiology 87: 1938–1947.
Park, S.H., Y.B. Sim, S.M. Choi, Y.J. Seo, M.S. Kwon, J.K. Lee, and H.W. Suh. 2009. Antinociceptive profiles and mechanisms of orally administered vanillin in the mice. Archives of Pharmacal Research 32: 1643–1649.
Pasquali, R., V. Vicennati, F. Calzoni, U. Gnudi, A. Gambineri, L. Ceroni, P. Cortelli, R. Menozzi, R. Sinisi, and G.D. Rio. 2000. alpha2-adrenoceptor regulation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenocortical axis in obesity. Clinical Endocrinology (Oxf) 52: 413–421.
Plum, L., B.F. Belgardt, and J.C. Brüning. 2006. Central insulin action in energy and glucose homeostasis. Journal of Clinical Investigation 116(7): 1761–1766.
Saitoh, Y., and M. Ui. 1976. Stimulation of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis by epinephrine independent of its beta-adrenergic function in perfused rat liver. Biochemical Pharmacology 25: 841–845.
Sallinen, J., I. Höglund, M. Engström, J. Lehtimäki, R. Virtanen, J. Sirviö, S. Wurster, J.M. Savola, and A. Haapalinna. 2007. Pharmacological characterization and CNS effects of a novel highly selective alpha2C-adrenoceptor antagonist JP-1302. British Journal of Pharmacology 150: 391–402.
Schmidt, M.E., D.S. Goldstein, J.L. Schouten, J.A. Matochik, H.G. Kim, and W.Z. Potter. 1997. Acute alpha 2 blockade by idazoxan increases insulin and lowers plasma glucose during positron emission tomography. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 33: 253–259.
Seo, Y.J., M.S. Kwon, E.J. Shim, S.H. Park, O.S. Choi, and H.W. Suh. 2006. Changes in pain behavior induced by formalin, substance P, glutamate and pro-inflammatory cytokines in immobilization-induced stress mouse model. Brain Research Bulletin 71: 279–286.
Sim, Y.B., S.H. Park, Y.J. Kang, S.M. Kim, J.K. Lee, J.S. Jung, and H.W. Suh. 2010. The regulation of blood glucose level in physical and emotional stress models: Possible involvement of adrenergic and glucocorticoid systems. Archives of Pharmacal Research 33: 1679–1683.
Skoglund, G., I. Lundquist, and B. Ahrén. 1986. Effects of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptor stimulation and blockade on plasma insulin levels in the mouse. Pancreas 1: 415–420.
Subbarao, K.V., and L. Hertz. 1990. Effect of adrenergic agonists on glycogenolysis in primary cultures of astrocytes. Brain Research 536: 220–226.
Suh, H.W., D.K. Song, S.O. Huh, and Y.H. Kim. 2000. Involvement of dynorphin in immobilization stress-induced antinociception in the mouse. European Neuropsychopharmacology 10(5): 407–413.
Surwit, R.S., M.S. Schneider, and M.N. Feinglos. 1992. Stress and diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 15: 1413–1422.
Tanaka, M. 1999. Emotional stress and characteristics of brain noradrenaline release in the rat. Industrial Health 37: 143–156.
Tjurmina, O.A., D.S. Goldstein, M. Palkovits, and I.J. Kopin. 1999. Alpha2-adrenoceptor-mediated restraint of norepinephrine synthesis, release, and turnover during immobilization in rats. Brain Research 826: 243–252.
Ullrich, S., and C.B. Wollheim. 1984. Islet cyclic AMP levels are not lowered during alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of insulin release. The Journal of biological chemistry 259: 4111–4115.
Uresin, Y., B. Erbas, M. Ozek, E. Ozkök, and A.O. Gürol. 2004. Losartan may prevent the elevation of plasma glucose, corticosterone and catecholamine levels induced by chronic stress. Journal of the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System 5: 93–96.
Zacny, E., and J. Bugajski. 1983. The effect of clonidine injected centrally on serum-free fatty acids and glucose concentration in the rat. Metabolism 32: 938–942.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Priority Research Centers (NRF-2009-0094071) Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and Hallym University Research Fund (HRF-S-2012-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yu-Jung Kang and Yun-Beom Sim have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, YJ., Sim, YB., Park, SH. et al. Involvement of α2-adrenergic receptor in the regulation of the blood glucose level induced by immobilization stress. Arch. Pharm. Res. 38, 921–929 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0430-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0430-5