Abstract
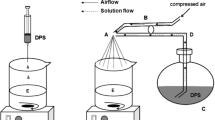
In the present work we investigated the feasibility of chitosan treated Ca-alginate microparticles for delivery of naproxen in lower parts of GIT and evaluated influence of formulation factors on their physicochemical characteristics and drug release profiles. Investigated factors were drug/polymer ratio, chitosan molecular weight, chitosan concentration in hardening medium, and hardening time. Sixteen microparticle formulations were prepared utilizing 24 full factorial design (each factor was varied at two levels). Microparticles size varied between 262.3 ± 14.9 and 358.4 ± 21.7 μm with slightly deformed spherical shape. Low naproxen solubility and rapid reaction of ionotropic gelation resulted in high encapsulation efficiency (> 75.19%). Under conditions mimicking those in the stomach, after two hours, less than 6.18% of naproxen was released. Significant influence of all investigated factors on drug release rate was observed in simulated small intestinal fluid. Furthermore, experimental design analysis revealed that chitosan molecular weight and its concentration had the most pronounced effect on naproxen release. Release data kinetics indicated predominant influence of a pH-dependent relaxation mechanism on drug release from microparticles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acartürk, F. and Takka, S., Calcium alginate microparticles for oral administration: II. Effect of formulation factors on drug release and drug entrapment efficiency. J. Microencapsul., 16, 291–301 (1999).
Brazel, C. S. and Peppas, N. A., Mechanisms of solute and drug transport in relaxing, swellable, hydrophilic glassy polymers. Polymer, 40, 3383–3398 (1999).
Cárdenas, A., Argüelles-Monal, W., Goycoolea, F. M., Higuera-Ciapara, I., and Peniche, C., Diffusion through membranes of the polyelectrolyte complex of chitosan and alginate. Macromol. Biosci., 3, 535–539 (2003).
Çaykara, T., Demirci, S., Eroğlu, M. S., and Güven, O., Poly(ethylene oxide) and its blends with sodium alginate. Polymer, 46, 10750–10757 (2005).
Cekić, N. D., Milić, J. R., Savić, S. D., Savić, M. M., Jović, Z., and Daniels, R., Influence of the preparation procedure and chitosan type on physicochemical properties and release behavior of alginate-chitosan microparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 35, 1092–1102 (2009).
Dai, Y. N., Li, P., Zhang, J. P., Wang, A. Q., and Wei, Q., Swelling characteristics and drug delivery properties of nifedipine-loaded pH sensitive alginate-chitosan hydrogel beads. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater., 86, 493–500 (2008).
Dong, Y., Ruan, Y., Wang, H., Zhao, Y., and Bi, D., Studies on glass transition temperature of chitosan with four techniques. J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 93, 1553–1558 (2004).
Eskilson, C., Controlled release by microencapsulation. Manufacturing Chemist., 56, 33–39 (1985).
Ferreira, A. P. and Almeida, A. J., Cross-linked alginategelatine beads: a new matrix for controlled release of pindolol. J. Control. Release, 97, 431–439 (2004).
Gåserød, O., Smidsrød, O., and Skjåk-Bræk, G., Microcapsules of alginate-chitosan-I. A quantitative study of the interaction between alginate and chitosan. Biomaterials, 19, 1815–1825 (1998).
Grant, G. T., Morris, E. R., Rees, D. A., Smith, P. J. C., and Thom, D., Biological interactions between polysaccharides and divalent cations: the egg-box model. FEBS Lett., 32, 195–198 (1973).
Higuchi, T., Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. J. Pharm. Sci., 52, 1145–1149 (1963).
Huguet, M. L. and Dellacherie, E., Calcium alginate beads coated with chitosan: effect of the structure of encapsulated materials on their release. Process Biochem., 31, 745–751 (1996).
Iruín, A., Fernández-Arévalo, M., Alvarez-Fuéntes, J., Fini, A., and Holgado, M. A., Elaboration and “in vitro” characterization of 5-ASA beads. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 31, 231–239 (2005).
Kim, C.-K. and Lee, E.-J., The controlled release of blue dextran from alginate beads. Int. J. Pharm., 79, 11–19 (1992).
Kim, S. J., Yoon, S. G., and Kim, S. I., Synthesis and characteristics of interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels composed of alginate and poly(diallydimethylammonium chloride). J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 91, 3705–3709 (2004).
Korsmeyer, R. W., Gurny, R., Doelker, E., Buri, P., and Peppas, N. A., Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm., 15, 25–35 (1983).
Kramer, J. and Blume, H., Biopharmaceutical aspects of multiparticulates. In Ghebre-Sellasie, Y. (Ed.). Multiparticulate Oral Drug Delivery. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp. 307–332, (1994).
Llabot, J. M., Manzo, R. H., and Allemandi, D. A., Drug release from carbomer:carbomer sodium salt matrices with potential use as mucoadhesive drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm., 276, 59–66 (2004).
Maghsoodi, M., Physicomechanical properties of naproxenloaded microparticles prepared from Eudragit L100. AAPS PharmSciTech, 10, 120–128 (2009).
Martinsen, A., Skjåk-Bræk, G., and Smidsrød, O., Alginate as immobilization materials: I. Correlation between chemical and physical properties of alginate gel beads. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 33, 79–89 (1989).
Morris, E. R., Rees, D. A., Thom, D., and Boyd, J., Chiroptical and stoichiometric evidence of a specific, primary dimerisation process in alginate gelation. Carbohydr. Res., 66, 145–154 (1978).
Murata, Y., Maeda, T., Miyamoto, E., and Kawashima, S., Preparation of chitosan-reinforced alginate gel beads — effects of chitosan on gel matrix erosion. Int. J. Pharm., 96, 139–145 (1993).
Neto, C. G. T., Giacometti, J. A., Job, A. E., Ferreira, F. C., Fonseca, J. L. C., and Pereira, M. R., Thermal Analysis of Chitosan Based Networks. Carbohydr. Polym., 62, 97–103 (2005).
Otero-Espinar, F. J., Anguiano-Igea, S., Blanco-Méndez, J., and Vila-Jato, J. L., Reduction in the ulcerogenicity of naproxen by complexation with β-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm., 70, 35–41 (1991).
Peppas, N. A. and Sahlin, J. J., A simple equation for the description of solute release. III. Coupling of diffusion and relaxation. Int. J. Pharm., 57, 169–172 (1989).
Polk, A., Amsden, B., De Yao, K., Peng, T., and Goosen, M. F. A., Controlled release of albumin from chitosan-alginate microcapsules. J. Pharm. Sci., 83, 178–185 (1994).
Ribeiro, A. J., Neufeld, R. J., Arnaud, P., and Chaumeil, J. C., Microencapsulation of lipophilic drugs in chitosancoated alginate microspheres. Int. J. Pharm., 187, 115–123 (1999).
Simsek-Ege, F. A., Bond, G. M., and Stringer, J., Polyelectrolyte complex formation between alginate and chitosan as a function of pH. J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 88, 346–351 (2003).
Sweetman, S. C., Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. Pharmaceutical Press, London, pp. 60, (2002).
Tønnesen, H. H. and Karlsen, J., Alginate in drug delivery systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 28, 621–630 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Čalija, B., Cekić, N., Savić, S. et al. An investigation of formulation factors affecting feasibility of alginate-chitosan microparticles for oral delivery of naproxen. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 919–929 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0609-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0609-y