Abstract
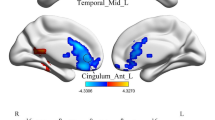
Tension-type headache (TTH) is the most prevalent type of primary headache. Many studies have shown that the pathogenesis of primary headache is associated with fine structural or functional changes. However, these studies were mainly based on migraine. The present study aimed to investigate whether TTH patients show functional disturbances compared with healthy subjects. We used restingstate functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and regional homogeneity (ReHo) analysis to identify changes in the local synchronization of spontaneous activity in patients with TTH. Ten patients with TTH and 10 age-, gender-, and education-matched healthy controls participated in the study. After demographic and clinical characteristics were acquired, a 3.0-T MRI system was used to obtain resting-state fMRIs. Compared with healthy controls, the TTH group exhibited significantly lower ReHo values in the bilateral caudate nucleus, the precuneus, the putamen, the left middle frontal gyrus, and the superior frontal gyrus. There was no correlation between mean ReHo values in TTH patients and duration of TTH, number of attacks, duration of daily attacks, Visual Analogue Scale score, or Headache Impact Test-6 score. These results suggest that TTH patients exhibit reduced synchronization of neuronal activity in multiple regions involved in the integration and processing of pain signals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendtsen L, Evers S, Linde M, Mitsikostas DD, Sandrini G, Schoenen J, et al. EFNS guideline on the treatment of tension-type headache — report of an EFNS task force. Eur J Neurol 2010, 17: 1318–1325.
Stovner L, Hagen K, Jensen R, Katsarava Z, Lipton R, Scher A, et al. The global burden of headache: a documentation of headache prevalence and disability worldwide. Cephalalgia 2007, 27: 193–210.
Rasmussen BK, Jensen R, Schroll M, Olesen J. Epidemiology of headache in a general population—a prevalence study. J Clin Epidemiol 1991, 44: 1147–1157.
Rasmussen BK. Epidemiology of headache. Cephalalgia 2001, 21: 774–777.
Bendtsen L, Fumal A, Schoenen J. Tension-type headache: mechanisms. Handb Clin Neurol 2010, 97: 359–366.
Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 2004, 24Suppl 1: 9–160.
Schmidt-Wilcke T, Leinisch E, Straube A, Kampfe N, Draganski B, Diener HC, et al. Gray matter decrease in patients with chronic tension type headache. Neurology 2005, 65: 1483–1486.
Baumgartner R, Somorjai R, Summers R, Richter W. Assessment of cluster homogeneity in fMRI data using Kendall’s coefficient of concordance. Magn Reson Imaging 1999, 17: 1525–1532.
Yu D, Yuan K, Zhao L, Zhao L, Dong M, Liu P, et al. Regional homogeneity abnormalities in patients with interictal migraine without aura: A resting state study. NMR Biomed 2012, 25: 806–812.
Lai C-H, Wu Y-T. Frontal regional homogeneity increased and temporal regional homogeneity decreased after remission of first-episode drug-naïve major depressive disorder with panic disorder patients under duloxetine therapy for 6weeks. J Affect Disord 2012, 136: 453–458.
Zhu Y, Gao B, Hua J, Liu W, Deng Y, Zhang L, et al. Effects of methylphenidate on resting-state brain activity in normal adults: an fMRI study. Neurosci Bull 2013, 29: 16–27.
Zuo XN, Xu T, Jiang L, Yang Z, Cao XY, He Y, et al. Toward reliable characterization of functional homogeneity in the human brain: preprocessing, scan duration, imaging resolution and computational space. Neuroimage 2013, 65: 374–386.
Liu Y, Liang M, Zhou Y, He Y, Hao Y, Song M, et al. Disrupted small-world networks in schizophrenia. Brain 2008, 131: 945–961.
Song XW, Dong ZY, Long XY, Li SF, Zuo XN, Zhu CZ, et al. REST: a toolkit for resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data processing. PLoS One 2011, 6: e25031.
Zang Y, Jiang T, Lu Y, He Y, Tian L. Regional homogeneity approach to fMRI data analysis. Neuroimage 2004, 22: 394–400.
Guo W-b, Sun X-l, Liu L, Xu Q, Wu R-r, Liu Z-n, et al. Disrupted regional homogeneity in treatment-resistant depression: a resting-state fMRI study. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2011, 35: 1297–1302.
Power JD, Barnes KA, Snyder AZ, Schlaggar BL, Petersen SE. Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. Neuroimage 2012, 59: 2142–2154.
Graybiel AM. Network-level neuroplasticity in cortico-basal ganglia pathways. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2004, 10: 293–296.
Chudler EH, Dong WK. The role of the basal ganglia in nociception and pain. Pain 1995, 60: 3–38.
Apkarian AV, Bushnell MC, Treede RD, Zubieta JK. Human brain mechanisms of pain perception and regulation in health and disease. Eur J Pain 2005, 9: 463–463.
Borsook D, Upadhyay J, Chudler EH, Becerra L. A key role of the basal ganglia in pain and analgesia-insights gained through human functional imaging. Mol Pain 2010, 6: 27.
Maleki N, Becerra L, Nutile L, Pendse G, Brawn J, Bigal M, et al. Migraine attacks the basal ganglia. Mol Pain 2011, 7: 71.
Yang FC, Chou K H, Fuh JL, Huang CC, Lirng JF, Lin YY, et al. Altered gray matter volume in the frontal pain modulation network in patients with cluster headache. Pain 2013, 154(6): 801–807.
Absinta M, Rocca MA, Colombo B, Falini A, Comi G, Filippi M. Selective decreased grey matter volume of the pain-matrix network in cluster headache. Cephalalgia 2012, 32: 109–115.
Lutz J, Jäger L, de Quervain D, Krauseneck T, Padberg F, Wichnalek M, et al. White and gray matter abnormalities in the brain of patients with fibromyalgia: a diffusion tensor and volumetric imaging study. Arthritis Rheum 2008, 58: 3960–3969.
Margulies DS, Vincent JL, Kelly C, Lohmann G, Uddin LQ, Biswal BB, et al. Precuneus shares intrinsic functional architecture in humans and monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106: 20069–20074.
Goffaux P, Girard-Tremblay L, Marchand S, Daigle K, Whittingstall K. Individual differences in pain sensitivity vary as a function of precuneus reactivity. Brain Topogr 2014, 27: 366–374.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Du, H., Chen, N. et al. Regional homogeneity abnormalities in patients with tensiontype headache: a resting-state fMRI study. Neurosci. Bull. 30, 949–955 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-013-1468-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-013-1468-6