Abstract
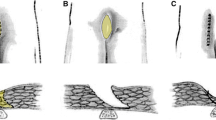
We report our experience of technique of V-Y-plasty in treatment of pilonidal sinus. A retrospective study of 25 patients performed from 2005 to 2010 at Deenanath Mangeshkar Hospital and Sassoon General Hospitals, Pune, was performed. The unilateral or bilateral V-Y advancement flap technique was used in the management of these patients. The outcome was assessed on the basis of efficacy of flap surgery in achieving wound healing and recurrence. The follow-up ranged from 6 months to 5 years. The study included 25 cases of pilonidal sinus. Nineteen patients (76%) underwent unilateral V-Y-plasty and six patients (24%) underwent bilateral V-Y-plasty. Eighty-four percent cases were from the age group of 21–30 years. Sixty-eight percent patients were mobilized on the fourth postoperative day and 32% patients were mobilized on the third postoperative day. No recurrence was found in any of the patients. Itching and hypertrophic scar were found in two cases (8%), and decreased sensation was found in one patient (4%). The V-Y advancement flap technique for the treatment of pilonidal sinus is efficient and can reduce recurrence. Unilateral/bilateral V-Y flap achieves suture line away from midline, obliteration of natal fold and coverage of defect without tension. In follow-up none of the patients showed recurrence. This technique has distinctly less morbidity and avoids of multiple dressings, reducing the total cost of the treatment. V-Y advancement flap is distinctly better choice among the available flaps as it is less time-consuming, requires less technical expertise as compared to Z-plasty and perforator flaps, and is reliable and easy to plan.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sebastian M (1997) Pilonidal cysts and sinuses. In: Principles of surgery, pp 1330–4, 1234–5
Klass AA (1956) The so-called pilonidal sinus. Can Med Assoc J 75:737–742
Berry DP (1992) Pilonidal sinus disease. J Wound Care 1(3):29–32
Stansby G, Greatorex R (1989) Phenol treatment of pilonidal sinus of the natal cleft. Br J Surg 76(7):729–730
Jacobsen P (1959) Pilonidal disease: management without excision. Am Acad GP xix:3
Kronberg I, Christensen KI, Zimmerman-Nielson O (1986) Chronic pilonidal disease: a randomised trial with complete three year follow up. Br J Surg 72:303–304
Jones DJ (1992) ABC of colorectal diseases. Pilonidal sinus. BMJ 305:410–412
Sondenaa K, Diab R, Nesvik I et al (2002) Influence of failure of primary wound healing on subsequent recurrence of pilonidal sinus. Eur J Surg 168(11):614–618
Hull TL, Wu J (2002) Pilonidal disease. Surg Clin North Am 82:1169–1185
Bascom J, Bascom T (2002) Failed pilonidal sinus surgery: new paradigm and new operation leading to cures. Arch Surg 137:1146–1150
Kitchen PR (1996) Pilonidal sinus: experience with the Karydakis flap. Br J Surg 83:1452–1455
Akinci OF, Bozer M, Uzunkoy A (1999) Incidence and etiological factors in pilonidal sinus among Turkish soldiers. Eur J Surg 165:339–342
Bose B, Candy J (1970) Radical cure of pilonidal sinus by Z-plasty. Am J Surg 120:783–786
Armstrong JH, Barcia PJ (1994) Pilonidal sinus disease. The conservative approach. Arch Surg 129:914–919
Fuzun M, Bakir H, Soylu M, Tansug T, Kaymak E, Harmancioglu O (1994) Which technique for pilonidal sinus—open or closed? Dis Colon Rectum 37:1148–1150
Khanzada TW, Samad A (2007) Recurrence after excision and primary closure of pilonidal sinus. Pak J Med Sci 23(3):375–379
Iesalnieks I, Furst A, Rentsch M, Jauch KW (2003) Primary midline closure after excision of a pilonidal sinus is associated with a high recurrence rate. Chirurg 74:461
Khatri V, Espinosa MH, Amin AK (1994) Management of recurrent pilonidal sinus by simple V-Y Fasciocutaneous flap. Dis Colon Rectum 37:1232–1235
Nessar G, Kayaalp C, Seven C (2004) Elliptical rotation flap for pilonidal sinus. Am J Surg 187:300–303
Lamke LO, Larsson J, Nylen B (1979) Treatment of pilonidal sinus by radical excision and reconstruction by rotation flap surgery of Z-plasty technique. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg 13:351–353
Koshima I, Moriguchi T, Soeda S, Kawata S, Ohta S, Ikeda A (1993) The gluteal perforator-based flap for repair of sacral pressure sores. Plast Reconstr Surg 91:678–683
Lamke LO, Larsson J, Nylen B (1979) Treatment of pilonidal sinus by radical excision and reconstruction by rotation flap surgery of Z-plasty technique. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg 13:351–353
Quinodoz PD, Chilcott M, Grolleau JL, Chavoin JP, Costagliola M (1999) Surgical treatment of sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus disease by excision and skin flaps: the toulouse experience. Eur J Surg 11:1061–1065
Monro SR, MacDermot FT (1965) The elimination of causal factors in pilonidal sinus treated by Z-plasty. Br J Surg 52:177–181
Roth RF, Moorman WL (1977) Treatment of pilonidal sinus and cyst by conservative excision and W-plasty closure. Plast Reconst Surg 60:412–415
Urhan MK, Kucukel F, Topgul K, Ozer I, Sari S (2002) Rhomboid excision and Limberg flap for managing pilonidal sinus. Dis Colon Rectum 45:656–659
Cherry JK (1986) Primary closure of pilonidal sinus. Surg Gynecol Obst 126:1263–1269
Aston SJ, Beasley RW, Thorne CHM (1997) Grabb and Smith’s plastic surgery, 5th edn. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, p 17
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Deparments of Surgery at Deenanath Mangeshkar and Sassoon General Hospitals Pune for their continuing support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahasrabudhe, P., Panse, N., Waghmare, C. et al. V-Y Advancement Flap Technique in Resurfacing Postexcisional Defect in Cases with Pilonidal Sinus Disease—Study of 25 Cases. Indian J Surg 74, 364–370 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-011-0403-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-011-0403-6