Abstract
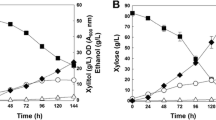
Kluyveromyces marxianus has the capability of producing xylitol from xylose because of the endogenous xylose reductase (KmXYL1) gene. In this study, we cloned KmXYL1 genes and compared amino acid sequences of xylose reductase (XR) from four K. marxianus strains (KCTC 7001, KCTC 7155, KCTC 17212, and KCTC 17555). Four K. marxianus strains showed high homologies (99%) of amino acid sequences with those from other reported K. marxianus strains and around 60% homologies with that from Scheffersomyces stipitis. For XR enzymatic activities, four K. marxianus strains exhibited thermostable XR activities up to 45°C and K. marxianus KCTC 7001 showed the highest XR activity. When reaction temperatures were increased from 30 to 45°C, NADH-dependent XR activity from K. marxianus KCTC 7001 was highly increased (46%). When xylitol fermentations were performed at 30 or 45°C, four K. marxianus strains showed very poor xylitol production capabilities regardless fermentation temperatures. Xylitol productions from four K. marxianus strains might be limited because of low xylose uptake rate or cell growth although they have high thermostable XR activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mäkinen, K. (1992) Dietary prevention of dental caries by xylitol-clinical effectiveness and safety. J Appl. Nutr. 44: 16–28.
Hyvonen, L., P. Koivistoinen, and F. Voirol (1982) Food technological evaluation of xylitol. Adv. Food Res. 28: 373–403.
Sasaki, M., T. Jojima, M. Inui, and H. Yukawa (2010) Xylitol production by recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum under oxygen deprivation. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 86: 1057–1066.
Mussatto, S. and I. Roberto (2004) Kinetic behavior of Candida guilliermondii yeast during xylitol production from highly concentrated hydrolysate. Proc. Biochem. 39: 1433–1439.
Prakash, G., A. Varma, A. Prabhune, Y. Shouche, and M. Rao (2011) Microbial production of xylitol from d-xylose and sugarcane bagasse hemicellulose using newly isolated thermotolerant yeast Debaryomyces hansenii. Bioresour. Technol. 102: 3304–3308.
Rao, R. S., C. P. Jyothi, R. Prakasham, P. Sarma, and L. V. Rao (2006) Xylitol production from corn fiber and sugarcane bagasse hydrolysates by Candida tropicalis. Bioresour. Technol. 97: 1974–1978.
Rodrigues, R. C., W. R. Kenealy, and T. W. Jeffries (2011) Xylitol production from DEO hydrolysate of corn stover by Pichia stipitis YS-30. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot. 38: 1649–1655.
Sampaio, F. C., V. M. Chaves-Alves, A. Converti, F. M. L. Passos, and J. L. C. Coelho (2008) Influence of cultivation conditions on xylose-to-xylitol bioconversion by a new isolate of Debaryomyces hansenii. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 502–508.
Tada, K., J.-I. Horiuchi, T. Kanno, and M. Kobayashi (2004) Microbial xylitol production from corn cobs using Candida magnoliae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 98: 228–230.
Vandeska, E., S. Amartey, S. Kuzmanova, and T. Jeffries (1996) Fed-batch culture for xylitol production by Candida boidinii. Proc. Biochem. 31: 265–270.
Walther, T., P. Hensirisak, and F. A. Agblevor (2001) The influence of aeration and hemicellulosic sugars on xylitol production by Candida tropicalis. Bioresour. Technol. 76: 213–220.
Oh, E. J., S. -J. Ha, S. R. Kim, W. -H. Lee, J. M. Galazka, J. H. Cate, and Y. -S. Jin (2013) Enhanced xylitol production through simultaneous co-utilization of cellobiose and xylose by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab. Eng. 15: 226–234.
Zhang, B., L. Li, J. Zhang, X. Gao, D. Wang, and J. Hong (2013) Improving ethanol and xylitol fermentation at elevated temperature through substitution of xylose reductase in Kluyveromyces marxianus. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot. 40: 305–316.
Zhang, B., L. Zhang, D. Wang, X. Gao, and J. Hong (2011) Identification of a xylose reductase gene in the xylose metabolic pathway of Kluyveromyces marxianus NBRC1777. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot. 38: 2001–2010.
Jang, S. -W., J. -S. Kim, J. -B. Park, J. -H. Jung, C. -S. Park, W. C. Shin, and S. -J. Ha (2015) Characterization of the starch degradation activity from newly isolated Rhizopus oryzae WCS-1 and mixed cultures with Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient ethanol production from starch. Food Sci. Biot. 24: 1805–1810.
Park, J. -B., J. -S. Kim, S. -W. Jang, E. Hong, and S. -J. Ha (2015) The application of thermotolerant yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus as a potential industrial workhorse for biofuel production. KSBB J. 30: 125–131.
Zhang, J., B. Zhang, D. Wang, X. Gao, and J. Hong (2014) Xylitol production at high temperature by engineered Kluyveromyces marxianus. Bioresour. Technol. 152: 192–201.
Kim, J. -S., J. -B. Park, S. -W. Jang, and S. -J. Ha (2015) Enhanced xylitol production by mutant Kluyveromyces marxianus 36907-FMEL1 due to improved xylose reductase activity. Appl. Biochem. Biot. 176: 1975–1984.
Rodrussamee, N., N. Lertwattanasakul, K. Hirata, S. Limtong, T. Kosaka, and M. Yamada (2011) Growth and ethanol fermentation ability on hexose and pentose sugars and glucose effect under various conditions in thermotolerant yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 90: 1573–1586.
Morton, R. E. and T. A. Evans (1992) Modification of the bicinchoninic acid protein assay to eliminate lipid interference in determining lipoprotein protein content. Anal. Biochem. 204: 332–334.
Boontham, W., N. Srisuk, K. Kokaew, P. Treeyoung, S. Limtong, A. Thamchaipenet, and H. Yurimoto (2014) Xylitol production by thermotolerant methylotrophic yeast Ogataea siamensis and its xylose reductase gene (XYL1) cloning. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 41: 491–502.
Zeng, Q. -K., H. -L. Du, J. F. Wang, D. -Q. Wei, X. -N. Wang, Y. -X. Li, and Y. Lin (2009) Reversal of coenzyme specificity and improvement of catalytic efficiency of Pichia stipitis xylose reductase by rational site-directed mutagenesis. Biotechnol. Lett. 31: 1025–1029.
Zhang, F., D. Qiao, H. Xu, C. Liao, S. Li, and Y. Cao (2009) Cloning, expression, and characterization of xylose reductase with higher activity from Candida tropicalis. The J. Microbiol. 47: 351–357.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, JB., Kim, JS., Jang, SW. et al. Sequence analysis of KmXYL1 genes and verification of thermotolerant enzymatic activities of xylose reductase from four Kluyveromyces marxianus strains. Biotechnol Bioproc E 21, 581–586 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-016-0363-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-016-0363-6