Abstract
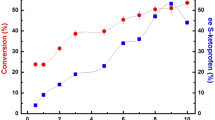
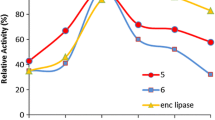
A lipase from the Burkholderia cepacia strain G63 immobilized on resin was used for the resolution of ketoprofen. To study its catalytic properties in enantioselective esterication, different alcohols and solvents were tested to select the most suitable acyl acceptor and reaction medium. Compared with the low activity of the free lipase, the enzyme activity and E value of the immobilized lipase were significantly enhanced. The enantioselectivity of the immobilized lipase could also be markedly improved by adding a small amount of 18-crown-6. RSM was employed to optimize the reaction parameters. The optimal reaction conditions were: reaction time 22.50 h, additives dosage 0.4322 g (0.33 mmol/mL), and substrate molar ratio 54.11:1. Under optimal conditions, the maximal E value was up to 10.01, which exhibited a better enantioselectivity than some commercial lipases, such as Novozym 435, Lipozyme RM IM and LipozymeTL IM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghanem, A., M. N. Aboul-Enein, A. El-Azzouny, and M. F. El-Behairy (2010) Lipase-mediated enantioselective kinetic resolution of racemic acidic drugs in non-standard organic solvents: Direct chiral liquid chromatography monitoring and accurate determination of the enantiomeric excesses. J. Chromatogr. A 1217: 1063–1074.
Duan, G., C. B. Ching, E. Lim, and C. H. Ang (1997) Kinetic study of enantioselective esterification of ketoprofen with n-propanol catalysed by anlipase in an organic medium. Biotechnol. Lett. 19: 1051–1055.
Lee, K. W., G. S. Shin, H. A. Bae, H. D. Shin, and Y. H. Lee (2005) Isolation and characterization of Acinetobacter sp. ES-1 excreting a lipase with high enantioselectivity for (S)-ketoprofen ethyl ester. Biotechnol. Lett. 26: 1639–1642.
Zhao, D., E. Xun, J. Wang, R. Wang, X. Wei, L. Wei, and Z. Wang (2011) Enantioselective esterification of ibuprofen by a novel thermophilic biocatalyst: APE1547. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 16: 638–644.
Bornscheuer, U. T. (2002) Methods to increase enantioselectivity of lipases and esterases. Curr. Opin. Biotechol. 13: 543–547.
David, G., C. Salagnad, P. Monsan, M. R. Simeona, and V. Tranc (2003) Towardsa novel explanation of Pseudomonas cepacia lipase enantioselectivity via molecular modelling of the enantiomer trajectory into the active site. Tetrahedron-Asymmetry 14: 1807–1817.
French, A. N. (2010) Clean, green chiral reactions-just add a salt. Science 328: 1365–1366.
Park, H. J., W. J. Choi, E. C. Huh, E. Y. Lee, and C. Y. Choi (1999) Production of optically active ketoprofen by direct enzymatic esterification. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 87: 545–547.
Wu, J. C., H. R. Low, Y. Leng, Y. Chow, R. Li, M. M. R. Talukder, and W. J. Choi (2006) Ketoprofen resolution by enzymatic esterification and hydrolysis of the ester product. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 11: 211–214.
Yang, J. K., D. Y. Guo, and Y. Yan (2007) Cloning, expression and characterization of a novel thermal stable and short-chain alcohol tolerant lipase from G63. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enz. 45: 91–96.
Jia, B., J. K. Yang, W. S. Liu, L. Xu, and Y. J. Yan (2010) Homologous overexpression of a lipase from Burkholderia cepacia using the lambda Red recombinase system. Biotechnol. Lett. 32: 521–526.
Jia, B., W. Liu, J. Yang, X. Wang, C. Ye, and Y. Yan (2010) Isolation and identification of lipase-producing Burkholderia cepacia in the soil. Biotechnol. Bull. 4: 183–188.
Yun, L., T. Liu, X. Wang, L. Xu, and Y. Yan (2011) Biodiesel synthesis catalyzed by Burkholderia cenocepacia lipase supported on macroporous resin NKA in solvent-free and isooctane systems. Energ. Fuel 25: 1206–1212.
Qin, L. and Y. J. Yan (2010) Production of biodiesel catalyzed by immobilized Pseudomonas cepacia lipase from Sapium sebiferum oil in micro-aqueous phase. Appl. Energ. 87: 3148–3154.
Qin, L., J. Zheng, and Y. J. Yan (2010) Biodiesel preparation catalyzed by compound-lipase in co-solvent. Fuel Proc. Technol. 91: 1229–1234.
Tomic, S., B. Bertosa, B. Kojic-Prodic, and I. Kolosvaruy (2004) Stereoselectivity of Burkholderia cepacia lipase towards secondary alcohols: Molecular modelling and 3D QSAR approach. Tetrahedron-Asymmetry 15: 1163–1172.
Liu, Y., X. Zhang, H. Tan, Y. J. Yan, and B. H. Hameed (2010) Effect of pretreatment by different organic solvents on esterification activity and conformation of immobilized Pseudomonas cepacia lipase. Proc. Biochem. 45: 1176–1180.
Rui, T., C. Yang, X. Wei, E. Xun, R. Wang, S. Cao, Z. Wang, and L. Wang (2011) Optimization of APE1547-catalyzed enantioselective transesterification of (R/S)-2-methyl-1-butanol in an ionic liquid. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 16: 337–342.
Petkar, M., A. Lali, P. Caimi, and M. Daminati (2006) Immobilization of lipases for nonaqueous synthesis. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enz. 39: 83–90.
Chen, C. S., Y. Fujimoto, G. Girdaukas, and C. J. Sih (1982) Quantitative analyses of biochemical kinetic resolutions of enantiomers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 104: 7294–7299.
Nicola, D. A., P. Lombardi, G. Nicolosi, and G. Salvo (2002) Large scale preparation of enantiopure S-ketoprofen by biocatalysed kinetic resolution. Proc. Biochem. 38: 373–377.
Holmquist, M., F. Haeffner, T. Norin, and K. Hult (1996) A structural basis for enantioselective inhibition of Candida rugosa lipase by long-chain aliphatic alcohols. Protein Sci. 5: 83–88.
Klibanov, A. M. (2001) Improving enzymes by using them in organic solvents. Nature 409: 241–246.
Wescott, C. R. and A. M. Klibanov (1993) Solvent variation inverts substrate specificity of an enzyme. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115: 1629–1631.
Wescott, C. R. and A. M. Klibanov (1997) Thermodynamic analysis of solvent effect on substrate specificity of lyophilized enzymes suspended in organic media. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 56: 340–344.
Laane, C., S. Boeren, K. Vos, and C. Veeger (2009) Rules for optimization of biocatalysis in organic solvents. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 102: 1–8.
Gregory, D. C., A. Ducret, M. Trani, and R. Lortie (2000) Enantioselective esterification of racemic ketoprofen in non-aqueous solvent under reduced pressure. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enz. 9: 49–56.
Ong, A. L., A. H. Kamaruddin, S. Bhatia, W. S. Long, S. T. Lim, and R. Kumari (2006) Performance of free Candida antarctica lipase B in the enantioselective esterification of (R)-ketoprofen. Enz. Microb. Tech. 39: 924–929.
Cong, F. D., Y. H. Wang, C. Y. Ma, H. F. Yu, S. P. Han, J. Tao, and S. G. Cao (2005) A way for resolution of (R, S)-2-octanol by combining dynamic kinetic resolution with double kinetic resolution. Enz. Microb. Tech. 36: 595–599.
Francisco, J. H. F., A. P. Rios, M. Rubio, D. Gomez, and G. Villora (2007) Enhancement of activity and selectivity in lipase-catalyzed transesterification in ionic liquids by the use of additives. J. Chem. Technol. Biotech. 82: 882–887.
Fritz, T. (2000) Enhancement of selectivity and reactivity of lipases by additives. Tetrahedron 56: 2905–2919.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Liu, T., Xu, L. et al. Resolution of racemic ketoprofen in organic solvents by lipase from Burkholderia cepacia G63. Biotechnol Bioproc E 17, 1147–1155 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0279-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0279-8