Abstract
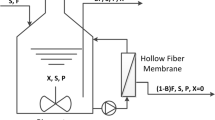
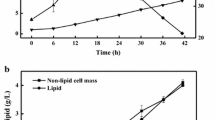
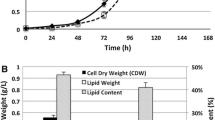
Volatile fatty acids (VFAs), acetic acid, acetates, and ethanol were used as carbon sources for the production of microbial lipids using Cryptococcus albidus in batch cultures. C. albidus utilized organic acids less than glucose in the production of lipids, resulting in a lipid yield coefficient on VFAs of 0.125 g/g. In a two-stage batch culture, the lipid content increased to 43.8% (w/w) when VFAs were used as the sole carbon source in the second stage, which was two times higher than that of the batch culture. Furthermore, a 192 h, two-stage fed-batch cultivation of C. albidus produced a dry cell weight, lipid concentration, and lipid content of 26.4 g/L, 14.5 g/L, and 55.1% (w/w), respectively. The fed-batch culture model used in this study featured pure VFA solutions, with intermittent feeding, under oxygen-enriched air supply conditions. This study investigated several alternative carbon sources to reduce the cost of microbial lipids production and proved the feasibility of using VFAs as the carbon source for the provision of a high lipid content and productivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xue, F. Y., J. X. Miao, X. Zhang, H. Luo, and T. W. Tan (2008) Studies on lipid production by Rhodotorula glutinis fermentation using monosodium glutamate wastewater as culture medium. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 5923–5927.
Meng, X., J. M. Yang, X. Xu, L. Zhang, Q. J. Nie, and M. Xian (2009) Review: Biodiesel production from oleaginous microorganisms. Renew. Ener. 34: 1–5.
Ratledge, C. (1991) Microorganisms for lipids. Acta Biotechnol. 11: 429–438.
Hansson, L. and M. Dostfilek (1986) Influence of cultivation conditions on lipid production by Cryptococcus albidus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24: 12–18.
Liang, Y. N., Y. Cui, J. Trushenski, and J. W. Blackburn (2010) Converting crude glycerol derived from yellow grease to lipids through yeast fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 101: 7581–7586.
Chang, H. N., N. J. Kim, J. W. Kang, C. M. Jeong, JDR Choi, F. Qiang, B. J. Kim, S. H. Kwon, S. Y. Lee, and J. B. Kim (2011) Multi-stage high cell continuous fermentation for high productivity and titer. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng DOI 10.1007/s00449-010-0485-8.
Li, Y. H., Z. B. Zhao, and F. W. Bai (2007) High-density cultivation of oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides Y4 in fedbatch culture. Enz. Microb. Technol. 41:312–317.
Fei, Q., H. N. Chang, L. A. Shang, J. D. R. Choi, N. J. Kim, and J. W. Kang (2011) The effect of volatile fatty acids as a sole carbon source on lipid accumulation by Cryptococcus albidus for biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 102: 2695–2701.
Lim, S. J., B. J. Kim, C. M. Jeong, J. D. R. Choi, Y. H. Ahn, and H. N. Chang (2008) Anaerobic organic acid production of food waste in once-a-day feeding and drawing-off bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 7866–7874.
Chang, H. N., N. J. Kim, J. W. Kang, and C. M. Jeong (2010) Biomass-derived volatile fatty acid platform for fuels and chemicals. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 15: 1–10.
Chang, H. N., M. I. Kim, Q. Fei, J. D. R. Choi, L. A. Shang, N. J. Kim, J. A. Kim, and H. G. Park (2010) Economic evaluation of Off-gas recycle pressure swing adsorption (PSA) on industrial scale poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) fermentation. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 15: 905–910.
Li, H., N. J. Kim, M. Jiang, J. W. Kang, and H. N. Chang (2009) Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of lignocellulose residues pretreated with phosphoric acid-acetone for bioethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 100: 3245–3251.
Li, X. F., H. Xu, and Q. Y. Wu (2007) Large-scale biodiesel production from microalga Chlorella protothecoides through heterotrophic cultivation in bioreactors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 98: 764–771.
Ratledge, C. (2004) Fatty acid biosynthesis in microorganisms being used for single cell oil production. Biochimie 86: 807–815.
Meesters, P., G. Huijberts, and G. Eggink (1996) High-cell-density cultivation of the lipid accumulating yeast Cryptococcus curvatus using glycerol as a carbon source. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 45: 575–579.
Kavadia, A., M. Komaitis, I. Chevalot, F. Blanchard, I. Marc, and G. Aggelis (2001) Lipid and gamma-linolenic acid accumulation in strains of Zygomycetes growing on glucose. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 78: 341–346.
Steen, E. J., Y. S. Kang, G. Bokinsky, Z. H. Hu, A. Schirmer, A. McClure, S. B. D. Cardayre, and J. D. Keasling (2010) Microbial production of fatty-acid-derived fuels and chemicals from plant biomass. Nature 463: 559–562.
Shang, L. A., P. Y. Tian, N. J. Kim, H. N. Chang, and M. S. Hahm (2009) Effects of oxygen supply modes on the production of human growth hormone in different scale bioreactors. Chem. Eng. Technol. 32: 600–605.
Youn, J. K., L. A. Shang, M. I. Kim, M. J. Chang, H. N. Chang, M. S. Hahm, S. K. Rhee, and H. A. Kang (2010) Enhanced production of human serum albumin by fed-batch culture of Hansenula polymorpha with high purity oxygen. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 20: 1534–1538.
Pan, J. G., M. Y. Kwak, and J. S. Rhee (1986) High density cell culture of Rhodotorula glutinis using oxygen-enriched air. Biotechnol. Lett. 8: 715–718.
Rodrigues, G. and C. Pais (2000) The influence of acetic and other weak carboxylic acids on growth and cellular death of the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 38: 27–32.
Yahara, G. A., M. A. Javier, M. J. M. Tulio, G. R. Javier, and A. U. M. Guadalupe (2007) Modeling of yeast Brettanomyces bruxellensis growth at different acetic acid concentrations under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Bioproc. Biosyst. Eng. 30: 389–395.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fei, Q., Chang, H.N., Shang, L. et al. Exploring low-cost carbon sources for microbial lipids production by fed-batch cultivation of Cryptococcus albidus . Biotechnol Bioproc E 16, 482–487 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-010-0370-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-010-0370-y