Abstract
Background
Bilateral breast cancer (BBC) is an unusual clinical entity. Unlike unilateral breast cancer, there is fewer data regarding clinicopathological aspects and treatment guidelines in BBC. The present study was carried out at a tertiary oncology center in South India to analyze the clinicopathological profile of patients diagnosed with BBC.
Methods
This was a retrospective observational study of patients diagnosed with BBC in the department of medical oncology from August 2012 to July 2013.
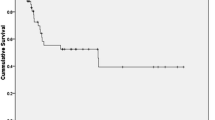
Results
Out of a total of 300 breast cancer patients during a 1-year period, 15 had BBC. Synchronous and metachronous breast cancers were seen in six and nine patients, respectively. The median age at presentation for BBC was 40 years. Family history of breast cancer was present only in two cases. The median age of menarche and first child birth was 13 and 22 years, respectively. History of breast feeding was positive in all except one who was nulliparous. Out of the 15 patients, 11 were premenopausal and 4 postmenopausal. Contralateral breast cancer was detected mammographically in 4 patients and by clinical examination in 11. Out of 30 tumors, all were invasive ductal carcinomas (IDC). Nine patients had bilateral mastectomy, and five had unilateral mastectomy. Out of 30 tumors, 14 were triple negative, 9 estrogen receptor (ER)/progesterone (PR) positive, and 7 Her2neu positive. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) was given in four synchronous and three metachronous breast cancer cases for contralateral breast cancer. All patients received chemotherapy during the course in the form of either adjuvant or palliative chemotherapy.
Conclusions
BBC is an uncommon clinical entity. For women with younger premenopausal age, the incidence of BBC is higher compared with older women. As the prognosis of BBC is poor, it is crucial to be aware of this entity, and every patient with breast cancer should be regularly followed up. These patients require individualized treatment planning based on the tumor factors and treatment factors of the primary lesion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaudary MA, Millis RR, Hoskins EO, et al. Bilateral primary breast cancer: a prospective study of disease incidence. Br J Surg. 1984;71:711–4.
El Hanchi Z, Berrada R, Fadli A, et al. Bilateral breast cancer: incidence and risk factors. Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2004;32:128–34. In French.
Heron DE, Komarnicky LT, Hyslop T, Schwartz GF, Mansfield CM. Bilateral breast carcinoma: risk factors and outcomes for patients with synchronous and metachronous disease. Cancer. 2000;88:2739–50.
Al-Jurf AS, Jochimsen PR, Urdaneta LF, Scott DH. Factors influencing survival in bilateral breast cancer. J Surg Oncol. 1981;16:343–8.
Cody HS, 3rd. Routine contralateral breast biopsy: helpful or irrelevant? Experience in 871 patients, 1979–1993. Ann Surg. 1997;225:370–6.
Chen Y, Thompson W, Semenciw R, et al. Epidemiology of contralateral breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1999;8:855–61.
Hislop TG, Elwood JM, Coldman AJ, Spinelli JJ, Worth AJ, Ellison LG. Second primary cancers of the breast: incidence and risk factors. Br J Cancer. 1984;49:79–85.
Jobsen JJ, van der Palen J, Ong F, Meerwaldt JH. Synchronous, bilateral breast cancer: prognostic value and incidence. Breast. 2003;12(2):83–8.
Robinson E, Rennert G, Rennert HS, Neugut AI. Survival of first and second primary breast cancer. Cancer. 1993;71:172–6.
Haagensen CD. The natural history of breast cancer. In: Diseases of the breast. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1971. S. 380–465.
MacMahon B, Cole P, Lin TM, Lowe CR, Mirra AP, et al. Age at first birth and breast cancer risk. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(2):209–21.
Bernstein JL, Thompson WD, Risch N, Holford TR. Risk factors predicting the incidence of second primary breast cancer among women diagnosed with a first primary breast cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 1992;136(8):925–36.
Horn PL, Thompson D. Risk of contralateral breast cancer: associations with factors related to initial breast cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 1988;128:309–23.
Khairy GA, Guraya SY, Ahmed ME, Ahmed MA. Bilateral breast cancer. Incidence, diagnosis and histological patterns. Saudi Med J. 2005;26(4):612–5.
Slack NH, Bross ID, Nemoto T, Fisher B. Experience with bilateral primary carcinoma of the breast. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1973;136(3):433–40.
Hankey BF, Curtis RE, Naughton MD, Boice JD, Jr., Flannery JT. A retrospective cohort analysis of second breast cancer risk for primary breast cancer patients with an assessment of the effect of radiation therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983;70(5):797–804.
Storm HH, Jensen OM. Risk of contralateral breast cancer in Denmark 1943–80. Br J Cancer. 1986;54(3):483–92.
Robbins GF, Berg JW. Bilateral primary breast cancer, a prospective clinicopathological study. Cancer. 1964;17:1501–27.
Suryanarayana Deo V, Shridhar D, Shukla NK, Kumar S, Purkayastha J, Raina V, Rath GK. Clinical profile and management of bilateral breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2005;7(Suppl. 1):P6. doi:10.1186/bcr1240.
Bernstein JL, Lapinski RH, Thakore SS, Doucette JT, Thompson WD. The descriptive epidemiology of second primary breast cancer. Epidemiology. 2003;14(5):552–8.
Li CI, Malone KE, Porter PL, Daling JR. Epidedmiologic and molecular risk factors for contralateral breast cancer among young women. Br J Cancer. 2003;89(3):513–8.
Gong SJ, Rha SY, Jeung HC, Roh JK, Yang WI, Chung HC. Bilateral breast cancer: differential diagnosis using histological and biological parameters. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2007;37:487–92.
Henderson IC, Patek AJ. The relationship between prognostic and predictive factors in management of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998;52(1–3):261–88.
Anderson WF, Chatterjee N, Ershler WB, Brawley OW. Estrogen receptor breast cancer phenotypes in the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results database. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2002;76(1):27–36.
Horn PL, Thompson WD. Risk of contralateral breast cancer. Association with histologic, clinical, and therapeutic factors. Cancer. 1988;62(2):412–4.
Mariani L, Coradini D, Biganzoli E, Boracchi P, Marubini E, Pilotti S, Salvadori B, Silvestrini R, Veronesi U, Zucali R, Rilke F. Prognosic factors for metachronous contralateral breast cancer: a comparison of linear Cox regression model and its artificial neural network expression. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1997;44(2):167–78.
Safal M, Lower EE, Hasselgren PO, Hungness ES, Gazder P, Aron B, Shaughnessy EA, Yassin R. Bilateral synchronous breast cancer and HER-2/neu overexpression. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2002;72(3):195–201.
van Agthoven T, Timmermans M, Dorssers LC, Henzen-Logmans SC. Expression of estrogen, progesterone and epidermal growth factor receptor in primary and metastatic breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1995;63:790–3.
Acknowledgement
Department of Pathology, Surgical Oncology and Pathology, Kidwai Memorial Institute of Oncology, Bangalore.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article was published as a poster in Indian Cancer Congress 2013, Delhi.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakshmaiah, K., Das, U., Babu, K. et al. Clinicopathological profile of bilateral breast cancer at a tertiary cancer center in South India. memo 7, 157–161 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12254-014-0153-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12254-014-0153-9