Abstract
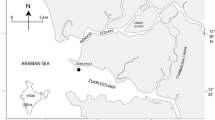
Picophytoplankton (Pico) seasonal dynamics and ecology were investigated in three eutrophic coastal lagoons (Calich, Santa Giusta, and Corru S’Ittiri) located in the same geographic region (Sardinia, Mediterranean Sea). Pico dynamics were examined to determine a relationship with variability in environmental conditions characterizing the three sites, and identify which parameters affected observed Pico dynamics. Results showed Pico density reached 108 cells L−1 and biomass values did not exceed 72.8 μg C L−1. Statistical analyses detected significant differences in hydrographic and nutrient conditions among lagoons, which were also characterized by variable Pico seasonal dynamics and composition. Calich and Santa Giusta were dominated all year around by picocyanobacteria. Maximum picocyanobacteria abundance was observed during summer in both lagoons, associated with the highest temperatures recorded. Picocyanobacteria abundance and nutrient concentrations showed a significant negative and positive correlation in Calich and Santa Giusta, respectively. In contrast, picoeukaryotes dominated Pico assemblages in Corru S’Ittiri, where the highest transparency and salinity and the lowest seasonal variation in salinity were recorded. In Corru S’Ittiri, the maximum Pico abundance was observed in autumn, when lower temperature and the highest nutrient concentrations were observed. Our study provides information on Pico assemblage ecology, which remains scarce in coastal and transitional environments, particularly in Mediterranean climate regimes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bazzoni, A.M., S. Pulina, B.M. Padedda, C.T. Satta, A. Lugliè, N. Sechi, and C. Facca. 2013. Water quality evaluation in Mediterranean lagoons using the Multimetric Phytoplankton Index (MPI): study cases from Sardinia. Transitional Waters Bulletin 7(1): 64–71.
Bec, B., Y. Collos, P. Souchu, A. Vaquer, J. Lautier, A. Fiandrino, L. Benau, V. Orsoni, and T. Laugier. 2011. Distribution of picophytoplankton and nanophytoplankton along an anthropogenic eutrophication gradient in French Mediterranean coastal lagoons. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 63: 29–45.
Bec, B., J. Husseini-Ratrema, Y. Collos, P. Souchu, and V. Vaquer. 2005. Phytoplankton seasonal dynamics in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon: emphasis on the picoeukaryote community. Journal of Plankton Research 27(9): 881–894.
Bernardi Aubry, F., F. Acri, M. Bastianini, A. Pugnetti, and G. Socal. 2006. Picophytoplankton contribution to phytoplankton community structure in the Gulf of Venice (NW Adriatic Sea). International Review of Hydrobiology 91: 51–70.
Bratbak, G. 1985. Bacterial biovolume and biomass estimation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 49: 1488–1493.
Bratbak, G. 1993. Microscope methods for measuring bacterial biovolume: epifluorescence microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. In Handbook of methods in aquatic microbial ecology, eds. P.F. Kemp, B.F. Sherr, E.B. Sherr, and J.J. Cole, 309–317. USA: Lewis Publisher.
Calvo-Díaz, A., X. Anxelu, G. Morán, and L.Á. Suárez. 2008. Seasonality of picophytoplankton chlorophyll a and biomass in the central Cantabrian Sea, southern Bay of Biscay. Journal of Marine Systems 72: 271–281.
Caroppo, C. 2000. The contribution of picophytoplankton to community structure in a Mediterranean brackish environment. Journal of Plankton Research 22(2): 381–397.
Caroppo, C. 2015. Ecology and biodiversity of picoplanktonic cyanobacteria in coastal and brackish environments. Biodiversity and Conservation 24: 949–971.
Carrick, H.J., and C.L. Schelske. 1997. Have we overlooked the importance of small phytoplankton in productive waters? Limnology and Oceanography 42: 1613–1621.
Cloern, J.E., and D.J. Jassby. 2010. Patterns and scales of phytoplankton variability in estuarine–coastal ecosystems. Estuaries and Coasts 33: 230–241.
Collos, Y., B. Bec, C. Jauzein, E. Abadie, T. Laugier, A. Pastoureaud, P. Souchu, A. Vaquer, and J. Lautier. 2009. Oligotrophication and emergence of picocyanobacteria and a toxic dinoflagellate in Thau lagoon, southern France. Journal of Sea Research 61: 68–75.
Flombaum, P., J.L. Gallegos, R.A. Gordillo, J. Rincón, L.L. Zabala, D.M. Karl, W.K.W. Li, M.W. Lomas, D. Veneziano, N. Jiao, C.S. Veraand, A.C. Martiny, and J.A. Vrugt. 2013. Present and future global distributions of the marine cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 110(24): 9824–9829.
Gaulke, A.K., M.S. Wetz, and H.W. Paerl. 2010. Picophytoplankton: a major contributor to planktonic biomass and primary production in a eutrophic, river-dominated estuary. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 90: 45–54.
Harris, G.P. 1994. Pattern, process and prediction in aquatic ecology. A limnological view of some general ecological problems. Freshwater Biology 32: 143–160.
Hein, M., M.F. Pedersen, and K. Sand-Jensen. 1995. Dependent nitrogen uptake in micro- and macroalgae. Marine Ecology Progress Series 118: 247–253.
Kuosa, H. 1991. Picoplanktonic algae in the northern Baltic Sea: seasonal dynamics and flagellate grazing. Marine Ecology Progress Series 73: 269–276.
Lugliè, A., N. Sechi, G. Oggiano, G. Sanna, and A. Tapparo. 2002. Ecological assessment of Santa Giusta lagoon (Sardinia, Italy). Annali di Chimica 92: 239–247.
MacIsaac, E.A., and J.G. Stockner. 1993. Enumeration of phototrophic picoplankton by autofluorescence microscopy. In Handbook of methods in aquatic microbial ecology, eds. P.F. Kemp, B.F. Sherr, E.B. Sherr, and J.J. Cole, 187–197. USA: Lewis Publisher.
Magazzù, G., and F. Decembrini. 1995. Primary production, biomass and abundance of phototrophic picoplankton in the Mediterranean Sea: a review. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 9: 97–104.
Ning, X., J.E. Cloern, and B.E. Cole. 2000. Spatial and temporal variability of picocyanobacteria Synechococcus sp. in San Francisco Bay. Limnology and Oceanography 45(3): 695–702.
Paoli, A., M. Celussi, A. Valeri, C. Larato, A. Bussani, S. Fonda Umani, M.R. Vadrucci, C. Mazziotti, and P. Del Negro. 2007. Picocyanobacteria in Adriatic transitional environments. Estuaries and coastal shelf. Science 75: 13–20.
R Core Team. 2012. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna. ISBN 3–900051–07-0. http://www.R-project.org/.
Satta, C.T., S. Anglès, E. Garcés, N. Sechi, S. Pulina, B.M. Padedda, D. Stacca, and A. Lugliè. 2014. Dinoflagellate cyst assemblages in surface sediments from three shallow Mediterranean lagoons (Sardinia, north western Mediterranean Sea. Estuaries and Coasts 37: 646–663.
Schapira, M., M.J. Buscot, T. Pollet, S.C. Leterme, and L. Seuront. 2010. Distribution of picophytoplankton communities from brackish to hypersaline waters in a south Australian coastal lagoon. Saline Systems 6: 2.
Sechi, N., F. Fiocca, A. Sannio, and A. Lugliè. 2001. Santa Giusta lagoon (Sardinia): phytoplankton and nutrients before and after waste water diversion. Journal of Limnology 60(2): 194–200.
Siokou-Frangou, I., U. Christaki, M.G. Mazzocchi, M. Montresor, M. Ribera D’Alcalá, D. Vaqué, and A. Zingone. 2010. Plankton in the open Mediterranean Sea: a review. Biogeosciences 7: 1543–1586.
Sorokin, Y.I., P.Y. Sorokin, and A. Gnes. 1996. Structure and functioning of the anthropogenically transformed Comacchio lagoonal ecosystem (Ferrara, Italy). Marine Ecological Progressive Series 133: 57–71.
Stockner, J.G. 1988. Phototrophic picoplankton: an overview from marine and freshwater ecosystems. Limnology and Oceanography 33(4): 765–775.
Strickland, J.D.H., and T.R. Parsons. 1972. A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Vol. 167. Ottawa: Fisheries Research Board of Canada.
Tamigneaux, E., E. Vasquez, M. Mingelbier, B. Klei, and L. Legendre. 1995. Environmental control of phytoplankton assemblages in nearshore waters, with special emphasis on phototrophic ultraplankton. Journal of Plankton Research 17: 1421–1447.
Thingstad, T.F., and F. Rassoulzadegan. 1999. Conceptual models for the biogeochemical role of the photic zone microbial food web, with particular reference to the Mediterranean Sea. Progress in Oceanography 44: 271–286.
Underwood, A.J. 1997. Experiments in ecology: their logical design and interpretation using analysis of variance, 504. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Vaquer, A., M. Troussellier, C. Courties, and B. Bibent. 1996. Standing stock and dynamics of picophytoplankton in the Thau lagoon (Northwest Mediterranean coast. Limnology and Oceanography 41: 1821–1828.
Worden, A.Z., J.K. Nolan, and B. Palenik. 2004. Assessing the dynamics and ecology of marine picophytoplankton: The importance of the eukaryotic component. Limnology and Oceanography 49(1): 168–179.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank colleagues of the Aquatic Ecology group of University of Sassari for nutrient analyses, Fabrizio Bernardi-Aubry for his support in Pico analysis, and Silvia Anglès for her contribution to the linguistic revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Charles Simenstad
Electronic supplementary material
Online Resource 1
(DOC 41 kb)
Online Resource 2
(DOC 47 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pulina, S., Satta, C.T., Padedda, B.M. et al. Picophytoplankton Seasonal Dynamics and Interactions with Environmental Variables in Three Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons. Estuaries and Coasts 40, 469–478 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-016-0154-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-016-0154-5