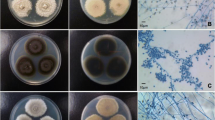
Abstract
Gordonia spp. are members of the actinomycete family, and the environment, especially soil, is the natural habitat of this genus of bacteria. Gordonia spp. are important for two aspects: first, some Gordonia species cause a broad spectrum of diseases in healthy and immunocompromised individuals; second, these bacteria are capable of producing useful secondary metabolites, which may be used in various industries; therefore, discrimination of the genus Gordonia from other genera in the actinomycete family is important. Phenotypic and molecular techniques are necessary for accurate identification of Gordonia at the species level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arenskötter M, Bröker D, Steinbüchel A (2004) Biology of the metabolically diverse genus Gordonia. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3195–3204
Aoyama K, Kang Y, Yazawa K, Gonoi T, Kamei K, Mikami Y (2009) Characterization of clinical isolates of Gordonia species in Japanese clinical samples during 1998–2008. Mycopathologia 168:175–183
Blanc V, Dalle M, Markarian A, Debunne M, Duplay E, Rodriguez-Nava V, Boiron P (2007) Gordonia terrae: a difficult-to-diagnose emerging pathogen? J Clin Microbiol 45:1076–1077
Blaschke AJ, Bender J, Byington CL, Korgenski K, Daly J, Petti CA, Pavia AT, Ampofo K (2007) Gordonia species: emerging pathogens in pediatric patients that are identified by 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing. Clin Infect Dis 45:483–486
Brandao PF, Maldonado LA, Ward AC, Bull AT, Goodfellow M (2001) Gordonia namibiensis sp. nov., a novel nitrile metabolising actinomycete recovered from an African sand. Syst Appl Microbiol 24:510–515
Brust JC, Whittier S, Scully BE, McGregor CC, Yin MT (2009) Five cases of bacteraemia due to Gordonia species. J Med Microbiol 58:1376–1378
Cha JH, Cha CJ (2013) Gordonia alkaliphila sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from tidal flat sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:327–331
De Mennezes CBA, Afonso RS, De Souza WR, Parma DMIS, Zucchi TD, Fantinatti-Garboggini F (2016) Gordonia didemni sp. nov. an actinomycete isolated from the marine ascidium Didemnum sp. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 109:297–303
Drancourt M, Pelletier J, Cherif AA, Raoult D (1997) Gordona terrae central nervous system infection in an immunocompetent patient. J Clin Microbiol 35:379–382
Drancourt M, McNeil MM, Brown JM, Lasker BA, Maurin M, Choux M, Raoult D (1994) Brain abscess due to Gordona terrae in an immunocompromised child: case report and review of infections caused by G. terrae. Clin Infect Dis 19:258–262
Drzyzga O (2012) The strengths and weaknesses of Gordonia: a review of an emerging genus with increasing biotechnological potential. Crit Rev Microbiol 38:300–316
Franzetti A (2007) Surface active compounds by Gordonia and their applications in environmental remediation. Thesis, Università degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca.
Gil-Sande E, Brun-Otero M, Campo-Cerecedo F, Esteban E, Aguilar L, García-de-Lomas J (2006) Etiological misidentification by routine biochemical tests of bacteremia caused by Gordonia terrae infection in the course of an episode of acute cholecystitis. J Clin Microbiol 44:2645–2647
Goodfellow M, Peter K, Busse H Jr, Trujillo ME, Ludwig W, Suzuki K-I, Parte A (2012) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology: volume 5: the actinobacteria. springer, New York
Gupta M, Prasad D, Khara HS, Alcid D (2010) A rubber-degrading organism growing from a human body. Int J Infect Dis 14:75–76
Hamid ME, Musa MT, El-Sanousi SM, El Hassan MM, Martin J, Goodfellow M (2015) Characterization of Gordonia sinesedis isolated from a zebu cow suffering from lymphadenitis. Br Microbiol Res J 5:216–226
Herath H, Athukoralage P, Jamie JF (2000) Two oleanane triterpenoids from Gordonia ceylanica and their conversions to taraxarane triterpenoids. Phytochemistry 54:823–827 http://www.dsmz.de
Iida S, Taniguchi H, Kageyama A, Yazawa K, Chibana H, Murata S, Nomura F, Kroppenstedt RM, Mikami Y (2005) Gordonia otitidis sp. nov., isolated from a patient with external otitis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1871–1876
Jannat-Khah DP, Halsey ES, Lasker BA, Steigerwalt AG, Hinrikson HP, Brown JM (2009) Gordonia araii infection associated with an orthopedic device and review of the literature on medical device-associated Gordonia infections. J Clin Microbiol 47:499–502
Johnson JA, Onderdonk AB, Cosimi LA, Yawetz S, Lasker BA, Bolcen SJ, Brown JM, Marty FM (2011) Gordonia bronchialis bacteremia and pleural infection: case report and review of the literature. J Clin Microbiol 49:1662–1666
Kampfer P, Martin K, Dott W (2013) Gordonia phosphorivorans sp. nov., isolated from a wastewater bioreactor with phosphorus removal. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:230–235
Kageyama A, Iida S, Yazawa K, Kudo T, Suzuki S, Koga T, Saito H, Inagawa H, Wada A, Kroppenstedt RM, Mikami Y (2006) Gordonia araii sp. nov. and Gordonia effusa sp. nov., isolated from patients in Japan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1817–1821
Kampfer P, Young CC, Chu JN, Frischmann A, Busse HJ, Arun A, Shen FT, Rekhan P (2011) Gordonia humi sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:65–70
Kang YQ, Ming H, Gonoi T, Chen Y, Cao Y, Wang YY, Cheng J, Koga T, Mikami Y, Li WJ (2014) Gordonia iterans sp. nov., isolated from a patient with pneumonia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:3520–3525
Kempf V, Schmalzing M, Yassin A, Schaal KP, Baumeister D, Arenskötter M, Steinbüchel A, Autenrieth IB (2004) Gordonia polyisoprenivorans septicemia in a bone marrow transplant patient. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 23:226–228
Kofteridis DP, Valachis A, Scoulica E, Christidou A, Maraki S, Samonis G (2011) Hickman catheter-related bacteremia caused by Gordonia sputi in a patient with breast cancer. J Infect Dev Ctries 6:188–191
Kondo T, Yamamoto D, Yokota A, Suzuki A, Nagasawa H, Sakuda S (2000) Gordonan, an acidic polysaccharide with cell aggregation-inducing activity in insect BM-N4 cells, produced by Gordonia sp. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:2388–2394
Kummer C, Schumann P, Stackebrandt E (1999) Gordonia alkanivorans sp. nov., isolated from tar-contaminated soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 49:1513–1522
Kuwabara M, Onitsuka T, Nakamura K, Shimada M, Ohtaki S, Mikami Y (1999) Mediastinitis due to Gordona sputi after CABG. J Cardiovasc Surg 40:675–677
Lai C-C, Hsieh J-H, Tsai H-Y, Liao C-H, Hsueh P-R (2012) Cutaneous infection caused by Gordonia amicalis after a traumatic injury. J Clin Microbiol 50:1821–1822
Lai C, Wang C, Liu C, Tan CK, Lin SH, Liao CH, Chou CH, Huang YT, Lin HI, Hsueh PR (2010) Infections caused by Gordonia species at a medical centre in Taiwan, 1997 to 2008. Clin Microbiol Infect 16:1448–1453
Le Roes M, Goodwin CM, Meyers PR (2008) Gordonia lacunae sp. nov., isolated from an estuary. Syst Appl Microbiol 31:17–23
Lesens O, Hansmann Y, Riegel P, Heller R, Benaissa-Djellouli M, Martinot M, Petit H, Christmann D (2000) Bacteremia and endocarditis caused by a Gordonia species in a patient with a central venous catheter. Emerg Infect Dis 6:382
Li SH, Jin Y, Cheng J, Park DJ, Kim CJ, Hozzein WN, Wadaan MA, Shu WS, Ding LX, Li WJ (2014) Gordonia jinhuaensis sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium, isolated from a VBNC (viable but non-culturable) state in pharmaceutical wastewater. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 106:347–356
Linos A, Steinbüchel A, Spröer C, Kroppenstedt RM (1999) Gordonia polyisoprenivorans sp. nov., a rubber-degrading actinomycete isolated from an automobile tyre. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 49:1785–1791
Liu Y, Ge F, Chen G, Li W, Ma P, Zhang G, Zeng L (2011) Gordonia neofelifaecis sp. nov., a cholesterol side-chain-cleaving actinomycete isolated from the faeces of Neofelis nebulosa. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:165–169
Luo H, Gu Q, Xie J, Hu C, Liu Z, Huang Y (2007) Gordonia shandongensis sp. nov., isolated from soil in China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:605–608
Ma TKW, Chow KM, Kwan BCH, Lee KP, Leung CB, Li PKT, Szeto CC (2014) Peritoneal-dialysis related peritonitis caused by Gordonia species: report of 4 cases and review of literature. Nephrology 19:379–383
Mikolasch A, Hammer E, Schauer F (2003) Synthesis of imidazol-2-yl amino acids by using cells from alkane-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1670–1679
Moser BD, Pellegrini GJ, Lasker BA, Brown JM (2012) Pattern of antimicrobial susceptibility obtained from blood isolates of a rare but emerging human pathogen, Gordonia polyisoprenivorans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:4991–4993
Mukherjee S, Das P, Sen R (2006) Towards commercial production of microbial surfactants. Trends Biotechnol 24:509–515
Nawaz SZ, Miles J, Skinner JA (2010) Gordonia terrae causing metatarsal osteomyelitis in an immunocompetent patient: a case report. Eur Orthop Traumatol 1:139–141
Nguyen DB, Gupta N, Abou-Daoud A, Klekamp BG, Rhone C, Winston T, Hedberg T, Scuteri A, Evans C, Jensen B, Moulton-Meissner H, Török T, Berríos-Torres SI, Noble-Wang J, Kallen A (2014) A polymicrobial outbreak of surgical site infections following cardiac surgery at a community hospital in Florida, 2011-2012. Am J Infect Control 42:432–435
Nishiuchi Y, Baba T, Yano I (2000) Mycolic acids from Rhodococcus, Gordonia, and Dietzia. J Microbiol Methods 40:1–9
Park S, Kang SJ, Kim W, Yoon JH (2009) Gordonia hankookensis sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:3172–3175
Pham AS, Dé I, Rolston KV, Tarrand JJ, Han XY (2003) Catheter-related bacteremia caused by the nocardioform actinomycete Gordonia terrae. Clin Infect Dis 36:524–527
Ramanan P, Deziel PJ, Wengenack NL (2013) Gordonia bacteremia. J Clin Microbiol 51:3443–3447
Renvoise A, Harle J-R, Raoult D, Roux V (2009) Gordonia sputi bacteremia. Emerg Infect Dis 15:1535
Richet HM, Craven PC, Brown JM, Lasker BA, Cox CD, McNeil MM, Tice AD, Jarvis WR, Tablan OC (1991) A cluster of Rhodococcus (Gordona) bronchialis sternal-wound infections after coronary-artery bypass surgery. N Engl J Med 324:104–109
Schneider K, Graf E, Irran E, Nicholson G, Stainsby FM, Goodfellow M, Borden SA, Keller S, Süssmuth RD, Fiedler HP (2008) Bendigoles A approximately C, new steroids from Gordonia australis acta 2299. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 61:356–364
Shen F-T, Goodfellow M, Jones AL, Chen YP, Arun AB, Lai WA, Rekha PD, Young CC (2006) Gordonia soli sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2597–2601
Singh P, Cameotra SS (2004) Potential applications of microbial surfactants in biomedical sciences. Trends Biotechnol 22:142–146
Sng L-H, Koh T, Toney S, Floyd M, Butler W, Tan B (2004) Bacteremia caused by Gordonia bronchialis in a patient with sequestrated lung. J Clin Microbiol 42:2870–2871
Soddell JA, Stainsby FM, Eales KL, Seviour RJ, Goodfellow M (2006) Gordonia defluvii sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from activated sludge foam. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2265–2269
Srinivasan S, Park G, Yang H, Hwang S, Bae Y, Jung YA, Kim MK, Lee M (2012) Gordonia caeni sp. nov., isolated from sludge of a sewage disposal plant. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:2703–2709
Stackebrandt E, Smida J, Collins MD (1988) Evidence of phylogenetic heterogeneity within the genus Rhodococcus: revival of the genus Gordona (Tsukamura). J Gen Appl Microbiol 34:341–348
Stackebrandt E, Rainey FA, Ward-Rainey NL (1997) Proposal for a new hierarchic classification system, actinobacteria classis nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 47:479–491
Steingrube VA, Wilson RW, Brown BA, Jost K, Blacklock Z, Gibson JL, Wallace R (1997) Rapid identification of clinically significant species and taxa of aerobic actinomycetes, including Actinomadura, Gordona, Nocardia, Rhodococcus, Streptomyces, and Tsukamurella isolates, by DNA amplification and restriction endonuclease analysis. J Clin Microbiol 35:817–822
Takeuchi M, Hatano K (1998) Gordonia rhizosphera sp. nov. isolated from the mangrove rhizosphere. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:907–912
Veiga-Crespo P, Blasco L, Rosa dos Santos F, Poza M, Villa TG (2010) Influence of culture conditions of Gordonia jacobaea MV-26 on canthaxanthin production. Int Microbiol 8:55–58
Verma P, Brown JM, Nunez VH, Morey RE, Steigerwalt AG, Pellegrini GJ, Kessler HA (2006) Native valve endocarditis due to Gordonia polyisoprenivorans: case report and review of literature of bloodstream infections caused by Gordonia species. J Clin Microbiol 44:1905–1908
Vidal C, Padilla E, Alcacer P, Campos E, Prieto F, Santos C (2014) Breast abscess caused by Gordonia bronchialis and the use of 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis for its definitive identification. JMM Case Reports. doi:10.1099/jmmcr.0.001248
Werno AM, Anderson TP, Chambers ST, Laird HM, Murdoch DR (2005) Recurrent breast abscess caused by Gordonia bronchialis in an immunocompetent patient. J Clin Microbiol 43:3009–3010
Yassin A, Shen FT, Hupfer H, Arun A, Lai WA, Rekha P, Young CC (2007) Gordonia malaquae sp. nov., isolated from sludge of a wastewater treatment plant. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1065–1068
Yoon JH, Lee JJ, Kang SS, Takeuchi M, Shin YK, Lee ST, Kang KH, Park YH (2000) Gordonia nitida sp. nov., a bacterium that degrades 3-ethylpyridine and 3-methylpyridine. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1203–1210
Zardawi IM, Jones F, Clark DA, Holland J (2004) Gordonia terrae-induced suppurative granulomatous mastitis following nipple piercing. Pathology 36:275–278
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andalibi, F., Fatahi-Bafghi, M. Gordonia: isolation and identification in clinical samples and role in biotechnology. Folia Microbiol 62, 245–252 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-017-0491-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-017-0491-1