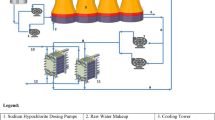
Abstract
The use of Shitalakhya River Water (SRW) as makeup water in power plant cooling systems is a matter of great concern due to its degraded water quality resulting from polluted discharges from different industries. The present study assesses corrosion and scaling scenarios in closed-loop recirculating cooling systems while using SRW at 2.5 cycles of concentration, the recommended concentration for SRW in a proposed cooling systems. Computation of Langelier Saturation Index and Ryznar Stability Index showed very high corrosion and low scaling potential of the cooling water. A synthetic recipe, prepared considering typical concentrations of inorganic constituents of the cooling water, was used in bench-scale experiments with mild steel and copper alloys. The corrosiveness of the cooling water towards mild steel and copper alloys was found to be unacceptable according to corrosion criteria. Use of sodium nitrite, an anodic corrosion inhibitor, reduced the corrosion rate of both metal alloys by more than 90% and within acceptable range. Presence of organic matter in the SRW reduced the corrosion rate of the metal alloys. Surface analysis of exposed metal alloy samples indicated formation of fewer corrosion products while using sodium nitrite corrosion inhibitor. No mineral scaling was observed on the metal alloy specimens from surface analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam, M. A., Badruzzaman, A. B. M., and Ali, M. A. (2012). “Spatiotemporal assessment of water quality of the Sitalakhya River, Bangladesh.” International Journal of Engineering and Technology, Vol. 2, No. 6, pp. 953–962, 10.1.1.412.1111
An, Y., Yang, F., Wong, F. S., and Chua, H. C. (2009). “Effect of recirculation ratio on simultaneous methanogenesis and nitrogen removal using a combined upflow anaerobic sludge blanket — Membrane bioreactor.” Environmental Engineering Science, Vol. 26, Issue 6, pp. 1047–1053, DOI: 10.1089/ees.2007.0317.
Asano, T., Burton, F., and Leverenz, H. (2003). Water reuse: Issues, technologies, and applications, McGraw-Hill, New York, N.Y.
ASTM Standard D2688-05 (2005). Standard test method for corrosivity of water in the absence of heat transfer (weight loss method), American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, DOI: 10.1520/D2688-05.
ASTM Standard G1-03 (2005). Standard practice for preparing, cleaning, and evaluating corrosion test specimens. American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, DOI: 10.1520/G0001-03.
AWWA, APHA, and WEF (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th Edition, American Water Works Association (AWWA), American Public Health Association (APHA), Water Environment Federation (WEF).
Bernat, K. and Wojnowska-Baryla, I. (2007). “Carbon source in aerobic denitrification.” Biochemical Engineering Journal, Vol. 36, Issue 2, pp. 116–122, DOI: 10.1016/j.bej.2007.02.007.
Breistein, L. and Tucker, R. C. (1986). Water reuse and recycle in the U.S. steam electric generating industry-an assessment of current practice and potential for future applications, Report No. PB-86-167657/XAB, U.S. Geological Survey, Reston, VA.
Broo, A. E., Berghult, B., and Hedberg, T. (1998). “Copper corrosion in water distribution systems-the influence of Natural Organic Matter (NOM) on the solubility of copper corrosion products.” Corrosion Science, Vol. 40, Issue 9, pp. 1479–1489, DOI: 10.1016/S0010-938X(98)00059-6.
Broo, A. E., Berghult, B., and Hedberg, T. (1999). “Drinking water distribution–The effect of Natural Organic Matter (NOM) on the corrosion of iron and copper.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 40, No. 9, pp. 17–24, DOI: 10.1016/S0273-1223(99)00635-6.
Bureau of Research, Testing and Consultation (BRTC) (2012). Final report: Environmental impact assessment of the World Bank Financed 335 MW combined cycle power plant at Siddhirganj, Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET).
Choudhury, M. R., Hsieh, M. K., Vidic, R. D., and Dzombak, D. A. (2012). “Corrosion management in power plant cooling systems using tertiary-treated municipal wastewater as makeup water.” Corrosion Science, Vol. 61, pp. 231–241, DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2012.04.042.
Chowdhury, N., Nakhla, G., and Zhu, J. (2008). “Load maximization of a liquid–solid circulating fluidized bed bioreactor for nitrogen removal from synthetic municipal wastewater.” Chemosphere, Vol. 71, Issue 5, pp. 807–815, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.11.070.
Dangcong, P., Bernet, N., Delgenes, J. P., and Moletta, R. (2001). “Simultaneous organic carbon and nitrogen removal in an SBR controlled at low dissolved oxygen concentration.” Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, Vol. 76, Issue 6, pp. 553–558, DOI: 10.1002/jctb.419.
Dean, S. W. Jr., Derby, R., and Bussche, G. T. V. D. (1981). “Inhibitor Types.” Mater. Performance, Vol. 20, No. 12, pp. 47–51.
Edwards, M. and Sprague, N. (2001). “Organic matter and copper corrosion by-product release: A mechanistic study.”. Corrosion Science, Vol. 43, No. 1, pp. 1–18, DOI: 10.1016/S0010-938X(00)00071-8.
Environmental Conservation Rules (ECR), Bangladesh (1997). Schedule — 10: Standards for waste from industrial units or projects waste, http://www.moef.gov.bd/html/laws/env_law/178-189.pdf.
Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) (2003). Use of degraded water sources as cooling water in power plants, EPRI Report No. 1005359, http://www.energy.ca.gov/reports/2004-02-23_500-03-110.PDF.
Eriksson, R., Merta, J., and Rosenholm, J. B. (2007). “The calcite/water interface: I. Surface charge in indifferent electrolyte media and the influence of low-molecular-weight polyelectrolyte.” Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, Vol. 313, No. 1, pp. 184–193, DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2007.04.034.
Frayne, C. (1999). Cooling water treatment-principles and practice, Chemical Publishing Co., Inc., New York, NY.
Goldstein, D., Casana, J., and Wei, I. (1981). “Municipal wastewater reuse as makeup to cooling towers.” Proc., The Water Reuse Symposium II, AWWA Research Foundation, Washington, DC., USA, August 23–28.
Hayyan, M., Sameh, S. A., Hayyan, A., and Nashef, I. M. A. (2012). “Utilizing of sodium nitrite as inhibitor for protection of carbon steel in salt solution.” International Journal of Electrochemical Science, Vol. 7, No. 8, pp. 6941–6950.
Herro, H. M. and Port, R. D. (1993). The Nalco guide to cooling water system failure analysis, McGraw-Hill Inc., New York, N.Y.
Holakoo, L., Nakhla, G., Bassi, A. S., and Yanful, E. K. (2009). “Long term performance of MBR for biological nitrogen removal from synthetic municipal wastewater.” Chemosphere, Vol. 66, Issue 5, pp. 849–857, DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.06.026.
Hsieh, M. K., Li, H., Chien, S. H., Monnell, J. D., Chowdhury, I., Dzombak, D. A., and Vidic, R. D. (2010). “Corrosion control when using secondary treated municipal wastewater as alternative makeup water for cooling tower systems.” Water Environment Research, Vol. 82, No. 12, pp. 2346–2356, DOI: 10.2175/106143010X12681059117094.
Kimura, K., Naruse, T., and Watanabe, Y. (2009). “Changes in characteristics of soluble microbial products in membrane bioreactors associated with different solid retention times: relation to membrane fouling.” Water Research, Vol. 43, Issue 4, pp. 1033–1039, DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.11.024.
Li, H., Hsieh, M. K., Chien, S. H., Monnell, J. D., Dzombak, D. A., and Vidic, R. D. (2011). “Control of mineral scale deposition in cooling systems using secondary-treated municipal wastewater.” Water Research, Vol. 45, No. 2, pp. 748–760, DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.08.052.
Miller, W. G. (2006). “Integrated concepts in water reuse: managing global water needs.” Desalination, Vol. 187, Nos. 1–3, pp. 65–75, DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2005.04.068.
Naghizadeh, A., Mahvi, A. H., Vaezi, F., and Naddafi, K. (2008). “Evaluation of hollow fiber membrane bioreactor efficiency for municipal wastewater treatment.” Iraian Journal of Environmental Health Science & Engineering, Vol. 5, Issue 4, pp. 257–268.
Rafferty, K. (1999). Scaling in geothermal heat pump systems, U.S. Department of Energy, Idaho Operations Office. Available at: http://geoheat.oit.edu/otl/scaleghp.pdf.
Rehring, J. P. and Edwards, M. (1996). “Copper corrosion in potable water systems: Impacts of natural organic matter and water treatment processes.” Corrosion, Vol. 52, No. 4, pp. 307–317, DOI: 10.5006/1.3293642.
Rozenfeld, I. L. (1981). Corrosion inhibitors, McGraw-Hill Inc., New York, N.Y.
Sastri, V. S. (1998). Corrosion Inhibitors: Principles and Applications, John Wiley and Sons, Chichester.
Selby, K. A. and Helm, K. R. (1996). “The use of reclaimed water in electric power stations and other industrial facilities.” Water, Air and Soil Pollution, Vol. 90, Nos. 1–2, pp. 183–193, DOI: 10.1007/BF00619280.
Sen, S. and Demirer, G. N. (2003). “Anaerobic treatment of real textile wastewater with a fluidized bed reactor.” Water Research, Vol. 37, Issue 8, pp. 1868–1878, DOI: 10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00577-8.
Southern Illinois University (SIU) (2006). Water use benchmarks for thermoelectric power generation, Project Completion Report USGS National Competitive Grants Program, Carbondale, IL, http://web.extension.illinois.edu/iwrc/pdf/238.pdf.
Stansbury, E. E. and Buchanan, R. A. (2000). Fundamentals of electrochemical corrosion, ASM International, Ohio.
Tosun, A. and Ergun, M. (2006). “Protection of corrosion of carbon steel by inhibitors in chloride containing solutions.” G.U. Journal of Science, Vol. 19, No. 3, pp. 149–154.
Veil, J. A. (2007). Use of reclaimed water for power plant cooling, Report No. ANL/EVS/R-07/3, U.S. Department of Energy, National Energy Technology Laboratory, Pittsburgh, PA.
Weinberger, L.W., Stephan, D. G., and Middleton, F. M. (1966). “Solving our water problems-water renovation and reuse.”. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, Vol. 136, No. 5, pp. 131–154, DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb31410.x
Williams, R. B. (1982). “Wastewater reuse-An assessment of the potential and technology.” Water Reuse, Ann Arbor Science, Inc., Michigan, pp. 88–136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhury, M.R., Siddik, M.A.Z. & Salam, M.Z.E.I. Use of Shitalakhya River Water as makeup water in power plant cooling system. KSCE J Civ Eng 20, 571–580 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-015-1369-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-015-1369-x