Abstract
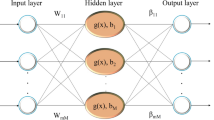
Due to the presence of solid matter in the flow passing through sewer pipes, determining the minimum velocity that prevents sediment deposition is essential. In this study, the Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) network optimized with three different training algorithms, including variable learning rate (MLP-GDX), resilient back-propagation (MLP-RP) and Levenberg-Marquardt (MLP-LM) is studied in terms of ability to estimate sediment transport in a clean pipe. The results indicate that for all algorithms, model ANN(d) that uses volumetric sediment concentration (C V ), median relative size of particles (d/D), ratio of median diameter particle size to hydraulic radius (d/R) and overall sediment friction factor (λ s ) as input parameters, is more accurate than the other models. In predicting Fr, the results of MLP-LM (R 2 = 0.98, RMSE = 0.02 and MAPE = 5.13) are better than MLP-GDX (R 2 = 0.96, RMSE = 0.03 and MAPE = 5.9) and MLP-RP (R 2 = 0.95, RMSE = 0.26 and MAPE = 5.74). A comparison of the model selected in this study with existing equations of sediment transport in sewer pipes also indicates that ANN(d)-LM (RMSE = 0.025 & MAPE = 5.78) perform better than existing equations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ab Ghani, A. (1993). Sediment transport in sewers, PhD Thesis,University of Newcastle Upon Tyne, UK.
Ackers, J. C., Butler, D., and May, R. W. P. (1996). Design of sewers to control sediment problems, Report No. CIRIA 141, Construction Industry Research and Information Association, London.
Almedeij, J. (2012). “Rectangular storm sewer design under equal sediment mobility.” American Journal of Environmental Science, Vol. 8, No. 4, pp. 376–384.
Almedeij, J. and Almohsen, N. (2010). “Remarks on Camp criterion for self-cleansing storm sewer.” Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, Vol. 136, No. 2, pp. 145–148. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE) IR.1943-4774.0000129.
Alp, M. H. and Cigizoglu, K. (2007). “Suspended sediment load simulation by two artificial neural network methods using hydrometeorological data.” Environmental Modeling and Software, Vol. 22, No. 1, pp. 2–13, DOI: 10.1016/j.envsoft.2005.09.009.
Azamathulla, H. Md., Ab Ghani, A., and Fei, S. Y. (2012). “ANFIS–based approach for predicting sediment transport in clean sewer.” Journal of Applied Soft Computing, Vol. 12, No. 3, pp. 1227–1230, DOI: 10.1016/j.asoc.2011.12.003.
Azamathulla, H. Md., and Zakaria, N. A. (2011). “Prediction of scour below submerged pipeline crossing a river using ANN.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 63, No. 10, pp. 2225–2230, DOI: 10.2166/wst.2011.459.
Baghalian, S., Bonakdari, H., Nazari, F., and Fazli, M. (2012). “Closedform solution for flow field in curved channels in comparison with experimental and numerical analyses and Artificial Neural Network.” Engineering Application of Computational Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 514–526.
Banasiak, R. (2008). “Hydraulic performance of sewer pipes with deposited sediments.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 57, No. 11, pp. 1743–1748, DOI: 10.2166/wst.2008.287.
Bonakdari, H., Baghalian, S., Nazari, F., and Fazli, M. (2011). “Numerical analysis and prediction of the velocity field in curved open channel using Artificial Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm.” Engineering Application of Computational Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 5, No. 3, pp. 384–396.
Bonakdari, H. and Ebtehaj, I. (2014). “Verification of equation for nondeposition sediment transport in flood water canals.” 7th International Conference on Fluvial Hydraulics, RIVER FLOW 2014, Lausanne, Switzerland, pp. 1527–1533.
Bonakdari, H. and Larrarte, F. (2006). “Experimental and numerical investigation on self-cleansing and shear in sewers.” 2nd International IWA Conference, Sewer Operation and Maintenance, SOM 06, Vienna, Austria, pp. 19–26.
Bong, C. H. J., Lau, T. L., and Ab Ghani, A. (2013). “Verification of equations for incipient motion studies for a rigid rectangular channel.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 67, No. 2, pp. 395–403, DOI: 10.2166/wst.2012.580.
Bong, C. H. J., Lau, T. L., and Ab Ghani, A. (2014). “Self-cleansing design of rectangular open storm sewer.” 13th International Conference on Urban Drainage, Sarawak, Malaysia.
Butler, D., May, R. W. P., and Ackers, J. (2003). “Self-cleansing sewer design based on sediment transport principles.” Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, Vol. 129, No. 4, pp. 276–282, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE) 0733-9429(2003)129:4(276).
Ebtehaj, I. and Bonakdari, H. (2013). “Evaluation of sediment transport in sewer using artificial Neural Network.” Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 7, No. 3, pp. 382–392.
Ebtehaj, I. and Bonakdari, H. (2014). “Performance evaluation of adaptive neural fuzzy inference system for sediment transport in Sewers.” Water Resource Management, Vol. 28, No. 13, pp. 4765:4779, DOI: 10.1007/s11269-014-0774-0.
Ebtehaj, I, Bonakdari, H., and Sharifi, A. (2014). “Design criteria for sediment transport in sewers based on self-cleansing concept.” Journal of Zhejiang University Science-A, Vol. 15, No. 11, pp. 914–924, DOI: 10.1631/jzus.A1300135.
Cigizoglu, H. K. (2003). “Estimation, forecasting and extrapolation of flow data by artificial neural networks.” Hydrological Sciences Journal, Vol. 48, No. 3, pp. 349–361, DOI: 10.1623/hysj.48.3.349.45288.
Dawson, W. C. and Wilby, R. (1998). “An artificial neural network approach to rainfall-runoff modelling.” Hydrological Sciences Journal, Vol. 43, No. 1, pp. 47–66, DOI: 10.1080/02626669809492102.
Hornik, K., Stinchcombe, M., and White, H. (1989). “Multilayer feed forward networks are universal approximators.” Neural Networks, Vol. 2, No. 5, pp. 359–366, DOI: 10.1016/0893-6080(89)90020-8).
Jain, S. K., Nayak, P. C., and Sudheer, K. P. (2008). “Models for estimating evapotranspiration using artificial neural networks, and their physical interpretation.” Hydrological Processes, Vol. 22, No. 13, pp. 2225–2234, DOI: 10.1002/hyp.6819.
Jalili-Ghazi Zade, M. and Noori, R. (2008). “Prediction of municipal solid waste generation by use of artificial neural network: A case study of Mashhad.” International Journal of Environmental Research, Vol. 2, No. 1, pp. 13–22.
Kisi, O. (2007). “Streamflow forecasting using different artificial neural network algorithms.” Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, Vol. 12, No. 5, pp. 532–539, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(2007)12:5(532).
Macke, E. (1982). “About sediment at low concentrations in partly filled pipes.” Mitteilungen, Leichtweiss institut fur Wasserbau der technischen Universitat Braunschweig, Heft, Vol. 71, pp. 1–151.
May, R. W. P. (1993). Sediment transport in pipes and sewers with deposited beds, Hydraulic Research Ltd., Wallingford, England, Report SR 320.
May, R. W. P., Ackers, J. C., Butler, D., and Johnt, S. (1996). “Development of design methodology for self-cleansing sewers.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 33, No. 9, pp. 195–205, DOI: 10.1016/0273- 1223(96)00387-3.
May, R. W. P., Brown, P. M., Hare, G. R., and Jones, K. D. (1989). Selfcleansing conditions for sewers carrying sediment, Hydraulics Research Ltd., Wallingford, England, Report SR 221.
Mayerle, R., Nalluri, C., and Novak, P. (1991). “Sediment transport in rigid bed conveyance.” Journal of Hydraulic Research, Vol. 29, No. 4, pp. 475–495, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(2007)12:5(532).
Melesse, A. M., Ahmad, S., McClain, M. E., and Lim, Y. H. (2011). “Suspended sediment load prediction of river systems: An artificial neural network approach.” Agricultural Water Management, Vol. 98, No. 5, pp. 855–866, DOI: 10.1016/j.agwat.2010.12.012.
More, J. J. (1977). The Levenberg—Marquardt algorithm: Implementation and theory, Numerical Analysis. In: Watson GA (ed) Lecture notes in mathematics 630, Springer, New York, pp. 105–116.
Nagy, H., Watanabe, K., Hirano, M. (2002). “Prediction of sedimentload concentration in rivers using artificial Neural Network Model.” Journal of. Hydraulic Engineering, Vol. 128, No. 6, pp. 588–595, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2002)128:6(588).
Nalluri, C. (1985). Sediment transport in rigid boundary channels, Proceeding. Euromech 192: Transport of Suspended Solids in Open channels, Neubiberg, Germany, pp. 101–104.
Nalluri, C., Ab Ghani, A., and El-Zaemey, A. K. S. (1994). “Sediment transport over deposited beds in sewers.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 29, Nos. 1–2, pp. 125–133.
Nalluri, C. and Kithsiri, M. M. A. U. (1992). “Extended data on sediment transport in rigid bed rectangular channel.” Journal of Hydraulic Research, Vol. 30, No. 6, pp. 851–856. DOI: 10.1080/ 00221689209498914.
Novak, P. and Nalluri, C. (1975). “Sediment transport in smooth fixed bed channels.” Journal of Hydraulic Division, ASCE, Vol. 101, pp. 1139–1154.
Noori, R., Hoshyaripour, G., Ashrafi, K., and Nadjar-Araabi, B. (2010). “Uncertainty analysis of developed ANN and ANFIS models in prediction of carbon monoxide daily concentration.” Atmospheric Environment, Vol. 44, No. 4, pp. 476–482. DOI: 10.1016/j.atmosenv. 2009.11.005.
Nour, M. H., Smith, D. W. and Prepas, E. E. (2006). “Neural networks modelling of streamflow, phosphorus, and suspended solids: Application to the Canadian Boreal forest.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 53, No. 10, pp. 91–99.
Nourouzi, M. M., Chuah, T. G., and Choong, T. S. Y. (2011). “Optimisation of reactive dye removal by sequential electrocoagulation–flocculation method: Comparing ANN and RSM prediction.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 63, No. 5, pp. 985–995. DOI: 10.2166/wst.2011.280.
Ota, J. J. and Nalluri, C. (2003). “Urban storm sewer design: Approach in consideration of sediments.” Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, Vol. 129, No. 4, pp. 291–297, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2003) 129:4(291).
Ota J. J. and Perrusquia, G. S. (2013). “Particle velocity and sediment transport at the limit of deposition in sewers.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 67, No. 5, pp. 959–967, DOI: 10.2166/wst.2013.646.
Partal, T. (2009). “River flow forecasting using different artificial neural network algorithms and wavelet transform.” Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, Vol. 36, No. 1, pp. 26–38. DOI: 10.1139/L08-090.
Rezaeian Zadeh, M., Amin, S., Khalili, D., and Singh, V. P. (2010). “Daily outflow prediction by multilayer perceptron with logistic sigmoid and tangent sigmoid activation functions.” Water Resource Management, Vol. 24, No. 11, pp. 2673–2688, DOI: 10.1007/ s11269-009-9573-4.
Riedmiller, M. and Braun, H. (1993). “A direct adaptive method for faster back propagation learning: The RPROP algorithm.” Proceedings of IEEE international joint conference on neural networks, San Francisco, pp. 586–591.
Sarangi, A. and Bhattacharya, A. K. (2005). “Comparison of Artificial Neural Network and regression models for sediment loss prediction from Banha watershed in India.” Agricultural Water Management, Vol. 78, pp. 195–208, DOI: 10.1016/j.agwat.2005.02.001.
Schulz, F. H., Wolf, H., Jansen, H. W., and Van der Veer, P. (2005). “Applications of artificial neural networks in integrated water management: fiction or future?.” Water Science and Technology, Vol. 52, No. 9, pp. 21–31.
Shahin, M. A., Jaksa, M. B., and Maier, H. R. (2008). “State of the art of artificial neural networks in geotechnical engineering.” Electronic Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, Vol. 8, pp. 1–26.
Sudheer, K. P., and Jain, A. (2004). “Explaining the internal behavior of artificial neural network river flow models.” Hydrological Processes, Vol. 18, No. 4, pp. 833–844, DOI: 10.1002/hyp.5517.
Vongvisessomjai, N., Tingsanchali, T., and Babel, M. S. (2010). “Nondeposition design criteria for sewers with part-full flow.” Urban Water Journal, Vol. 7, No. 1, pp. 61–77, DOI: 10.1080/15730620903242824.
Yonaba, H., Anctil, F., and Fortin, V. (2010). “Comparing sigmoid transfer functions for neural network multistep ahead streamflow forecasting.” Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, ASCE, Vol. 15, No. 4, pp. 275–283, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000188.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebtehaj, I., Bonakdari, H. Bed load sediment transport estimation in a clean pipe using multilayer perceptron with different training algorithms. KSCE J Civ Eng 20, 581–589 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-015-0630-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-015-0630-7