Abstract
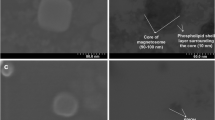
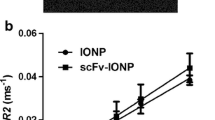
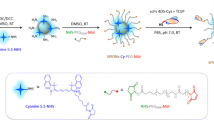
The combination of liposomes with magnetic nanoparticles, because of their strong effect on T2 relaxation can open new ways in the innovative cancer therapy and diagnosis. In order to design an intelligent contrast agent in MRI, we chose anti-HER2 nanobody the smallest fully functional antigen-binding fragments evolved from the variable domain, the VHH, of a camel heavy chain-only antibody. These targeted magnetoliposomes bind to the HER2 antigen which is highly expressed on breast and ovarian cancer cells so reducing the side effects as well as increasing image contrast and effectiveness. Cellular iron uptake analysis and in vitro MRI of HER2 positive cells incubated with targeted nanoparticles show specific cell targeting. In vitro MRI shows even at the lowest density (200 Cells/μl), dark spots corresponding to labeled cells which were still detectable. These results suggest that this new type of nanoparticles could be effective antigen-targeted contrast agents for molecular imaging.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonnet, C. S., Tóth É. MRI contrast agents. In: Ligand Design in Medicinal Inorganic Chemistry, 2014, pp. 321–354.
Clift, M. J., B. Rothen-Rutishauser, D. M. Brown, R. Duffin, K. Donaldson, L. Proudfoot, et al. The impact of different nanoparticle surface chemistry and size on uptake and toxicity in a murine macrophage cell line. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 232(3):418–427, 2008.
De Cuyper, M., S. J. Soenen, K. Coenegrachts, and L. T. Beek. Surface functionalization of magnetoliposomes in view of improving iron oxide-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents: anchoring of gadolinium ions to a lipophilic chelate. Anal. Biochem. 367(2):266–273, 2007.
De Meyer, T., S. Muyldermans, and A. Depicker. Nanobody-based products as research and diagnostic tools. Trends Biotechnol. 32(5):263–270, 2014.
Faria, M., M. Cruz, M. Gonçalves, A. Carvalho, G. Feio, and M. Martins. Synthesis and characterization of magnetoliposomes for MRI contrast enhancement. Int. J. Pharm. 446(1):183–190, 2013.
Frascione, D., C. Diwoky, G. Almer, P. Opriessnig, C. Vonach, K. Gradauer, et al. Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide (USPIO)-based liposomes as magnetic resonance imaging probes. Int. J. Nanomed. 7:2349, 2012.
Jamnani, F. R., F. Rahbarizadeh, M. A. Shokrgozar, D. Ahmadvand, F. Mahboudi, and Z. Sharifzadeh. Targeting high affinity and epitope-distinct oligoclonal nanobodies to HER2 over-expressing tumor cells. Exp. Cell Res. 318(10):1112–1124, 2012.
Jamnani, F. R., F. Rahbarizadeh, M. A. Shokrgozar, F. Mahboudi, D. Ahmadvand, Z. Sharifzadeh, et al. T cells expressing VHH-directed oligoclonal chimeric HER2 antigen receptors: towards tumor-directed oligoclonal T cell therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 1840(1):378–386, 2014.
Khaleghi, S., F. Rahbarizadeh, D. Ahmadvand, M. Malek, and H. R. Madaah Hosseini. The effect of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles surface engineering on relaxivity of magnetoliposome. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 11:340, 2016.
Lima-Tenório, M. K., E. A. G. Pineda, N. M. Ahmad, H. Fessi, and A. Elaissari. Magnetic nanoparticles: in vivo cancer diagnosis and therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 493(1):313–327, 2015.
Lu, R.-M., Y.-L. Chang, M.-S. Chen, and H.-C. Wu. Single chain anti-c-Met antibody conjugated nanoparticles for in vivo tumor-targeted imaging and drug delivery. Biomaterials 32(12):3265–3274, 2011.
Moghimi, S. M., F. Rahbarizadeh, D. Ahmadvand, and L. Parhamifar. Heavy chain only antibodies: a new paradigm in personalized HER2+ breast cancer therapy. BioImpacts: BI 3(1):1, 2013.
Oliveira, S., R. M. Schiffelers, J. van der Veeken, R. van der Meel, R. Vongpromek, P. M. V. B. en Henegouwen, et al. Downregulation of EGFR by a novel multivalent nanobody-liposome platform. J. Control. Release 145(2):165–175, 2010.
Reynolds, J. G., E. Geretti, B. S. Hendriks, H. Lee, S. C. Leonard, S. G. Klinz, et al. HER2-targeted liposomal doxorubicin displays enhanced anti-tumorigenic effects without associated cardiotoxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 262(1):1–10, 2012.
Rotman, M., M. M. Welling, A. Bunschoten, M. E. de Backer, J. Rip, R. J. Nabuurs, et al. Enhanced glutathione PEGylated liposomal brain delivery of an anti-amyloid single domain antibody fragment in a mouse model for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Control. Release 203:40–50, 2015.
Sabaté, R., R. Barnadas-Rodríguez, J. Callejas-Fernández, R. Hidalgo-Álvarez, and J. Estelrich. Preparation and characterization of extruded magnetoliposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 347(1):156–162, 2008.
Sadeqzadeh, E., F. Rahbarizadeh, D. Ahmadvand, M. J. Rasaee, L. Parhamifar, and S. M. Moghimi. Combined MUC1-specific nanobody-tagged PEG-polyethylenimine polyplex targeting and transcriptional targeting of tBid transgene for directed killing of MUC1 over-expressing tumour cells. J. Control. Release 156(1):85–91, 2011.
Sharifzadeh, Z., F. Rahbarizadeh, M. A. Shokrgozar, D. Ahmadvand, F. Mahboudi, F. R. Jamnani, et al. Genetically engineered T cells bearing chimeric nanoconstructed receptors harboring TAG-72-specific camelid single domain antibodies as targeting agents. Cancer Lett. 334(2):237–244, 2013.
Shinkai, M., M. Suzuki, S. Iijima, and T. Kobayashi. Antibody-conjugated magnetoliposomes for targeting cancer cells and their application in hyperthermia. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 21(2):125–137, 1995.
Singh, A., and S. K. Sahoo. Magnetic nanoparticles: a novel platform for cancer theranostics. Drug Discov. Today 19(4):474–481, 2014.
Soenen, S. J., J. Baert, and M. De Cuyper. Optimal conditions for labelling of 3T3 fibroblasts with magnetoliposomes without affecting cellular viability. Chembiochem 8(17):2067–2077, 2007.
Soenen, S. J., M. De Cuyper, S. C. De Smedt, and K. Braeckmans. Investigating the toxic effects of iron oxide nanoparticles. Methods Enzymol. 509:195–224, 2012.
Soenen, S. J., S. F. De Meyer, T. Dresselaers, G. V. Velde, I. M. Pareyn, K. Braeckmans, et al. MRI assessment of blood outgrowth endothelial cell homing using cationic magnetoliposomes. Biomaterials 32(17):4140–4150, 2011.
Soenen, S. J., G. V. Velde, A. Ketkar-Atre, U. Himmelreich, and M. De Cuyper. Magnetoliposomes as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 3(2):197–211, 2011.
Steinhauser, I., B. Spänkuch, K. Strebhardt, and K. Langer. Trastuzumab-modified nanoparticles: optimisation of preparation and uptake in cancer cells. Biomaterials 27(28):4975–4983, 2006.
Van de Broek, B., N. Devoogdt, A. D’Hollander, H.-L. Gijs, K. Jans, L. Lagae, et al. Specific cell targeting with nanobody conjugated branched gold nanoparticles for photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 5(6):4319–4328, 2011.
Wray, W., T. Boulikas, V. P. Wray, and R. Hancock. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 118(1):197–203, 1981.
Yigit, M. V., A. Moore, and Z. Medarova. Magnetic nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Pharm. Res. 29(5):1180–1188, 2012.
Conflict of Interest
The authors (Sepideh Khaleghi, Fatemeh Rahbarizadeh, Davoud Ahmadvand, Hamid Reza Madaah Hosseini) declare to have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants and animals performed by any of the authors.
Funding
This paper was supported by Faculty of Medical Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran and School of Allied Medical Sciences, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran reference 16550.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Partha Roy oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khaleghi, S., Rahbarizadeh, F., Ahmadvand, D. et al. Anti-HER2 VHH Targeted Magnetoliposome for Intelligent Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Breast Cancer Cells. Cel. Mol. Bioeng. 10, 263–272 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-017-0481-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-017-0481-z