Abstract
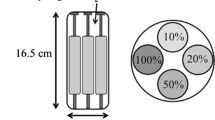
Chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) is a new contrast enhancement approach for imaging exogenous or endogenous substances such as creatine (Cr), amide protons, and glutamate in the human body. An increase in field strength is beneficial for CEST imaging because of the increased chemical shift and longer longitudinal relaxation time (T1). In high-field magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), establishing and evaluating the CEST effect is important for optimizing the magnetization transfer (MT) saturation radio frequency (RF) pulses. In this study, the CEST effect on Cr was evaluated at different concentrations in pH phantoms by appropriately selecting MT saturation RF pulses using 11.7 T MRI. The results showed that the CEST efficiency increased gradually with increasing applied saturation RF pulse power and that it was affected by the number of saturation RF pulses and their bandwidths. However, spillover effects were observed with higher saturation RF pulse powers. In conclusion, we successfully performed in vitro Cr CEST imaging under optimized conditions of MT saturation RF pulses.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CEST:
-
Chemical exchange saturation transfer
- Cr:
-
Creatine
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- MRS:
-
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- MT:
-
Magnetization transfer
- MTR:
-
Magnetization transfer ratio
- RARE:
-
Rapid acquisition with relaxation enhancement
- RF:
-
Radio frequency
- T1 :
-
Longitudinal relaxation time
- T2W:
-
T2-weighted images
References
Velan SS, Durst C, Lemieux SK, Raylman RR, Sridhar R, Spencer RG, et al. Investigation of muscle lipid metabolism by localized one- and two-dimensional MRS techniques using a clinical 3T MRI/MRS scanner. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;25:192–9. doi:10.1002/jmri.20786.
Usenius T, Usenius JP, Tenhunen M, Vainio P, Johansson R, Soimakallio S, et al. Radiation-induced changes in human brain metabolites as studied by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in vivo. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;33:719–24.
Ward KM, Aletras AH, Balaban RS. A new class of contrast agents for MRI based on proton chemical exchange dependent saturation transfer (CEST). J Magn Reson. 2000;143:79–87. doi:10.1006/jmre.1999.1956.
Haris M, Nanga RP, Singh A, Cai K, Kogan F, Hariharan H, et al. Exchange rates of creatine kinase metabolites: feasibility of imaging creatine by chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI. NMR Biomed. 2012;25:1305–9. doi:10.1002/nbm.2792.
Zhou J, Payen JF, Wilson DA, Traystman RJ, van Zijl PC. Using the amide proton signals of intracellular proteins and peptides to detect pH effects in MRI. Nat Med. 2003;9:1085–90. doi:10.1038/nm907.
Cai K, Haris M, Singh A, Kogan F, Greenberg JH, Hariharan H, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of glutamate. Nat Med. 2012;18:302–6. doi:10.1038/nm.2615.
Chan KW, McMahon MT, Kato Y, Liu G, Bulte JW, Bhujwalla ZM, et al. Natural d-glucose as a biodegradable MRI contrast agent for detecting cancer. Magn Reson Med. 2012;68:1764–73. doi:10.1002/mrm.24520.
Terreno E, Castelli DD, Aime S. Encoding the frequency dependence in MRI contrast media: the emerging class of CEST agents. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2010;5:78–98. doi:10.1002/cmmi.369.
Sun PZ, Benner T, Kumar A, Sorensen AG. Investigation of optimizing and translating pH-sensitive pulsed-chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging to a 3T clinical scanner. Magn Reson Med. 2008;60:834–41. doi:10.1002/mrm.21714.
Barker GJ, Simmons A, Arridge SR, Tofts PS. A simple method for investigating the effects of non-uniformity of radiofrequency transmission and radiofrequency reception in MRI. Br J Radiol. 1998;71:59–67. doi:10.1259/bjr.71.841.9534700.
Sun PZ, van Zijl PC, Zhou J. Optimization of the irradiation power in chemical exchange dependent saturation transfer experiments. J Magn Reson. 2005;175:193–200. doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2005.04.005.
Volz S, Noth U, Rotarska-Jagiela A, Deichmann R. A fast B1-mapping method for the correction and normalization of magnetization transfer ratio maps at 3 T. Neuroimage. 2010;49:3015–26. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.11.054.
Singh A, Cai K, Haris M, Hariharan H, Reddy R. On B1 inhomogeneity correction of in vivo human brain glutamate chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast at 7T. Magn Reson Med. 2013;69:818–24. doi:10.1002/mrm.24290.
Desmond KL, Stanisz GJ. Understanding quantitative pulsed CEST in the presence of MT. Magn Reson Med. 2012;67:979–90. doi:10.1002/mrm.23074.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mr. Junpei Ueda, Mr. Hisato Sasahara and Mr. Isamu Yabata (Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka University, Japan) for technical assistance. This work was partly supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (Kakenhi, Nos. 24791299 and 24300167) by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, S., Mori, Y., Tanki, N. et al. Factors affecting the chemical exchange saturation transfer of Creatine as assessed by 11.7 T MRI. Radiol Phys Technol 8, 146–152 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-014-0303-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-014-0303-0