Abstract
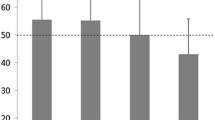
This study aimed to identify the optimal concentration, injection rate, and total volume of contrast medium (CM) for evaluating the hemodynamics of a hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) structure model of diameter 35 mm, using multi-level dynamic computed tomography (M-LDCT) with 64 detector rows. A tube was inserted in the model as a simulated vessel. Five CM concentrations were used: non-diluted, 2-, 3-, 6-, and 9-fold diluted. Five regions of interest were placed within the HCC structure model. Time–density curves were created for CM injection rates of 1, 2, and 3 ml/s for 10 s, and for a total volume of 10 ml, followed by saline injection at 1 ml/s. M-LDCT maximum intensity projection images were evaluated by four appraisers using a three-point scale (excellent, 2; good, 1; poor, 0). There was no significant difference between maximum CT values at 2 ml/s for 10 s and those at 3 ml/s; these values were both greater than those at 1 ml/s. The duration of the peak was maintained for longer at 3 ml/s for 10 s (5.2 ± 2.3 s) than at 2 ml/s (3.6 ± 0.9 s). Maximum CT values at 2 ml/s of a total volume of 10 ml were greater than those at 3 ml/s. The highest scores of 7 and 8 were found at 2 and 3 ml/s for 10 s, using 2-, 3-, or 6-fold diluted CM. The most appropriate CM rate for evaluating hemodynamics was 2 ml/s for 10 s, using 2-, 3-, or 6-fold diluted CM.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kojiro M. Pathological diagnosis of early hepatocellular carcinoma: a report of the international consensus group for hepatocellular neoplasia. Hepatology. 2009;49:658–64.
Matsui O, Kobayashi S, Sanada J, Kouda W, Ryu Y, Kozaka K, Nakamura K, Gabata T. Hepatocellular nodules in liver cirrhosis: hemodynamic evaluation (angiography-assisted CT) with special reference to multi-step hepatocarcinogenesis. Abdom Imaging. 2011;36:264–72.
Kitao A, Zen Y, Matsui O, Gabata T, Nakanuma Y. Hepatocarcinogenesis: multistep changes of drainage vessels at CT during arterial portography and hepatic arteriography—radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiology. 2009;252:605–14.
Kobayashi S, Matsui O, Gabata T, Sanada J, Koda W, Minami T, Ryu Y. Radiological and histopathological manifestations of hepatocellular nodular lesions concomitant with various congenital and acquired hepatic hemodynamic abnormalities. Jpn J Radiol. 2009;27:53–68.
Pugacheva O, Matsui O, Kozaka K, Minami T, Ryu Y, Koda W, Kobayashi S, Gabata T. Detection of small hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma by EASL criteria: comparison with double-phase CT during hepatic arteriography. Eur J Radiol. 2011;80:e201–6.
Ueda K, Matsui O, Kawamori Y, Kadoya M, Yoshikawa J, Gabata T, Nonomura A, Takashima T. Hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma: evaluation of hemodynamics with dynamic CT during hepatic arteriography. Radiology. 1998;206:161–6.
Kanamoto H, Horibe T, Kudo K, Taira J, Sugimoto K, Metoki R, Furuichi Y, Miyahara T, Moriyasu F. Utility of interventional-CT (IVR-CT) in transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) for hepatocellular carcinoma—a comparative study of TACE with and without IVR-CT. Kanzo. 2007;48:589–97.
Sultana S, Awai K, Nakayama Y, Nakaura T, Liu D, Hatemura M, Funama Y, Morishita S, Yamashita Y. Hypervascular hepatocellular carcinomas: bolus tracking with a 40-detector CT scanner to time arterial phase imaging. Radiology. 2007;243:140–7.
Murakami T, Kim T, Takamura M, Hori M, Takahashi S, Federie MP, Tsuda K, Osuga K, Nakamura H, Kudo M. Hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma: detection with double arterial phase multi-detector row helical CT. Radiology. 2001;218:763–7.
Yamaguchi I, Kidoya E, Suzuki M, Kimura H. Optimizing scan timing of hepatic arterial phase by physiologic pharmacokinetic analysis in bolus-tracking technique by multi-detector row computed tomography. Radiol Phys Technol. 2011;4:43–52.
Kitamura T, Ichikawa T, Erturk SM, Nakajima H, Araki T, Okada S, Enomoto N. Detection of hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma with multidetector-row CT; single arterial-phase imaging with computer-assisted automatic bolus-tracking technique compared with double arterial-phase imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2008;32:724–9.
Funabasama S, Tsushima Y, Sanada S, Inoue K. Hepatic perfusion CT imaging analyzed by the dual-input one-compartment model. Nihon Hoshasen Gijutu Gakkai Zasshi. 2003;59:1548–54.
Ichikawa T, Motosugi U, Morisaka H, Sou H, Onohara K, Sano K, Araki T. Optimal iodine dose for 3-dimensional multidetector-row CT angiography of the liver. Eur J Radiol. 2011 (epub).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Murotani, K., Kawai, N., Sato, M. et al. Optimal injection rate and volume of contrast medium for observing hemodynamics of a hepatocellular carcinoma structure model. Radiol Phys Technol 6, 78–85 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-012-0172-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-012-0172-3