Abstract
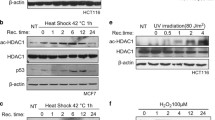
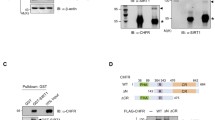
Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) plays an important role in stress responses such as misfolded protein-induced aggresomes, autophagy, and stress granules. However, precisely how HDAC6 manages response during and after cellular stress remains largely unknown. This study aimed to investigate the effect of HDAC6 on various stress and post-stress recovery responses. We showed that HIF-1α protein levels were reduced in HDAC6 knockout (KO) MEFs compared to wild-type (WT) MEFs in hypoxia. Furthermore, under hypoxia, HIF-1α levels were also reduced following rescue with either a catalytically inactive or a ubiqiutin-binding mutant HDAC6. HDAC6 deacetylated and upregulated the stability of HIF-1α, leading to activation of HIF-1α function under hypoxia. Notably, both the deacetylase and ubiquitin-binding activities of HDAC6 contributed to HIF-1α stabilization, but only deacetylase activity was required for HIF-1α transcriptional activity. Suppression of HDAC6 enhanced the interaction between HIF-1α and HSP70 under hypoxic conditions. In addition to hypoxia, depletion of HDAC6 caused hypersensitivity to cell death during oxidative stress and post-stress recovery. However, HDAC6 depletion had no effect on cell death in response to heat shock or ionizing radiation. Overall, our data suggest that HDAC6 may serve as a critical stress regulator in response to different cellular stresses.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HDAC:
-
Histone deacetylase
- HDACi:
-
HDAC inhibitor
- HIF-1:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- HRE:
-
Hypoxic response element
- HSP:
-
Heat shock protein
- KO:
-
Knockout
- MEF:
-
Mouse embryonic fibroblast
- ODD:
-
Oxygen-dependent degradation
- PTM:
-
Posttranslational modification
- SG:
-
Stress granule
- VHL:
-
von Hippel-Lindau
References
Anderson P, Kedersha N (2006) RNA granules. J Cell Biol 172:803–808
Arnesen T et al (2005) Interaction between HIF-1 alpha (ODD) and hARD1 does not induce acetylation and destabilization of HIF-1 alpha. FEBS Lett 579:6428–6432
Bardos JI, Ashcroft M (2005) Negative and positive regulation of HIF-1: a complex network. Biochim Biophys Acta 1755:107–120
Beere HM (2005) Death versus survival: functional interaction between the apoptotic and stress-inducible heat shock protein pathways. J Clin Invest 115:2633–2639
Bilton R et al (2005) Arrest-defective-1 protein, an acetyltransferase, does not alter stability of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and is not induced by hypoxia or HIF. J Biol Chem 280:31132–31140
Boyault C et al (2007) HDAC6 controls major cell response pathways to cytotoxic accumulation of protein aggregates. Genes Dev 21:2172–2181
Brostrom CO, Brostrom MA (1998) Regulation of translational initiation during cellular responses to stress. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 58:79–125
Bunz F et al (1998) Requirement for p53 and p21 to sustain G2 arrest after DNA damage. Science 282:1497–1501
DeGracia DJ, Hu BR (2007) Irreversible translation arrest in the reperfused brain. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 27:875–893
Fath DM et al (2006) Histone deacetylase inhibitors repress the transactivation potential of hypoxia-inducible factors independently of direct acetylation of HIF-alpha. J Biol Chem 281:13612–13619
Fisher TS et al (2005) Analysis of ARD1 function in hypoxia response using retroviral RNA interference. J Biol Chem 280:17749–17757
Fulda S, Gorman AM, Hori O, Samali A (2010) Cellular stress responses: cell survival and cell death. Int J Cell Biol 2010:214074
Gale M Jr, Tan SL, Katze MG (2000) Translational control of viral gene expression in eukaryotes. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:239–280
Geng H et al (2011) HDAC4 protein regulates HIF1alpha protein lysine acetylation and cancer cell response to hypoxia. J Biol Chem 286:38095–38102
Halford NG et al (2004) Highly conserved protein kinases involved in the regulation of carbon and amino acid metabolism. J Exp Bot 55:35–42
Hutt DM, Roth DM, Vignaud H, Cullin C, Bouchecareilh M (2014) The histone deacetylase inhibitor, Vorinostat, represses hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha expression through translational inhibition. PLoS One 9:e106224
Iida Y et al (2012) Hypoxia promotes glycogen synthesis and accumulation in human ovarian clear cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol 40:2122–2130
Isaacs JS, Jung YJ, Mimnaugh EG, Martinez A, Cuttitta F, Neckers LM (2002) Hsp90 regulates a von Hippel Lindau-independent hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha-degradative pathway. J Biol Chem 277:29936–29944
Iwata A, Riley BE, Johnston JA, Kopito RR (2005) HDAC6 and microtubules are required for autophagic degradation of aggregated huntingtin. J Biol Chem 280:40282–40292
Jeong JW et al (2002) Regulation and destabilization of HIF-1alpha by ARD1-mediated acetylation. Cell 111:709–720
Katschinski DM, Le L, Schindler SG, Thomas T, Voss AK, Wenger RH (2004) Interaction of the PAS B domain with HSP90 accelerates hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha stabilization. Cell Physiol Biochem 14:351–360
Kaufman RJ (1999) Stress signaling from the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum: coordination of gene transcriptional and translational controls. Genes Dev 13:1211–1233
Kawaguchi Y, Kovacs JJ, McLaurin A, Vance JM, Ito A, Yao TP (2003) The deacetylase HDAC6 regulates aggresome formation and cell viability in response to misfolded protein stress. Cell 115:727–738
Kim MS et al (2001) Histone deacetylases induce angiogenesis by negative regulation of tumor suppressor genes. Nat Med 7:437–443
Kong X, Lin Z, Liang D, Fath D, Sang N, Caro J (2006) Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce VHL and ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Mol Cell Biol 26:2019–2028
Kovacs JJ et al (2005) HDAC6 regulates Hsp90 acetylation and chaperone-dependent activation of glucocorticoid receptor. Mol Cell 18:601–607
Kwon S, Zhang Y, Matthias P (2007) The deacetylase HDAC6 is a novel critical component of stress granules involved in the stress response. Genes Dev 21:3381–3394
Lemoine M et al (2012) The pan-deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat induces cell death and synergizes with everolimus in Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines. Blood 119:4017–4025
Matthias P, Yoshida M, Khochbin S (2008) HDAC6 a new cellular stress surveillance factor. Cell Cycle 7:7–10
Maxwell PH et al (1999) The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 399:271–275
McEwen E et al (2005) Heme-regulated inhibitor kinase-mediated phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 inhibits translation, induces stress granule formation, and mediates survival upon arsenite exposure. J Biol Chem 280:16925–16933
Murray-Rust TA, Oldham NJ, Hewitson KS, Schofield CJ (2006) Purified recombinant hARD1 does not catalyse acetylation of Lys532 of HIF-1alpha fragments in vitro. FEBS Lett 580:1911–1918
Neckers L, Kern A, Tsutsumi S (2007) Hsp90 inhibitors disrupt mitochondrial homeostasis in cancer cells. Chem Biol 14:1204–1206
Oyadomari S, Mori M (2004) Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ 11:381–389
Panniers R (1994) Translational control during heat shock. Biochimie 76:737–747
Qian DZ et al (2006) Class II histone deacetylases are associated with VHL-independent regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Cancer Res 66:8814–8821
Ron D (2002) Translational control in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. J Clin Invest 110:1383–1388
Ron D (2004) Signaling cascades regulating NMDA receptor sensitivity to ethanol. Neuroscientist 10:325–336
Schoepflin ZR, Shapiro IM, Risbud MV (2016) Class I and IIa HDACs Mediate HIF-1alpha Stability through PHD2-Dependent Mechanism while HDAC6, a Class IIb Member, Promotes HIF-1alpha Transcriptional Activity in Nucleus Pulposus Cells of the Intervertebral Disc. J Bone Miner Res.
Semenza GL (2003) Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 3:721–732
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL (1995) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:5510–5514
Zhang K, Kaufman RJ (2006) The unfolded protein response: a stress signaling pathway critical for health and disease. Neurology 66:S102–S109
Zhang Y, Gilquin B, Khochbin S, Matthias P (2006) Two catalytic domains are required for protein deacetylation. J Biol Chem 281:2401–2404
Zhang Y et al (2008) Mice lacking histone deacetylase 6 have hyperacetylated tubulin but are viable and develop normally. Mol Cell Biol 28:1688–1701
Zhou J, Schmid T, Frank R, Brune B (2004) PI3K/Akt is required for heat shock proteins to protect hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha from pVHL-independent degradation. J Biol Chem 279:13506–13513
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Dr. Patrick Matthias (Friedrich Miescher Institute for Biomedical Research, Basel, Switzerland) for providing HDAC6 KO and mutant MEFs and an anti-mHDAC6 antibody. This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2014R1A1A2054026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryu, HW., Won, HR., Lee, D.H. et al. HDAC6 regulates sensitivity to cell death in response to stress and post-stress recovery. Cell Stress and Chaperones 22, 253–261 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-017-0763-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-017-0763-3