Abstract
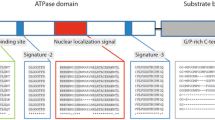
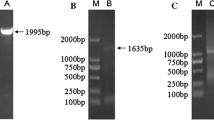
The genes encoding HSP70 and HSP90 proteins were isolated from kaluga by homologous cloning and rapid amplification of complementary DNA (cDNA) ends (RACE). HSP70 (GenBank accession no. KP050541) and HSP90 (GenBank accession no. KP050542) cDNAs were composed of 2275 and 2718 bp and encoded polypeptides of 650 and 725 amino acids, respectively. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) analysis showed that HSP70 and HSP90 of kaluga shared high identities with those of Acipenser ruthenus, Acipenser schrenckii, and Acipenser baerii (98–99 %). Fluorescent real-time RT-PCR under unstressed conditions revealed that HSP70 and HSP90 were expressed in 11 different tissues of kaluga. Messenger RNA (mRNA) expressions of both HSP70 and HSP90 were highest in the intestine and lowest in the muscle. In addition, the patterns of mRNA expression of HSP70 and HSP90 were similar, although the level of expression was more in HSP90 than in HSP70 (P < 0.05).We also analyzed patterns of HSP70 and HSP90 expression in the muscle, gill, and liver of kaluga under different combinations of temperature and salinity stress, including temperatures of 4,10, 25, and 28 °C at 0 ppt salinity, and salinities of 10, 20, 30, and 40 ppt at 16 °C, where 16 °C at 0 ppt (parts per thousand) served as the control. We found that levels of mRNA expression of both HSP70 and HSP90 were highest at 4 °C in the muscle, gill, and liver and changed little with salinity stress. These results increase understanding of the mechanisms of stress response of cold freshwater fish.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Airaksinen S, Råbergh CM, Sistonen L, Nikinmaa M (1998) Effects of heat shock and hypoxia on protein synthesis in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) cells. J Exp Biol 201:2543–2551
Andoh T, Nagasawa H, Matsubara T (2000) Multiple molecular forms of glucagon and insulin in the kaluga sturgeon, Huso dauricus. Peptides 21(12):1785–1792
Basu N, Todgham AE, Ackerman PA, Bibeau MR, Nakano K, Schulte PM, Iwama GK (2002) Heat shock protein genes and their functional significance in fish. Gene 295:173–183
Bausinger H, Lipsker D, Ziylan U, Manié S, Briand JP, Cazenave JP, Muller S, Haeuw JF, Ravanat C, Hdl S (2002) Endotoxin-free heatshock protein 70 fails to induce APC activation. Eur J Immunol 32:3708–3713
Boone AN, Vijayan MM (2002) Constitutive heat shock protein 70 (HSC70) expression in rainbow trout hepatocytes: effect of heat shock and heavy metal exposure. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 132:223–233
Carneiro PCF, Urbinati EC (2001) Salt as a stress response mitigator of matrinxã, Brycon cephalus (Günther), during transport. Aquac Res 32(12):297–304
Deane EE, Woo NYS (2004) Differential gene expression associated with euryhalinity in sea bream (Sparus sarba). Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 287:1054–1063
Demand J, Lüders J, Höhfeld J (1998) The carboxy-terminal domain of Hsc70 provides binding sites for a distinct set of chaperone cofactors. Mol Cell Biol 18(4):2023–2028
Dong Y, Dong S, Meng X (2008) Effects of thermal and osmotic stress on growth, osmoregulation and Hsp70 in sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus Selenka). Aquaculture 276:179–186
Downs CA, Fauth JE, Woodley CM (2001) Assessing the health of grass shrimp (Palaeomonetes pugio) exposed to natural and anthropogenic stressors: a molecular biomarker system. Mar Biotechnol 3:380–397
Elliott JA (1995) A comparison of thermal polygons for British freshwater teleosts. Freshwater Forum 5(3):178–184
Ellis RJ (1993) The general concept of molecular chaperones. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 339:257–261
Fu Y, Li C, Liu F, Dong Z, Ji X, Chen H (2014) Cloning, sequencing of the HSC70 gene in Ctenopharyngodon idella. Wuhan Univ J Nat Sci 19:235–244
Gamperl AK, Vijayan MM, Pereira C, Farrell AP (1998) β-Receptors and stress protein 70 expression in hypoxic myocardium of rainbow trout and chinook salmon. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 274:428–436
Georgopoulos C, Welch WJ (1993) Role of the major heat shock proteins as molecular chaperones. Annu Rev Cell Biol 9:601–634
Hamer B, Hamer DP, Müller WEG, Batel R (2004) Stress-70 proteins in marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis as biomarkers of environmental pollution: a field study. Environ Int 30:873–882
Ivanina AV, Sokolova IM, Sukhotin AA (2008) Oxidative stress and expression of chaperones in aging mollusks. Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 150:53–61
Jin M, Otaka M, Okuyama A, Itoh S, Otani S, Odashima M, Iwabuchi A, Konishi N, Wada I, Pacheco I (1999) Association of 72-kDa heat shock protein expression with adaptation to aspirin in rat gastric mucosa. Dig Dis Sci 44:1401–1407
Kiang JG, Tsokos GC (1998) Heat shock protein 70 kDa: molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology. Pharmacol Ther 80:183–201
Krykhtin ML, Gorbach EI (1996) Fecundity of the kaluga Huso dauricus and the Amur sturgeon Acipenser schrencki. J Ichthyol C/C of Voprosy Ikhtiologii 36:56–60
Lang L, Miskovic D, Lo M, Heikkila JJ (2000) Stress-induced, tissue-specific enrichment of hsp70 mRNA accumulation in Xenopus laevis embryos. Cell Stress Chaperones 5(1):36–44
Lin YQ, Zheng YC, Ji H, He QH, Huang JQ (2009) Cloning and tissue expression of HSP90 partial cDNA sequence in grass carp. Fish Sci 28(8):439–442
Liu J, Yang WJ, Zhu XJ, Karouna-Renier NK, Rao RK (2004) Molecular cloning and expression of two HSP70 genes in the prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Cell Stress Chaperones 9(3):313–323
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2002) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-timequantitative PCR and the 2-△△Ctmethod. Methods 25:402–408
Lu HS, Liu JK, Wang YS, Shi ZG, Li WL, Han J (2011) The growth characters of 1 year-old kaluga juvenile. J Hydroecol 32(5):78–82
Manchado M, Salas-Leiton E, Infante C, Ponce M, Asensio E, Crespo A, Zuasti E, Cañavate JP (2008) Molecular characterization, gene expression and transcriptional regulation of cytosolic HSP90genes in the flatfish Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup). Gene 416:77–84
Manzerra P, Rush SJ, Brown IR (1997) Tissue-specific differences in heat shock protein hsc70 and hsp70 in the control and hyperthermic rabbit. J Cell Physiol 170:130–137
Morimoto RI, Tissières A, Georgopoulos C (1990) Stress proteins in biology and medicine. CSHL Press, Cold Spring Harbor, pp 1–36
Mu WJ, Wen HS, Li JF, He F (2013) Cloning and expression analysis of a HSP70 gene from Korean rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli). Fish shellfish immunoly 35:1111–1121
Ni M, Wen HS, Li JF, Chi M, Ren YY, Song ZF, Ding HM (2014) Two HSPs gene from juvenile Amur sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii): cloning, characterization and expression pattern to crowding and hypoxia stress. Fish Physiol Biochem 40:1801–1816
Otaka M, Okuyama A, Otani S, Jin M, Itoh S, Itoh H, Iwabuchi A, Sasahara H, Odashima M, Tashima Y (1997) Differential induction of HSP60 and HSP72 by different stress situations in rats (correlation with cerulein-induced pancreatitis). Dig Dis Sci 42:1473–1479
Palmisano AN, Winton JR, Dickhoff WW (2000) Tissue-specific induction of Hsp90 mRNA and plasma cortisol response in chinook salmon following heat shock, seawater challenge, and handling challenge. Mar Biotechnol 2:329–338
Piano A, Franzellitti S, Tinti F, Fabbri E (2005) Sequencing and expression pattern of inducible heat shock gene products in the European flat oyster, Ostrea edulis. Gene 361:119–126
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Scheufler C, Brinker A, Bourenkov G, Pegoraro S, Moroder L, Bartunik H, Hartl FU, Moarefi I (2000) Structure of TPR domain–peptide complexes: critical elements in the assembly of the Hsp70-Hsp90 multichaperone machine. Cell 101:199–210
Shmigirilov AP, Mednikova AA, Israel JA (2007) Comparison of biology of the Sakhalin sturgeon, Amur sturgeon, and kaluga from the Amur River, Sea of Okhotsk, and Sea of Japan biogeographic Province. Environ Biol Fish 79(3–4):383–395
Sørensen JG, Kristensen TN, Loeschcke V (2003) The evolutionary and ecological role of heat shock proteins. Ecol Lett 6:1025–1037
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Vasil’ev VP, Vasil’eva ED, Shedko SV, Novomodny GV (2009) Ploidy levels in the kaluga, Huso dauricus and Sakhalin sturgeon Acipenser mikadoi (Acipenseridae, Pisces). Doklady Biol Sci MAIK Nauka/Interperiodica 426(1):228–231
Vayssier M, Leguerhier F, Fabien JF (1999) Cloning and analysis of a Trichinella briotovi gene encoding a cytoplasmic heat shock protein of 72 kD. Parasitology 119:81–93
Waagner D, Heckmann LH, Malmendal A, Nielsen NC, Holmstrup M, Bayley M (2010) Hsp70 expression and metabolite composition in response to short-term thermal changes in Folsomia candida (Collembola). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 157:177–183
Wan WJ, Wang JT, Shi CB, Wu SQ (2007) Gene expression of HSP70 in green swordtail Xiphophorus helleri exposed to Vibrio alginolyticus. J Dalian Fish Univ 22:330–334
Wegele H, Müller L, Buchner J (2004) Hsp70 and Hsp90-a relay team for protein folding. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 151:1–44
Welch NJ (1993) Heat shock proteins functioning as molecular chaperones: their roles in normal and stressed cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 339:327–333
Werner I (2004) The influence of salinity on the heat-shock protein response of Potamocorbula amurensis (Bivalvia). Mar Environ Res 58:803–807
Yenari MA, Giffard RG, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK (1999) The neuroprotective potential of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70). Mol Med Today 5:525–531
Yin HB, Sun ZW, Sun D, Qiu LJ et al (2004) Comparison of nutritive compositions in muscles among six farmed sturgeon species. J Dalian Fish Coll 19:92–96
Zakhartsev M, De Wachter B, Johansen T, Pörtner HO, Blust R (2005) Hsp70 is not a sensitive indicator of thermal limitation in Gadus morhua. J Fish Biol 67:767–778
Zhu X, Xiao H, Zhang DZ, Tang DM, Wang W, Jian JL (2012) Culture and artificial propagation of Siberian H. Sturgeon (kaluga) in Central China. Fish Sci 31(1):46–49
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, G., Zhao, W., Shi, Z. et al. Cloning HSP70 and HSP90 genes of kaluga (Huso dauricus) and the effects of temperature and salinity stress on their gene expression. Cell Stress and Chaperones 21, 349–359 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-015-0665-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-015-0665-1