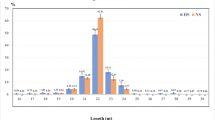
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small single-stranded non-coding RNAs that have an important regulatory function in animal growth and developmental processes. However, the differential expression of miRNA and the role of these miRNAs in heat-stressed Holstein cows are still unknown. In this study, the profile of differentially expressed miRNAs and the target genes analysis in the serum of heat-stressed and normal Holstein cows were investigated by a Solexa deep-sequencing approach and bioinformatics. The data identified 52 differentially expressed miRNAs in 486 known miRNAs which were changed significantly between heat-stressed and normal Holstein cows (fold change >2, P < 0.001). Target genes analysis showed that at least 7 miRNAs (miR-19a, miR-19b, miR-146a, miR-30a-5p, miR-345-3p, miR-199a-3p, and miR-1246) were involved in the response to stress, oxidative stress, development of the immune system, and immune response among the identified 52 differentially expressed miRNAs. Five miRNAs (miR-27b, miR-181a, miR-181b, miR-26a, and miR-146b) were involved in stress and immune responses and the expression of five miRNAs was striking (P < 0.001). In addition, RT-qPCR and deep-sequencing methods showed that 8 miRNAs among the 12 selected miRNAs (miR-19a, miR-19b, miR-27b, miR-30a-5p, miR-181a, miR-181b, miR-345-3p, and miR-1246) were highly expressed in the serum of heat-stressed Holstein cows. GO and KEGG pathway analysis showed that these differentially expressed miRNAs were involved in a pathway that may differentially regulate the expression of stress response and immune response genes. Our study provides an overview of miRNAs expression profile and the interaction between miRNAs and their target genes, which will lead to further understanding of the important roles of miRNAs in heat-stressed Holstein cows.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297
Bernabucci U, Biffani S, Buggiotti L, Vitali A, Lacetera N, Nardone A (2014) The effects of heat stress in Italian Holstein dairy cattle. J Dairy Sci 97(1):471–486
Chen C-Z, Li L, Lodish HF, Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 303(5654):83–86
Chen K, Rajewsky N (2006) Deep conservation of microRNA-target relationships and 3′ UTR motifs in vertebrates, flies, and nematodes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 71:149–156
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K, Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Guo X (2008) Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res 18(10):997–1006
Clarkson R, Wayland MT, Lee J, Freeman T, Watson CJ (2004) Gene expression profiling of mammary gland development reveals putative roles for death receptors and immune mediators in post-lactational regression. Breast Cancer Res 6(2):R92–R109
Consortium GO (2004) The Gene Ontology (GO) database and informatics resource. Nucleic Acids Res 32(1):D258–D261
Cui M, Wang Y, Sun B, Xiao Z, Ye L, Zhang X (2014) MiR-205 modulates abnormal lipid metabolism of hepatoma cells via targeting acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 1 (ACSL1) mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 444:270–275
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang J, Gao W, Lane HC, Lempicki RA (2003) DAVID: database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol 4(5):P3
Dilda F, Gioia G, Pisani L, Restelli L, Lecchi C, Albonico F, Ceciliani F (2012) Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharides and Taphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B differentially modulate inflammatory microRNAs in bovine monocytes. Vet J 192(3):514–516
Friedländer MR, Chen W, Adamidi C, Maaskola J, Einspanier R, Knespel S, Rajewsky N (2008) Discovering microRNAs from deep sequencing data using miRDeep. Nat Biotechnol 26(4):407–415
Gu Z, Eleswarapu S, Jiang H (2007) Identification and characterization of microRNAs from the bovine adipose tissue and mammary gland. FEBS Lett 581(5):981–988
Islam A, Deuster PA, Devaney JM et al (2013) An exploration of heat tolerance in mice utilizing mRNA and microRNA expression analysis. PLoS One 8(8):e72258
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75:843–854
Lewis BP, Shih I-h, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB (2003) Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115(7):787–798
Li M, Xia Y, Gu Y, Zhang K, Lang Q, Chen L, Guan J, Luo Z, Chen H, Li Y (2010) MicroRNAome of porcine pre-and postnatal development. PLoS One 5(7):e11541
Li Q-J, Chau J, Ebert PJ, Sylvester G, Min H, Liu G, Braich R, Manoharan M, Soutschek J, Skare P (2007) miR-181a is an intrinsic modulator of T cell sensitivity and selection. Cell 129(1):147–161
Li R, Sun Q, Jia Y, Cong R, Ni Y, Yang X, Jiang Z, Zhao R (2012) Coordinated miRNA/mRNA expression profiles for understanding breed-specific metabolic characters of liver between Erhualian and large white pigs. PLoS One 7(6):e38716
Li Z, Wang H, Chen L, Wang L, Liu X, Ru C, Song A (2014) Identification and characterization of novel and differentially expressed microRNAs in peripheral blood from healthy and mastitis Holstein cattle by deep sequencing. Anim Genet 45(1):20–27
Llave C, Kasschau KD, Rector MA, Carrington JC (2002) Endogenous and silencing-associated small RNAs in plants. Plant Cell 14(7):1605–1619
McConnell JR, Alexander LA, McAlpine SR (2014) A heat shock protein 90 inhibitor that modulates the immunophilins and regulates hormone receptors without inducing the heat shock response. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24:661–666
McDaneld T (2009) MicroRNA: mechanism of gene regulation and application to livestock. J Anim Sci 87(14 suppl):E21–E28
McKenna LB, Schug J, Vourekas A, McKenna JB, Bramswig NC, Friedman JR, Kaestner KH (2010) MicroRNAs control intestinal epithelial differentiation, architecture, and barrier function. Gastroenterology 139(5):1654–1664
Moyes K, Drackley J, Morin D, Bionaz M, Rodriguez-Zas S, Everts R, Lewin H, Loor J (2009) Gene network and pathway analysis of bovine mammary tissue challenged with Streptococcus uberis reveals induction of cell proliferation and inhibition of PPARγ signaling as potential mechanism for the negative relationships between immune response and lipid metabolism. BMC Genomics 10(1):542
Ogorevc J, Kunej T, Dovc A, Razpet P (2009) Database of cattle candidate genes and genetic markers for milk production and mastitis. Anim Genet 40(6):832–851
Place RF, Noonan EJ (2013) Non-coding RNAs turn up the heat: an emerging layer of novel regulators in the mammalian heat shock response. Cell Stress Chaperones 1–14
Rajewsky N (2006) microRNA target predictions in animals. Nat Genet 38:S8–S13
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR, Ruvkun G (2000) The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 403(6772):901–906
Salak-Johnson J, McGlone J (2007) Making sense of apparently conflicting data: stress and immunity in swine and cattle. J Anim Sci 85(13 suppl):E81–E88
Song H-M, Mu X-D, Gu D-E, Luo D, Yang Y-X, Xu M, Luo J-R, Zhang J-E, Hu Y-C (2013) Molecular characteristics of the HSP70 gene and its differential expression in female and male golden apple snails (Pomacea canaliculata) under temperature stimulation. Cell Stress Chaperones 1–11
West J (2003) Effects of heat-stress on production in dairy cattle. J Dairy Sci 86(6):2131–2144
Xu P, Vernooy SY, Guo M (2003) The Drosophila microRNA Mir-14 suppresses cell death and is required for normal fat metabolism. Curr Biol 13(9):790–795
Yang G, Yang L, Zhao Z, Wang J, Zhang X (2012) Signature miRNAs involved in the innate immunity of invertebrates. PLoS One 7(6):e39015
Zhang B, Wang Q, Pan X (2007) MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in animals and plants. J Cell Physiol 210(2):279–289
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (no. SBK201241530), the National Supporting Projects for Science and Techniques (no. 2011BAD28B02, 2012BAD12B10), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (no. KYZ201413).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y., Chen, Kl., Zheng, Xm. et al. Identification and bioinformatics analysis of microRNAs associated with stress and immune response in serum of heat-stressed and normal Holstein cows. Cell Stress and Chaperones 19, 973–981 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-014-0521-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-014-0521-8