Abstract
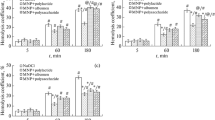
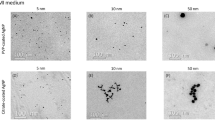
In the present study, the effects of 10- or 100-nm silica oxide (SiO2) NPs on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were examined. Cytotoxic effects and oxidative stress effects, including glutathione (GSH) depletion, the formation of protein radical species, and pro-inflammatory cytokine responses, were measured. PBMC exposed to 10-nm NP concentrations from 50 to 4,000 ppm showed concentration-response increases in cell death; whereas, for 100-nm NPs, PBMC viability was not lost at <500 ppm. Interestingly, 10-nm NPs were more cytotoxic and induced more oxidative stress than 100-nm NPs. Immunoelectron micrographs show the cellular distribution of GSH and NPs. As expected based on the viability data, the 10-nm NPs disturbed cell morphology to a greater extent than did the 100-nm NPs. Antibody to the radical scavenger, 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO), was used for Western blot analysis of proteins with radicals; more DMPO proteins were found after exposure to 10-nm NPs than 100-nm NPs. Examination of cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1ra, IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, and IFN-γ) indicated that different ratios of cytokines were expressed and released after exposure to 10- and 100-nm NPs. IL-1β production was enhanced by 10- and 100-nm NPs;, the cytotoxicity of the NPs was associated with an increase in the IL-1β/IL-6 ratio and 100-nm NPs at concentrations that did not induce loss of cell viability enhanced IL-1β and IL-6 to an extent similar to phytohemagglutinin (PHA), a T cell mitogen. In conclusion, our results indicate that SiO2 NPs trigger a cytokine inflammatory response and induce oxidative stress in vitro, and NPs of the same chemistry, but of different sizes, demonstrate differences in their intracellular distribution and immunomodulatory properties, especially with regard to IL-1β and IL-6 expression.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ault JG, Lawrence DA (2003) Glutathione distribution in normal and oxidatively stressed cells. Exp Cell Res 285:9–14
Balbus JM, Maynard AD, Colvin VL, Castranova V, Daston GP, Denison RA, Dreher KL, Goering PL, Goldberg AM, Kulinowski KM, Monteiro-Riviere NA, Oberdörster G, Omenn GS, Pinkerton KE, Ramos KS, Rest KM, Sass JB, Silbergeld EK, Wong BA (2007) Meeting report: hazard assessment for nanoparticles report from an interdisciplinary workshop. Environ Health Persp 115:1654–1659
Bhattacharya K, Davoren M, Boertz J, Schins RPF, Hoffmann E, Dopp E (2009) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and DNA-adduct formation but not DNA-breakage in human lung cells. Particle Fibre Toxicol 6:17
Chang J-S, Chang K, Hwang D-F, Kong Z-L (2007) In vitro cytotoxicitiy of silica nanoparticles at high concentrations strongly depends on the metabolic activity type of the cell line. Environ Sci Technol 41:2064–2068
De la Fuente M, Miquel J (2009) An update of the oxidation-inflammation theory of aging: the involvement of the immune system in oxi-inflamm-aging. Curr Pharm Des 15:3003–3026
Detweiler CD, Deterding LJ, Tomer KB, Chignell CF, Germolec D, Mason RP (2002) Immunological identification of the heart myoglobin radical formed by hydrogen peroxide. Free Radic Biol Med 33:364–369
Deterding LJ, Ramirez DC, Dubin JR, Mason RP, Tomer KB (2004) Identification of free radicals on hemoglobin from its self-peroxidation using mass spectrometry and immuno-spin trapping: observation of a histidinyl radical. J Biol Chem 279:11600–11607
Dickinson DA, Forman HJ (2002) Cellular glutathione and thiols metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol 64:1019–1026
Dimcheff DE, Faasse MA, McAtee FJ, Portis JL (2004) Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress induced by a neurovirulent mouse retrovirus is associated with prolonged BiP binding and retention of a viral protein in the ER. J Biol Chem 279:33782–33790
Eom H-J, Choi J (2009) Oxidative stress of silica nanoparticles in human bronchial epithelial cell, Beas-2B. Toxicol in Vitro 23:1326–1332
Fahmy B, Cormier SA (2009) Copper oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in airway epithelial cells. Toxicol in Vitro 23:1365–1371
Fei L, Perrett S (2009) Effect of nanoparticles on protein folding and fibrillogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 10:646–655
Flynn ER, Bryant HC (2005) A biomagnetic system for in vivo cancer imaging. Phys Med Biol 50:1273–1293
Fujii T, Hayashi S, Hogg JC, Mukae H, Suwa T, Goto Y, Vincent R, Van Eeden SF (2002) Interaction of alveolar macrophages and airway epithelial cells following exposure to particulate matter produces mediators that stimulate the bone marrow. Am J Respir Cell Molec Biol 27:34–41
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1999) Free radicals in biology and medicine. Oxford University Press, New York
Hamilton RF Jr, Thakur SA, Holian A (2008) Silica binding and toxicity in alveolar macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med 44:1246–1258
Harman D (1956) Aging: a theory based on free radical and radiation chemistry. J Gerontol 11:298–300
Ionita P, Spafiu E, Ghica C (2008) Dual behavior of gold nanoparticles, as generators and scavengers for free radicals. J Mater Sci 43:6571–6574
Kim HW, Ahn E-K, Jee BK, Yoon H-K, Lee KH, Lim Y (2009) Nanoparticulate-induced toxicity and related mechanism in vitro and in vivo. J Nanopart Res 11:55–65
Lanone S, Rogerieux F, Geys J, Dupont A, Maillot-Marechal E, Boczkowski J, Lacroix G, Hoet P (2009) Comparative toxicity of 24 manufactured nanoparticles in human alveolar epithelial and macrophage cell lines. Particle Fibre Toxicol 6:14
Lapotko DO, Lukianova E, Oraevsky AA (2006) Selective laser nano-thermolysis of human leukemia cells with microbubbles generated around clusters of gold nanoparticles. Lasers SurgMed 38:631–642
Lara HH, Ayala-Nuñez NV, Ixtepan-Turrent L, Rodriguez-Padilla C (2010) Mode of antiviral action of silver nanoparticles against HIV-1. JNanobiotechnol 8:1
Li W, Khor TO, Xu C, Shen G, Jeong WS, Yu S, Kong AN (2008) Activation of Nrf2-antioxidant signaling attenuates NFkappaB-inflammatory response and elicits apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol 76:1485–1489
Lin WS, Huang YW, Zhou XD, Ma YF (2006) In vitro toxicity of silica nanoparticles in human lung cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 217:252–259
Lindholm D, Wootz H, Korhonen L (2006) ER stress and neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Death Differ 13:385–392
Liu H, Miller E, Van de Water B, Stevens JL (1998) Endoplasmic reticulum stress proteins block oxidant-induced Ca2+ increases and cell death. J Biol Chem 273:12858–12862
Lynch I, Dawson KA, Linse S (2006) Detecting cryptic epitopes created by nanoparticles. Science 327:pe14
Magder S (2006) Reactive oxygen species: toxic molecules or spark of life? Crit Care 10:208
Mahmoudi M, Simchi A, Imani M (2009) Cytotoxicity of uncoated and polyvinyl alcohol coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 113:9573–9580
Martinon F (2010) Activation mechanisms: signaling by ROS drives inflammasome activation. Eur J Immunol 40:595–653
Medina C, Santos-Martinez MJ, Radomski A, Corrigan OI, Radomski MW (2007) Nanoparticles: pahrmacological and toxicological significance. Br J Pharmacol 150:552–558
Messina JP, Mazurkiewicz J, Lawrence DA (1987) Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to thiol-modified glutathione. In: Cerutti PA, Nygaard MG, Simic MG (eds) Anticarcinogenesis and radiation protection. Plenum New York, NY, pp 407–412
Miranda S, Opazo C, Larrondo LF, Muñoz FJ, Ruiz R, Leighton F, Inestrosa NC (2000) The role of oxidative stress in the toxicity induced by amyloid beta-peptide in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neurobiol 62:633–648
Nel A, Xia T, Madler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622–627
Oberdörster G, Maynard A, Donaldson K, Castranova V, Fitzpatrick J, Ausman K, Carter J, Karn B, Kreyling W, Lai D, Olin S, Monteiro-Riviere N, Warheit D, Yang H (2005a) Principles for characterizing the potential human health effects from exposure to nanomaterials: elements of a screening strategy. Particle Fibre Toxicol 2:1–35
Oberdörster G, Oberdörster E, Oberdörster J (2005b) Nanotoxicology: an emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ Health Persp 113:823–839
Pacurari M, Castranova V, Vallyathan V (2010) Single- and multi-wall carbon nanotubes versus asbestos: are the carbon nanotubes a new health risk to humans? J Toxicol Environ Health A 73:378–95
Park E-J, Park K (2009) Oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory responses induced by silica nanoparticles in vivo and in vitro. Toxicology Lett 184:18–25
Park E-J, Yi J, Chung K-H, Ryu D-Y, Choi J, Park K (2008) Oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in cultured BEAS-2B cells. Toxicology Lett 180:222–229
Patsoukis N, Georgiou CD (2004) Determination of the thiol redox state of organisms: new oxidative stress indicators. Anal Bioanal Chem 378:1783–1792
Pelka J, Gehrke H, Esselen M, Türk M, Crone M, Bräse, Muller ST, Blank H, Send W, Zibat V, Brenner P, Schneider R, Gerthsen D, Marko D (2009) Cellular uptake of platinum nanoparticles in human colon carcinoma cells and their impact on cellular redox systems and DNA integrity. Chem Res Toxicol 22:649–659
Petrarca C, Perrone A, Verna N, Verginelli F, Ponti J, Sabbioni E, Di Giampaolo L, Dadorante V, Schiavone C, Boscolo P, Mariani-Costantini R, Di Gioacchino M (2006) Cobalt nanoparticles modulate cytokine in vitro release by human mononuclear cells mimicking autoimmune disease. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 19:11–14
Rai M, Yadav A, Gade A (2009) Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol Adv 27:76–83
Salata OV (2004) Applications of nanoparticles in biology and medicine. Journal of Nanobiotechnol 2:3–9
Sayes CM, Reed KL, Warheit DB (2007) Assessing toxicity of fine and nanoparticles: comparing in vitro measurements to in vivo pulmonary toxicity profiles. Toxicol Sci 97:163–180
Sayre LM, Perry G, Smith MA (2008) Oxidative stress and neurotoxicity. Chem Res Toxicol 21:172–188
Schreck R, Baeurle PA (1991) A role of oxygen radicals as second messengers. Trends Cell Biol 1:39–42
Senarath-Yapa MD, Phimphivong S, Coym JW, Wirth MJ, Aspinwall CA, Saavedra SS (2007) Preparation and characterization of poly(lipid)-coated, fluorophore-doped silica nanoparticles for biolabeling and cellular imaging. Langmuir 23:12624–12633
Shi X, Castranova V, Halliwell B, Vallyathan V (1998) Reactive oxygen species and silica-induced carcinogenesis. J Toxicol Environ Health B 1:181–197
Shin SH, Ye MK, Kim HS, Kang HS (2007) The effects of nanosilver on the proliferation and cytokine expression by peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Int Immunopharmacol 7:1813–1818
Singh N, Manshian B, Jenkins GJS, Griffiths SM, Williams PM, Maffeis TGG, Wright CJ, Doak SH (2009) NanoGenotoxicology: The DNA damaging potential of engineered nanomaterials. Biomaterials 30:3891–3914
Singh S, Shi T, Duffin R, Albrecht C, Van Berlo D, Höhr D, Fubini B, Martra G, Fenoglio I, Borm PJA, Schins RPF (2007) Endocytosis, oxidative stress and IL-8 expression in human lung epithelial cells upon treatment with fine and ultrafine TiO2: role of the specific surface area and of surface methylation of the particles. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 222:141–151
Stadtman ER, Berlett BS (1998) Reactive oxygen-mediated protein oxidation in aging and disease. Drug Metab Rev 30:225–243
Stratmeyer, M.E., Goering, P.L., Hitchins, V.M., and Umbreit, T.H. (2008) Biomedical microdevices. Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2008
Thannickal VJ, Fanburg BL (2000) Reactive oxygen species in cell signaling. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 279:L1005–L1028
Unfried K, Sydlik U, Bierhals K, Weissenberg A, Abel J (2008) Carbon nanoparticle-induced lung epithelial cell proliferation is mediated by receptor-dependent Akt activation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294:L358–L367
Valko M, Izakovic M, Mazur M, Rhodes CJ, Telser J (2004) Role of oxygen radicals in DNA damage and cancer incidence. Mol Cell Biochem 266:37–56
Wang F, Gao F, Lan M, Yuan H, Huang Y, Liu J (2009) Oxidative stress contributes to silica nanoparticle-induced cytotoxicity in human embryonic kidney cells. Toxicol in Vitro 23:808–815
Wang S, Lu W, Tovmachenko O, Shanker Rai U, Yu H, Chandra Ray P (2008) Challenge in understanding size and shape dependent toxicity of gold nanomaterials in human skin keratinocytes. Chem Phys Lett 463:145–149
Wu X, Narsimhan G (2008) Effect of surface concentration on secondary and tertiary conformational changes of lysozyme adsorbed on silica nanoparticles. Biochim Biophys Acta 1784:1694–1701
Zhang K (2010) Integration of ER stress, oxidative stress and the inflammatory response in health and disease. Int J Clin Exp Med 3:33–40
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank The Nanobiotechnology Center at Cornell University (2007) and Texas Southern University Research Enhancement office (2007) for their funding support of J.A.T-H. (summer of 2007). Furthermore, we would like to thank The Quality Education Minorities Networks for research funding (2008) for support of J.A. T-H. AM was supported by a supplement to U01 ES016014 to DAL. The authors also want to recognize The Biochemistry and Immunology Cores of Wadsworth Center for their collaboration and assistance. The immunoelectron microscopy was done in collaboration between the Wadsworth Center Immunology and Electron Microscopy Core Facilities. The authors also want to thank Dr. Jane Kasten-Jolly for her assistance in obtaining volunteer donors and Adrianna Verschoor for her editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The first three authors are equal contributors to the study.
Jose A. Torres-Hernandez NBTC Research Experience for Undergraduates participant
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mendoza, A., Torres-Hernandez, J.A., Ault, J.G. et al. Silica nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and inflammation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cell Stress and Chaperones 19, 777–790 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-014-0502-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-014-0502-y