Abstract
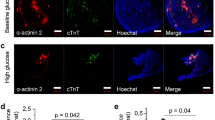
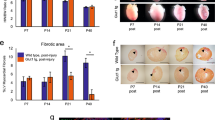
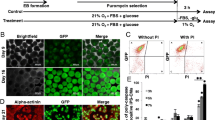
We previously found that endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) might be exhibited in the conventional protocol of the primary culture of neonate rat myocardial cells (NRMCs) and that the high glucose concentration (25 mmol/L) in the culture medium might be the cause. Here, we investigated if the high concentration of glucose might influence ERS in myocardial cells during culture. GRP78 expression (ERS marker) was similar in groups with tunicamycin (TM) and without TM in high glucose cultured cells (p > 0.01). Different glucose concentrations elicited different GRP78 expressions according to analyses of protein and RNA levels, which showed ERS in H/H groups. Finally, we found that GRP78 expression was higher in TM groups compared with M/M groups (p < 0.01). The conventional high-glucose culture media during primary culture of NRMCs induced ERS. We propose that medium-glucose culture media should be used and describe an improved protocol for the primary culture of NRMCs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chomczynski P, Sacchin N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Ann Biochem 162:156–159
Duan XH, Qi YF, Tang CS (2009) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and cardiovascular diseases. J Geriatr Cardiol 6:49–55
Eizirik DL, Cardozo AK, Cnop M (2008) The role for endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetes mellitus. Endocr Rev 29:42–61
Ishiyama M, Miyazono Y, Sasamoto K, Ohkura Y, Ueno K (1997) A highly water-soluble disulfonated tetrazolium salt as a chromogenic indicator for ADH as well as cell viability. Talanta 44:1299–1305
Kasten FH (1972) Rat myocardial cells in vitro: mitosis and differentiated properties. In Vitro 8:128–150
Mitcheson JS, Hancox JC, Levi AJ (1998) Cultured adult cardiac myocytes: future applications, culture methods, morphological and electrophysiological properties. Cardiovasc Res 39:280–300
Piper HM, Volz A, Schwartz P. (1990) Adult ventricular rat heart muscle cells. In: Piper HM (ed) Cell culture techniques in heart and vessel research. Springer, Berlin, pp 36–60
Shen J, Hughes C, Chao C, Cai J, Bartels C, Gessner T, Subjeck J (1987) Conduction of glucose regulated protein and doxorubicin resistance in Chinese hamster cells. Proc Nati Acad Sci 4:3278–3282
Simpson P, Savion S (1982) Differentiation of rat myocytes in single cell cultures with and without proliferating nonmyocardial cells. Cirac Res 50:101–106
Zingarelli B, Salzman AL, Szabo C (1998) Genetic disruption of poly (ADP-Ribose) synthetase inhibits the expression of P-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circ Res 83:85–94
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Science Foundation for Young Scholars of China (grant number 30900612), the Grant of Medical Science Research Foundation of Zhejiang Province (grant number 2009B127), and from the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (grant number Y2090393), People’s Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Jin, J., Guo, Z. et al. Improvements in the primary culture of neonate rat myocardial cells by study of the mechanism of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Stress and Chaperones 18, 367–375 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-012-0390-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-012-0390-y