Abstract
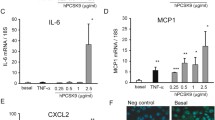
Heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) shows attenuated expression in human coronary arteries as the extent of atherosclerosis progresses. In mice, overexpression of HSP27 reduces atherogenesis, yet the precise mechanism(s) are incompletely understood. Inflammation plays a central role in atherogenesis, and of particular interest is the balance of pro- and anti-inflammatory factors produced by macrophages. As nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) is a key immune signaling modulator in atherogenesis, and macrophages are known to secrete HSP27, we sought to determine if recombinant HSP27 (rHSP27) alters NF-κB signaling in macrophages. Treatment of THP-1 macrophages with rHSP27 resulted in the degradation of an inhibitor of NF-κB, IκBα, nuclear translocation of the NF-κB p65 subunit, and increased NF-κB transcriptional activity. Treatment of THP-1 macrophages with rHSP27 yielded increased expression of a variety of genes, including the pro-inflammatory factors, IL-1β, and TNF-α. However, rHSP27 also increased the expression of the anti-inflammatory factors IL-10 and GM-CSF both at the mRNA and protein levels. Our study suggests that in macrophages, activation of NF-κB signaling by rHSP27 is associated with upregulated expression and secretion of key pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Moreover, we surmise that it is the balance in expression of these mediators and antagonists of inflammation, and hence atherogenesis, that yields a favorable net effect of HSP27 on the vessel wall.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Madhoun AS, Chen YX, Haidari L, Rayner K, Gerthoffer W, McBride H, O’Brien ER (2007) The interaction and cellular localization of HSP27 and ERbeta are modulated by 17beta-estradiol and HSP27 phosphorylation. Mol Cell Endocrinol 270:33–42
Arrigo AP (2007) The cellular “networking” of mammalian Hsp27 and its functions in the control of protein folding, redox state and apoptosis. Adv Exp Med Biol 594:14–26, Ref Type: Serial (Book,Monograph)
Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D (1989) A 65-kappaD subunit of active NF-kappaB is required for inhibition of NF-kappaB by I kappaB. Genes Dev 3:1689–1698
Benjamin IJ, McMillan DR (1998) Stress (heat shock) proteins molecular chaperones in cardiovascular biology and disease. Circ Res 83:117–132
Bruey JM, Ducasse C, Bonniaud P, Ravagnan L, Susin SA, az-Latoud C, Gurbuxani S, Arrigo AP, Kroemer G, Solary E, Garrido C (2000) Hsp27 negatively regulates cell death by interacting with cytochrome c. Nature Cell Biol 2:645–652
Caligiuri G, Rudling M, Ollivier V, Jacob MP, Michel JB, Hansson GK, Nicoletti A (2003) Interleukin-10 deficiency increases atherosclerosis, thrombosis, and low-density lipoproteins in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Mol Med 9:10–17
Chen Y-X, Zhao X, McNulty M, O’Brien ER (2009) Recombinant HSP27 therapy reduces serum cholesterol levels and experimental atherogenesis. Circulation 120:S1153, Ref Type: Abstract
Dabek J, Kulach A, Gasior Z (2010) Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kB): a new potential therapeutic target in atherosclerosis? Pharmacol Rep 62:778–783
De AK, Kodys KM, Yeh BS, Miller-Graziano C (2000) Exaggerated human monocyte IL-10 concomitant to minimal TNF-alpha induction by heat-shock protein 27 (Hsp27) suggests Hsp27 is primarily an antiinflammatory stimulus. J Immunol 165:3951–3958
Ditiatkovski M, Toh BH, Bobik A (2006) GM-CSF deficiency reduces macrophage PPAR-gamma expression and aggravates atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:2337–2344
George J, Schwartzenberg S, Medvedovsky D, Jonas M, Charach G, Afek A, Shamiss A (2012) Regulatory T cells and IL-10 levels are reduced in patients with vulnerable coronary plaques. Atherosclerosis 222:519–523
Ghosh CC, Ramaswami S, Juvekar A, Vu HY, Galdieri L, Davidson D, Vancurova I (2010) Gene-specific repression of proinflammatory cytokines in stimulated human macrophages by nuclear IkappaBalpha. J Immunol 185:3685–3693
Gordon JW, Shaw JA, Kirshenbaum LA (2011) Multiple facets of NF-kappaB in the heart: to be or not to NF-kappaB. Circ Res 108:1122–1132
Haghighat A, Weiss D, Whalin MK, Cowan DP, Taylor WR (2007) Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor exacerbate atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circulation 115:2049–2054
Han X, Kitamoto S, Wang H, Boisvert WA (2010) Interleukin-10 overexpression in macrophages suppresses atherosclerosis in hyperlipidemic mice. FASEB J 24:2869–2880
Jawan B, Kao YH, Goto S, Pan MC, Lin YC, Hsu LW, Nakano T, Lai CY, Sun CK, Cheng YF, Tai MH, Eng HL, Wang CS, Huang CJ, Lin CR, Chen CL (2008) Propofol pretreatment attenuates LPS-induced granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor production in cultured hepatocytes by suppressing MAPK/ERK activity and NF-kappaB translocation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 229:362–373
Kanters E, Pasparakis M, Gijbels MJJ, Vergouwe MN, Partouns-Hendriks I, Fijneman RJA, Clausen BE, Förster I, Kockx MM, Rajewsky K, Kraal G, Hofker MH, De Winther MPJ (2003) Inhibition of NF-kappaB activation in macrophages increases atherosclerosis in LDL receptor-deficient mice. J Clin Invest 112:1176–1185
Kanters E, Gijbels MJJ, Van Der Made I, Vergouwe MN, Heeringa P, Kraal G, Hofker MH, De Winther MPJ (2004) Hematopoietic NF-kappaB1 deficiency results in small atherosclerotic lesions with an inflammatory phenotype. Blood 103:934–940
Karban AS, Okazaki T, Panhuysen CI, Gallegos T, Potter JJ, Bailey-Wilson JE, Silverberg MS, Duerr RH, Cho JH, Gregersen PK, Wu Y, Achkar JP, Dassopoulos T, Mezey E, Bayless TM, Nouvet FJ, Brant SR (2004) Functional annotation of a novel NFKB1 promoter polymorphism that increases risk for ulcerative colitis. Hum Mol Genet 13:35–45
Lappas M, Yee K, Permezel M, Rice GE (2005) Sulfasalazine and BAY 11-7082 interfere with the nuclear factor-kappa B and I kappa B kinase pathway to regulate the release of proinflammatory cytokines from human adipose tissue and skeletal muscle in vitro. Endocrinology 146:1491–1497
Lawrence T, Fong C (2010) The resolution of inflammation: anti-inflammatory roles for NF-kappaB. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42:519–523
Ley K, Miller YI, Hedrick CC (2011) Monocyte and macrophage dynamics during atherogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:1506–1516
Mallat Z, Besnard S, Duriez M, Deleuze V, Emmanuel F, Bureau MF, Soubrier F, Esposito B, Duez H, Fievet C, Staels B, Duverger N, Scherman D, Tedgui A (1999) Protective role of interleukin-10 in atherosclerosis. Circ Res 85:e17–e24
Martin-Ventura JL, Duran MC, Blanco-Colio LM, Meilhac O, Leclercq A, Michel JB, Jensen ON, Hernandez-Merida S, Tuñón J, Vivanco F, Egido J (2004) Identification by a differential proteomic approach of heat shock protein 27 as a potential marker of atherosclerosis. Circulation 110:2216–2219
Martin-Ventura JL, Nicolas V, Houard X, Blanco-Colio LM, Leclercq A, Egido J, Vranckx R, Michel JB, Meilhac O (2006) Biological significance of decreased HSP27 in human atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:1337–1343
Miller H, Poon S, Hibbert B, Rayner K, Chen YX, O’Brien ER (2005) Modulation of estrogen signaling by the novel interaction of heat shock protein 27, a biomarker for atherosclerosis, and estrogen receptor beta: mechanistic insight into the vascular effects of estrogens. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:e10–e14
Miller-Graziano CL, De A, Laudanski K, Herrmann T, Bandyopadhyay S (2008) HSP27: an anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory stress protein acting to dampen immune function. 291:196–208. Ref Type: Serial (Book,Monograph)
Monaco C, Andreakos E, Kiriakidis S, Mauri C, Bicknell C, Foxwell B, Cheshire N, Paleolog E, Feldmann M (2004) Canonical pathway of nuclear factor kappa B activation selectively regulates proinflammatory and prothrombotic responses in human atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:5634–5639
Muller JM, Ziegler-Heitbrock HWL, Baeuerle PA (1993) Nuclear factor kappa B, a mediator of lipopolysaccharide effects. Immunobiology 187:233–256
Murray PJ (2006) Understanding and exploiting the endogenous interleukin-10/STAT3-mediated anti-inflammatory response. Curr Opin Pharmacol 6:379–386
Namiki M, Kawashima S, Yamashita T, Ozaki M, Sakoda T, Inoue N, Hirata KI, Morishita R, Kaneda Y, Yokoyama M (2004) Intramuscular gene transfer of interleukin-10 cDNA reduces atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice. Atherosclerosis 172:21–29
Nishibori M, Takahashi HK, Katayama H, Mori S, Saito S, Iwagaki H, Tanakac N, Morita K, Ohtsuka A (2009) Specific removal of monocytes from peripheral blood of septic patients by polymyxin B-immobilized filter column. Acta Med Okayama 63:65–69
Oeckinghaus A, Ghosh S (2009) The NF-kappaB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1
Parcellier A, Schmitt E, Gurbuxani S, Seigneurin-Berny D, Pance A, Chantôme A, Plenchette S, Khochbin S, Solary E, Garrido C (2003) HSP27 is a ubiquitin-binding protein involved in I-kappaBalpha proteasomal degradation. Mol Cell Biol 23:5790–5802
Park JY, Farrance IK, Fenty NM, Hagberg JM, Roth SM, Mosser DM, Wang MQ, Jo H, Okazaki T, Brant SR, Brown MD (2007) NFKB1 promoter variation implicates shear-induced NOS3 gene expression and endothelial function in prehypertensives and stage I hypertensives. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H2320–H2327
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Plenz G, Eschert H, Beissert S, Arps V, Sindermann JR, Robenek H, Völker W (2003) Alterations in the vascular extracellular matrix of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)-deficient mice. FASEB J 17:1451–1457
Pockley AG (2002) Heat shock proteins, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 105:1012–1017
Potteaux S, Esposito B, Van Oostrom O, Brun V, Ardouin P, Groux H, Tedgui A, Mallat Z (2004) Leukocyte-derived interleukin 10 is required for protection against atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:1474–1478
Rayner K, Chen YX, Mcnulty M, Simard T, Zhao X, Wells DJ, De Belleroche J, O’Brien ER (2008) Extracellular release of the atheroprotective heat shock protein 27 is mediated by estrogen and competitively inhibits acLDL binding to scavenger receptor-a. Circ Res 103:133–141
Rayner K, Sun J, Chen YX, Mcnulty M, Simard T, Zhao X, Wells DJ, De Belleroche J, O’Brien ER (2009) Heat shock protein 27 protects against atherogenesis via an estrogen-dependent mechanism: role of selective estrogen receptor beta modulation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:1751–1756
Shaposhnik Z, Wang X, Weinstein M, Bennett BJ, Lusis AJ (2007) Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor regulates dendritic cell content of atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:621–627
Sun J, Ma X, Chen YX, Rayner K, Hibbert B, Mcnulty M, Dhaliwal B, Simard T, Ramirez D, O’Brien E (2011) Attenuation of atherogenesis via the anti-inflammatory effects of the selective estrogen receptor beta modulator 8beta-VE2. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 58:399–405
ten Hove T, Vervoordeldonk MJBM, Dekkers PEP, Reitsma PH, van Deventer SJH (1999) Lps induced translocation of NF-kappaB occurs only in a subpopulation of CD14-positive mononuclear cells. Innate Immun 5:15–21
Voegeli TS, Wintink AJ, Chen Y, Currie RW (2008) Heat shock proteins 27 and 70 regulating angiotensin II-induced NF-kappaB: a possible connection to blood pressure control? Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 33:1042–1049
Vogel U, Jensen MK, Due KM, Rimm EB, Wallin H, Nielsen MRS, Pedersen APT, Tiønneland A, Overvad K (2011) The NFKB1 ATTG ins/del polymorphism and risk of coronary heart disease in three independent populations. Atherosclerosis 219:200–204
Wang X, Quinn PJ (2010) Lipopolysaccharide: biosynthetic pathway and structure modification. Prog Lipid Res 49:97–107
Weissen-Plenz G, Eschert H, Volker W, Sindermann JR, Beissert S, Robenek H, Scheld HH, Breithardt G (2008) Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor deficiency affects vascular elastin production and integrity of elastic lamellae. J Vasc Res 45:103–110
Xanthoulea S, Curfs DMJ, Hofker MH, De Winther MPJ (2005) Nuclear factor kappaB signaling in macrophage function and atherogenesis. Curr Opin Lipidology 16:536–542
Yoshioka T, Okada T, Maeda Y, Ikeda U, Shimpo M, Nomoto T, Takeuchi K, Nonaka-Sarukawa M, Ito T, Takahashi M, Matsushita T, Mizukami H, Hanazono Y, Kume A, Ookawara S, Kawano M, Ishibashi S, Shimada K, Ozawa K (2004) Adeno-associated virus vector-mediated interleukin-10 gene transfer inhibits atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Gene Ther 11:1772–1779
Zhang W, Xing SS, Sun XL, Xing QC (2009) Overexpression of activated nuclear factor-kappaB in aorta of patients with coronary atherosclerosis. Clin Cardiol 32:E42–E47
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by operating grants MOP 80204 from the Canadian Institute for Health Research (CIHR) and T6335 from the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Ontario. CIHR and Medtronic collectively provide EOB with a peer-reviewed Research Chair (URC #57093; IGO 94418). SS was supported by an Ontario Graduate Scholarship and a CIHR IGH Women’s Health Council Masters Award. TS was supported by a studentship from the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Ontario and by a CIHR Frederick Banting and Charles Best Canada Graduate Doctoral Award. JR was supported by a CIHR Frederick Banting and Charles Best Canada Graduate Doctoral Award. CMC was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from le Fonds de Recherche en Santé du Québec (FRSQ) and the Ernest and Margaret Ford cardiology endowed research fellowship from the University of Ottawa Heart Institute.
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Samira Salari and Tara Seibert contributed equally to this work
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Fig. 1
rHSP27 is not phosphorylated. a Western blot demonstrating rHSP27 is not phosphorylated b LC-MS/MS confirmed rHSP27 is not phosphorylated (PPT 184 kb)
Supplemental Fig. 2
Gel filtration of rHSP27 and rC1 to demonstrate molecular size in 1× PBS buffer (pH = 7.4). The size of rHSP27 and rC1 was measured by gel filtration. The size of most of rHSP27 (>90 %) is between 1,000—5,000 kD with <10 % in the range of 150 kD. The size of recombinant C1 appears to be around 100 kD (PPT 40 kb)
Supplemental Fig. 3
a Assays of cell viability and cytotoxicity. THP1 cells that were treated with rHSP27 (9.6 μM) or rC1 (9.6 μM) show no changes in viability or membrane integrity as demonstrated by MTT (a) and LDH (b) assays, respectively (PSD 2915 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salari, S., Seibert, T., Chen, YX. et al. Extracellular HSP27 acts as a signaling molecule to activate NF-κB in macrophages. Cell Stress and Chaperones 18, 53–63 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-012-0356-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-012-0356-0