Abstract
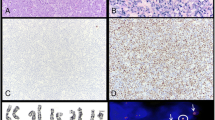
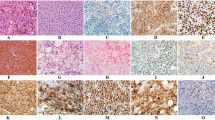
Plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL) is a rare AIDS-related malignancy with a poor prognosis. Little is known about this entity, and no standard treatment regimen has been defined. To establish an adequate treatment strategy, we investigated 24 cases of PBL arising in human immunodeficiency virus-positive individuals. Most of the patients were in the AIDS stage, with a median CD4 count of 67.5/µL. Lymph nodes (58 %), gastrointestinal tract (42 %), bone marrow (39 %), oral cavity (38 %), and CNS (18 %) were the most commonly involved sites. Histology findings for the following were positive at varying rates, as follows: CD10 (56 %); CD30 (39 %); CD38 (87 %); MUM-1 (91 %); CD138 (79 %); EBER (91 %); and LMP-1 (18 %). There was a marked increase in patients in 2011–12, and the cases found in that period appeared to be more aggressive, showing a higher rate of advanced-stage PBL. Fourteen cases were treated with CHOP, while the others were treated with more intensive regimens, including bortezomib and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. The overall median survival time was 15 months. A CD4 count of >100/µL at diagnosis and attaining complete remission in the first-line chemotherapy were associated with better outcomes (P = 0.027 and 0.0016, respectively). Host immune status and chemosensitivity are associated with improved prognosis in PBL.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delecluse HJ, Anagnostopoulos I, Dallenbach F, Hummel M, Marafioti T, Schneider U, et al. Plasmablastic lymphomas of the oral cavity: a new entity associated with the human immunodeficiency virus infection. Blood. 1997;89:1413–20.
Castillo J, Pantanowitz L, Dezube BJ. HIV-associated plasmablastic lymphoma: lessons learned from 112 published cases. Am J Hematol. 2008;83:804–9.
Castillo JJ, Winer ES, Stachurski D, Perez K, Jabbour M, Milani C, et al. Prognostic factors in chemotherapy-treated patients with HIV-associated plasmablastic lymphoma. Oncologist. 2010;15:293–9.
Castillo JJ, Furman M, Beltran BE, Bibas M, Bower M, Chen W, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated plasmablastic lymphoma: poor prognosis in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Cancer. 2012;118:5270–7.
Bibas M, Castillo JJ. Current knowledge on HIV-associated plasmablastic lymphoma. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2014;6:e2014064.
Dong HY, Scadden DT, de Leval L, Tang Z, Isaacson PG, Harris NL. Plasmablastic lymphoma in HIV-positive patients. An aggressive Epstein–Barr virus-associated extramedullary plasmacytic neoplasm. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005;29:1633–41.
Folk GS, Abbondanzo SL, Childers EL, Foss RD. Plasmablastic lymphoma: a clinicopathologic correlation. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2006;10:8–12.
Rafaniello Raviele P, Pruneri G, Maiorano E. Plasmablastic lymphoma: a review. Oral Dis. 2009;15:38–45.
Sarode SC, Sarode GS, Patil A. Plasmablastic lymphoma of the oral cavity: a review. Oral Oncol. 2010;46:146–53.
Shiels MS, Pfeiffer RM, Gail MH, Hall HI, Li J, Chaturvedi AK, et al. Cancer burden in the HIV-infected population in the US. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011;103:753–62.
Shiels MS, Pfeiffer RM, Hall HI, Li J, Goedert JJ, Morton LM, et al. Proportions of Kaposi sarcoma, selected non-Hodgkin lymphomas, and cervical cancer in the United States occurring in persons with AIDS, 1980-2007. JAMA. 2011;305:1450–9.
Robbins HA, Shiels MS, Pfeiffer RM, Engels EA. Epidemiologic contributions to recent cancer trends among HIV-infected people in the US. AIDS. 2014;28:881–90.
Nagai H, Iwasaki N, Odawara T, Okada S. Actual status of AIDS-related lymphoma management in Japan. Int J Hematol. 2008;87:442–3.
Ota Y, Hishima T, Mochizuki M, Kodama Y, Moritani S, Oyaizu N, et al. Classification of AIDS-related lymphoma cases between 1987 and 2012 in Japan based on the WHO classification of lymphomas, fourth edition. Cancer Med. 2014;3:143–53.
Carbone A, Gloghini A, Canzonieri V, Tirelli U. AIDS-related extranodal non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas with plasma cell differentiation. Blood. 1997;90:1337–8.
Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Shipp MA, Fisher RI, Connors JM, et al. Report of an international workshop to standardize response criteria for non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:1244–53.
Howe JG, Steitz JA. Localization of Epstein–Barr virus-encoded small RNAs by in situ hybridizaiton. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA. 1986;83:9006–10.
Foot NJ, Dunn RG, Geoghegan H, Wilkins BS, Neat MJ. Fluorescence in situ hybridisation analysis of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections in the diagnostic work-up of non-Burkitt high grade B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a single centre’s experience. J Clin Pathol. 2011;64:802–8.
Stein H, Harris NL, Campo E. Plasmablastic lymphoma. In: WHO classification of tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues, 4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC;2008 2008:P256–257.
Ustun C, Reid-Nicholson M, Nayak-Kapoor A, Jones-Crawford J, McDonald K, Jillella AP, et al. Plasmablastic lymphoma: CNS involvement, coexistence of other malignancies, possible viral etiology, and dismal outcome. Ann Hematol. 2009;88:351–8.
Nasta SD, Carrum GM, Shahab I, Hanania NA, Udden MM. Regression of a plasmablastic lymphoma in a patient with HIV on highly active antiretroviral therapy. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002;43:423–6.
Lester R, Li C, Phillips P, Shenkier TN, Gascoyne RD, Galbraith PF, et al. Improved outcome of human immunodeficiency virus-associated plasmablastic lymphoma of the oral cavity in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy: a report of two cases. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004;45:1881–5.
Panos G, Karveli EA, Nikolatou O, Falagas ME. Prolonged survival of an HIV-infected patient with plasmablastic lymphoma of the oral cavity. Am J Hematol. 2007;82:761–5.
Bose P, Thompson C, Gandhi D, Ghabach B, Ozer H. AIDS-related plasmablastic lymphoma with dramatic, early response to bortezomib. Eur J Haematol. 2009;82:490–2.
Bibas M, Grisetti S, Alba L, Picchi G, Del Nonno F, Antinori A. Patient with HIV-associated plasmablastic lymphoma responding to bortezomib alone and in combination with dexamethasone, gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, cytarabine, and pegfilgrastim chemotherapy and lenalidomide alone. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:e704–8.
Lipstein M, O’Connor O, Montanari F, Paoluzzi L, Bongero D, Bhagat G. Bortezomib-induced tumor lysis syndrome in a patient with HIV-negative plasmablastic lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2010;10:E43–6.
Dasanu CA, Bauer F, Codreanu I, Padmanabhan P, Rampurwala M. Plasmablastic haemato-lymphoid neoplasm with a complex genetic signature of Burkitt lymphoma responding to bortezomib. Hematol Oncol. 2013;31:164–6.
Yan M, Dong Z, Zhao F, Chauncey T, Deauna-Limayo D, Wang-Rodriguez J, et al. CD20-positive plasmablastic lymphoma with excellent response to bortezomib combined with rituximab. Eur J Haematol. 2014;93:77–80.
Castillo JJ, Reagan JL, Sikov WM, Winer ES. Bortezomib in combination with infusional dose-adjusted EPOCH for the treatment of plasmablastic lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2015;169:352–5.
Yotsumoto M, Hagiwara S, Ajisawa A, Tanuma J, Uehira T, Nagai H, et al. Clinical characteristics of human immunodeficiency virus-associated Hodgkin lymphoma patients in Japan. Int J Hematol. 2012;96:247–53.
Ansell SM. Brentuximab vedotin. Blood. 2014;124:3197–200.
Holderness BM, Malhotra S, Levy NB, Danilov AV. Brentuximab vedotin demonstrates activity in a patient with plasmablastic lymphoma arising from a background of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:e197–9.
Gandhi M, Petrich A. Brentuximab vedotin in patients with relapsed HIV-related lymphoma. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2014;12:16–9.
Popovic M, Tenner-Racz K, Pelser C, Stellbrink HJ, van Lunzen J, Lewis G, et al. Persistence of HIV-1 structural proteins and glycoproteins in lymph nodes of patients under highly active antiretroviral therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:14807–12.
Zelenetz AD, Abramson JS, Advani RH, Andreadis CB, Byrd JC, Czuczman MS, et al. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2010;8:288–334.
Bayraktar UD, Ramos JC, Petrich A, Gupta N, Lensing S, Moore PC, et al. Outcome of patients with relapsed/refractory acquired immune deficiency syndrome-related lymphoma diagnosed 1999–2008 and treated with curative intent in the AIDS Malignancy Consortium. Leuk Lymphoma. 2012;53:2383–9.
Barta SK, Lee JY, Kaplan LD, Noy A, Sparano JA. Pooled analysis of AIDS malignancy consortium trials evaluating rituximab plus CHOP or infusional EPOCH chemotherapy in HIV-associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer. 2012;118:3977–83.
Liu JJ, Zhang L, Ayala E, Field T, Ochoa-Bayona JL, Perez L, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-negative plasmablastic lymphoma: a single institutional experience and literature review. Leuk Res. 2011;35:1571–7.
Friis A, Åkerlund B, Christensson B, Gyllensten K, Aleman A, Zou JZ, et al. Epstein Barr virus DNA analysis in blood predicts disease progression in a rare case of plasmablastic lymphoma with effusion. Infect Agent Cancer. 2013;8:28.
Brown HJ, Song MJ, Deng H, Wu TT, Cheng G, Sun R. NF-B inhibits gammaherpesvirus lytic replication. J Virol. 2003;77:8532–40.
Shirley CM, Chen J, Shamay M, Li H, Zahnow CA, Hayward SD, et al. Bortezomib induction of C/EBPbeta mediates Epstein–Barr virus lytic activation in Burkitt lymphoma. Blood. 2011;117:6297–303.
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by Health and Labor Sciences Research Grants [Nos. H22-AIDS-I-002 and H25-AIDS-I-002] from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. A summary of relevant information will be published with the manuscript.
About this article
Cite this article
Koizumi, Y., Uehira, T., Ota, Y. et al. Clinical and pathological aspects of human immunodeficiency virus-associated plasmablastic lymphoma: analysis of 24 cases. Int J Hematol 104, 669–681 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-016-2082-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-016-2082-3