Abstract
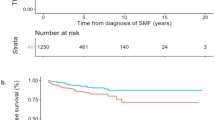
To find out risk factors of incidences of long-term complications of thrombosis, myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia (MMM) and evolution into malignance in Chinese PV patients, we evaluated 320 PV patients referred to our center from April 1984 to June 2005 by Kaplan–Meier estimation and Cox proportional hazards models. A total of 250 events of thrombosis were observed in 138 (43.13%) patients. Advanced age, prior thrombosis and hemoglobin out of control were statistically significant risk factors of incidences of thrombotic events. A total of 43 patients progressed into MMM at a median time of 84 (7–240) months, higher white blood cell (WBC) count, splenomegaly, receiving alkylating agent and hydroxycarbamide were associated with the progression into MMM. During the follow-up time, 11 and 2 patients died of fatal complications of thrombosis and acute myeloid leukaemia (AML), respectively. These results suggest that advanced age, prior thrombosis and hemoglobin out of control contributed to relatively high incidence of thromboembolism; higher WBC count, splenomegaly, receiving alkylating agent and hydroxycarbamide were risk factors of evolution to MMM. The main poor factors that influenced the survival of Chinese PV patients were incidences of thromboembolism and evolution into AML.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chim CS, Kwong YL, Chan PT, Liang R. Polycythemia vera in Chinese patients: thirty-six years of experience. Am J Hematol. 1997;56:59–62. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8652(199709)56:1<59::AID-AJH12>3.0.CO;2-Y.
Gruppo Italiano Studio Policitemia. Polycythemia vera: the natural history of 1213 patients followed for 20 years. Ann Intern Med. 1995;123:656–64. doi:10.1001/archinte.123.6.656.
Najean Y, Rani JD. The very long-term evolution of polycythemia vera: an analysis of 318 patients initially treated by phlebotomy or 32P between 1969 and 1981. Semin Hematol. 1997;34:6–16.
Passamonti F, Malabarba L, Orlandi E, et al. Polycythemia vera in young patients: a study on the long-term risk of thrombosis, myelofibrosis and leukemia. Haematologica. 2003;88:13–8.
Chievitz E, Thiede T. Complication and causes of death in polycythemia vera. Acta Med Scand. 1962;172:513–23.
Berk PD, Goldberg JD, Donovan PB, Fruchtman SM, Berlin NT, Wasserman LR. Therapeutic recommendations in polycytheia vera based on polycythemia vera study group protocols. Semin Hematol. 1986;23:132–43.
Rozman C, Giralt M, Feliu E, Rubio D, Cortes MT. Life expectancy of patients with chronic nonleukemic myeloproliferative disorders. Cancer. 1991;67:2658–63. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19910515)67:10<2658::AID-CNCR2820671042>3.0.CO;2-C.
Najean Y, Rain JD. Treatment of polycythemia vera: the use of hydroxyurea and pipobroman in 292 patients under the age of 65 years. Blood. 1997;90:3370–7.
Najean Y, Dresch C, Rain JD. The very-long-term course of polycythemia: a complement to the previously published data of the Polycythemia vera Study Group. Br J Haematol. 1994;86:233–5. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.1994.tb03289.x.
Weinfeld A, Swolin B, Westin J. Acute leukemia after hydroxyurea therapy in polycythemia vera and allied disorders: prospective study of efficacy and leukaemogenicity with therapeutic implications. Eur J Haematol. 1994;52:134–9.
Finazzi G, Ruggeri M, Rodeghiero F, Barbui T. Second malignancies in patients with essential thrombocythemia treated with busulphan and hydroxyurea: long-term follow up of a randomized clinical trial. Br J Haematol. 2000;110:577–83. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.2000.02188.x.
Lengfelder E, Berger U, Hehlman R. Interferon in the treatment of polycythemia vera. Ann Hematol. 2000;79:103–9. doi:10.1007/s002770050563.
Kiladjian JJ, Cassinat B, Turlure P, et al. High molecular response rate of polycythemia vera patients treated with pegylated interferon alpha-2a. Blood. 2006;108:2037–40. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-03-009860.
Polycythemia vera, Chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis, Acute myeloid leukaemia. In Pierre R, Imbert M, Thiele J, Brunning RD, Matutes E, Harris NL, et al., editors. World Health Organization classification of Tumours. lyon: IARC; 2001. pp. 32–75.
Najean Y, Mugnier P, Dresch C, Rain JD. Polycythemia vera in young people: an analysis of 58 cases diagnosed before 40 years. Br J Haematol. 1987;67:285–91. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb02349.x.
Di Nisio M, Barbui T, Di Gennaro L, et al. European collaboration on low-dose aspirin in polycythemia vera (ECLAP) investiagtors. The haematocrit and platelet target in polycythemia vera. Br J Haematol. 2007;136:249–59. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2006.06430.x.
Landolfi R, Marchioli R, Kutti J, et al. European collaboration on low-dose aspirin in polycythemia vera investigators. Efficacy and safety of low-dose aspirin in polycythemia vera. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:114–24. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa035572.
Finazzi G, Caruso V, Marchioli R, et al. ECLAP investigators. Acute leukemia in polycythemia vera: an analysis of 1638 patients enrolled in a prospective observational study. Blood. 2005;105:2664–70. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-09-3426.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, J., Xue, Y., Ye, L. et al. Risk factors of long-term incidences of thrombosis, myelofibrosis and evolution into malignance in polycythemia vera: a single center experience from China. Int J Hematol 88, 530–535 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-008-0188-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-008-0188-y