Abstract
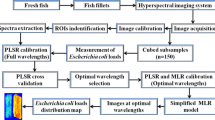
Enterobacteriaceae is one kind of harmful microorganisms commonly presented in raw fish products, and detection of Enterobacteriaceae plays a very important role in evaluating microbial contamination. This work was carried out to exploit the potential of emerging hyperspectral imaging technique to determine the Enterobacteriaceae contamination of salmon flesh during cold storage. The spectral information ranging from 900 to 1700 nm (239 wavelengths) was extracted to relate to the Enterobacteriaceae loads (recorded as log 10 CFU/g) using partial least square (PLS) regression, developing a PLS model with correlation coefficient of prediction (r P) of 0.94 and root mean square error of prediction (RMSEP) of 0.53 as well as residual predictive deviation (RPD) of 2.97. By applying successive projection algorithm (SPA), eight wavelengths at 924, 931, 964, 1068, 1262, 1373, 1628 and 1668 nm among the 239 wavelengths were selected as informative wavelengths to reduce the information redundancy and optimise the PLS model. With the eight informative wavelengths, a simplified PLS model defined as SPA-PLS was established with r P of 0.95, RMSEP of 0.47 and RPD of 3.23. To visualise the contamination degree of salmon flesh caused by Enterobacteriaceae, the SPA-PLS model was transferred to each pixel of images, and colourful distribution maps were produced with different colour represented different numbers of Enterobacteriaceae colonies. The results showed that hyperspectral imaging operating in 900–1700 nm is promising in evaluating Enterobacteriaceae contamination of salmon products. More studies are still required to further refine the multispectral imaging system to achieve online application.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Nour N, Ngadi M (2011) Int J Food Sci Nutr 62:418–422
Asche F, Roll KH, Sandvold HN, Sørvig A, Zhang D (2013) Aquac Econ Manag 17:322–339
Barbin DF, ElMasry G, Sun D-W et al (2012) Predicting quality and sensory attributes of pork using near-infrared hyperspectral imaging. Anal Chim Acta 719:30–42
Barbin DF, ElMasry G, Sun D-W, Allen P (2013) Food Chem 138:1162–1171
Botsoglou E, Govaris A, Christaki E, Botsoglou N (2010) Food Chem 121:17–22
Cozzolino D, Roumeliotis S, Eglinton J (2013) J Food Eng 114:545–549
Delgado AE, Sun D-W (2002a) Desorption isotherms for cooked and cured beef and pork. J Food Eng 51(2):163–170
Delgado AE, Sun D-W (2002b) Desorption isotherms and glass transition temperature for chicken meat. J Food Eng 55(1):1–8
Dissing B, Papadopoulou O, Tassou C, Ersbøll B, Carstensen J, Panagou E, Nychas G-J (2012) Food Bioprocess Technol 6:2268–2279
Dwivedi HP, Jaykus L-A (2011) Crit Rev Microbiol 37:40–63
ElMasry G, Wold JP (2008) J Agric Food Chem 56:7672–7677
ElMasry G, Sun D-W, Allen P (2011a) Food Res Int 44:2624–2633
ElMasry G, Sun D-W, Allen P (2011b) Non-destructive determination of water-holding capacity in fresh beef by using NIR hyperspectral imaging. Food Res Int 44(9):2624–2633
ElMasry G, Iqbal A, Sun D-W et al (2011c) Quality classification of cooked, sliced turkey hams using NIR hyperspectral imaging system. J Food Eng 103(3):333–344
ElMasry G, Barbin DF, Sun D-W, Allen P (2012a) Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 52:689–711
ElMasry G, Sun D-W, Allen P (2012b) Near-infrared hyperspectral imaging for predicting colour, pH and tenderness of fresh beef. J Food Eng 110(1):127–140
Feng Y-Z, Sun D-W (2013) Talanta 105:244–249
Feng Y-Z, ElMasry G, Sun D-W, Walsh D, Morcy N (2012) Food Chem 138:1829–1836
Gómez AH, He Y, Pereira AG (2006) J Food Eng 77:313–319
He H-J, Wu D, Sun D-W (2013) Innovative Food Sci Emerg Technol 18:237–245
He H-J, Wu D, Sun D-W (2014a) J Food Eng 126:156–164
He H-J, Wu D, Sun D-W (2014b) Food Chem 156:394–401
He H-J, Wu D, Sun D-W (2015) Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 55:864–886
Jackman P, Sun D-W, Du C-J et al (2008) Prediction of beef eating quality from colour, marbling and wavelet texture features. Meat Sci 80(4):1273–1281
Jackman P, Sun D-W, Du C-J et al (2009) Prediction of beef eating qualities from colour, marbling and wavelet surface texture features using homogenous carcass treatment. Pattern Recogn 42(5):751–763
Johnston IA, Li X, Vieira VLA, Nickell D, Dingwall A, Alderson R, Campbell P, Bickerdike R (2006) Aquaculture 256:323–336
Kamruzzaman M, ElMasry G, Sun D-W et al (2011) Application of NIR hyperspectral imaging for discrimination of lamb muscles. J Food Eng 104(3):332–340
Kamruzzaman M, ElMasry G, Sun D-W, Allen P (2012a) Anal Chim Acta 714:57–67
Kamruzzaman M, Barbin D, ElMasry G, Sun D-W, Allen P (2012b) Innovative Food Sci Emerg Technol 16:316–325
Keskin M, Dodd RB, Han YJ, Khalilian A (2004) Appl Eng Agric 20:851–860
Kiani H, Sun D-W (2011) Water crystallization and its importance to freezing of foods: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 22(8):407–426
Kuo J-T, Cheng C-Y, Huang H-H, Tsao C-F, Chung Y-C (2010) J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 37:237–244
Liu Y, Chen Y-R, Kim MS, Chan DE, Lefcourt AM (2007) J Food Eng 81:412–418
Liu C-C, Yeung C-Y, Chen P-H, Yeh M-K, Hou S-Y (2013) Food Chem 141:2526–2532
McDonald K, Sun D-W (2001) The formation of pores and their effects in a cooked beef product on the efficiency of vacuum cooling. J Food Eng 47(3):175–183
Morales-Sillero A, Fernández-Cabanás V-M, Casanova L, Jiménez M-R, Suárez M-P, Rallo P (2011) J Food Eng 107:99–106
Nicolaï BM, Beullens K, Bobelyn E, Peirs A, Saeys W, Theron KI, Lammertyn J (2007) Postharvest Biol Technol 46:99–118
Peng Y, Zhang J, Wu J, Hang H (2009) 73150Q–73150Q. doi: 10.1117/12.819424
Peng Y, Zhang J, Wang W, Li Y, Wu J, Huang H, Gao X, Jiang W (2011) J Food Eng 102:163–169
Pitout JDD, Laupland KB (2008) Lancet Infect Dis 8:159–166
Qin J, Chao K, Kim MS (2012) Food Chem 138:998–1007
Rajkumar P, Wang N, ElMasry G, Raghavan GSV, Gariepy Y (2012) J Food Eng 108:194–200
Ritthiruangdej P, Ritthiron R, Shinzawa H, Ozaki Y (2011) Food Chem 129:684–692
Sallam KI (2007) Food Chem 101:592–600
Shahin MA, Symons SJ, Hatcher DW (2013) Food Bioprocess Technol 7:224–234
Sivertsen AH, Heia K, Stormo SK, Elvevoll E, Nilsen H (2011) J Food Sci 76:S77–S83
Sone I, Olsen RL, Sivertsen AH, Eilertsen G, Heia K (2012) J Food Eng 109:482–489
Sun D-W (1997) Thermodynamic design data and optimum design maps for absorption refrigeration systems. Appl Therm Eng 17(3):211–221
Sun D-W (2004) Computer vision - an objective, rapid and non-contact quality evaluation tool for the food industry. J Food Eng 61(1):1–2
Sun D-W (2010) Hyperspectral imaging for food quality analysis and control. Academic Press/Elsevier, San Diego
Sun D-W, Eames IW, Aphornratana S (1996) Evaluation of a novel combined ejector-absorption refrigeration cycle .1. Computer simulation. Int J Refrig 19(3):172–180
Sun D-W, Woods JL (1997) Simulation of the heat and moisture transfer process during drying in deep grain beds. Dry Technol 15(10):2479–2508
Sun D-W, Byrne C (1998) Selection of EMC/ERH isotherm equations for rapeseed. J Agric Eng Res 69(4):307–315
Taghizadeh M, Gowen A, O’Donnell C (2009) Sens & Instrumen Food Qual 3:219–226
Tao F, Peng Y, Li Y, Chao K, Dhakal S (2012) Meat Sci 90:851–857
Teena M, Manickavasagan A, Mothershaw A, El Hadi S, Jayas D (2013) Food Bioprocess Technol 6:1621–1634
Tosukhowong A, Visessanguan W, Pumpuang L, Tepkasikul P, Panya A, Valyasevi R (2011) Food Chem 129:846–853
Valous NA, Mendoza F, Sun D-W et al (2009) Colour calibration of a laboratory computer vision system for quality evaluation of pre-sliced hams. Meat Sci 81(1):132–141
Wang HH, Sun D-W (2002) Melting characteristics of cheese: analysis of effect of cheese dimensions using computer vision techniques. J Food Eng 52(3):279–284
Wu D, Sun D-W (2013a) Innovative Food Sci Emerg Technol 19:1–14
Wu D, Sun D-W (2013b) Food Chem 145:417–426
Wu D, Sun D-W (2013c) Talanta 111:39–46
Wu D, Sun D-W (2013d) Talanta 116:266–276
Wu D, Wang S, Wang N, Nie P, He Y, Sun D-W, Yao J (2012a) Food Bioprocess Technol 6:2943–2958
Wu D, Sun D-W, He Y (2012b) Innovative Food Sci Emerg Technol 16:361–372
Wu D, Nie P, He Y, Bao Y (2012c) Food Bioprocess Technol 5:1402–1410
Wu D, Chen X, Cao F, Sun D-W, He Y, Jiang Y (2014) Food Bioprocess Technol 7:1555–1569
Xu SY, Chen XF, Sun D-W (2001) Preservation of kiwifruit coated with an edible film at ambient temperature. J Food Eng 50(4):211–216
Zaragozá P, Fuentes A, Fernández-Segovia I, Vivancos J-L, Rizo A, Ros-Lis JV, Barat JM, Martínez-Máñez R (2012) Food Chem 138:1374–1380
Zhu F, Zhang D, He Y, Liu F, Sun DW (2012) Food Bioprocess Technol 6:2931–2937
Acknowledgments
Hong-Ju He thanks the Chinese Scholarship Council for supporting his PhD study (under UCD-CSC funding programme).
Conflict of Interest
Hong-Ju He declares that he has no conflict of interest. Da-Wen Sun declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Compliance with Ethics Requirements
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, HJ., Sun, DW. Selection of Informative Spectral Wavelength for Evaluating and Visualising Enterobacteriaceae Contamination of Salmon Flesh. Food Anal. Methods 8, 2427–2436 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0122-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0122-x