Abstract
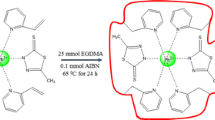
A solid-phase extraction method using Pb2+ ion-imprinted polymer (Pb2+-IIP) nanoparticles combined with flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry (FAAS) was developed for the preconcentration and trace monitoring of lead ions in environmental samples. The Pb2+-IIP nanoparticles were obtained by precipitation polymerization of 4-vinylpyridine (the functional monomer), ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (the cross-linker), 2,2′-azobisisobutyronitrile (the initiator), 4-(2-pyridylazo) resorcinol (the lead-binding ligand), and lead ions (the template ion) in acetonitrile solution. The Pb2+-IIP nanoparticles were characterized by Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetric and differential thermal analysis (TGA/DTA), and by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Different affecting parameters on the adsorption and desorption of this solid-phase extraction process were evaluated and optimized. Under the optimized conditions, the detection limit for the proposed method was found to be 0.9 μg L−1, while the relative standard deviation (RSD) for five replicate measurements was calculated to be <4 %. For proving that the proposed method is reliable, a range of food and water samples with different and complex matrices was used.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagheri A, Behbahani M, Amini MM, Sadeghi O, Taghizade M, Baghayi L, Salarian M (2012a) Simultaneous separation and determination of trace amounts of Cd(II) and Cu(II) in environmental samples using novel diphenylcarbazide modified nanoporous silica. Talanta 89:455–461
Bagheri A, Taghizadeh M, Behbahani M, Asgharinezhad AA, Salarian M, Dehghani A, Ebrahimzadeh H, Amini MM (2012b) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic metal-organic framework (MOF) as a novel sorbent, and its optimization by experimental design methodology for determination of palladium in environmental samples. Talanta 99:132–139
Bagheri A, Behbahani M, Amini MM, Sadeghi O, Tootoonchi A, Dahaghin Z (2012c) Preconcentration and separation of ultra-trace palladium ion using pyridine-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 178:261–268
Behbahani M, Taghizadeh M, Bagheri A, Hosseini H, Salarian M, Tootoonchi A (2012) A nanostructured ion-imprinted polymer for the selective extraction and preconcentration of ultra-trace quantities of nickel ions. Microchim Acta 178:429–437
Behbahani M, Bagheri A, Taghizadeh M, Salarian M, Sadeghi O, Adlnasab L, Jalali K (2013) Synthesis and characterization of nano structure lead (II) ion-imprinted polymer as a new sorbent for selective extraction and preconcentration of ultra-trace amounts of lead ions from vegetables, rice, and fish samples. Food Chem 138:2050–2056
Beltran A, Marcé RM, Cormack PAG, Borrull F (2009) Synthesis by precipitation polymerisation of molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres for the selective extraction of carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine from human urine. J Chromatogr A 1216:2248–2253
Cacho C, Turiel E, Martin-Esteban A, P´erez-Conde C, C´amara C (2004) Characterisation and quality assessment of binding sites on a propazine-imprinted polymer prepared by precipitation polymerization. J Chromatogr B 802:347–353
Cao J, Liang P, Liu Y (2008) Determination of trace lead in water samples by continuous flow microextraction combined with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 152:910–914
Chen JR, Xiao SM, Wu XH, Fang KM, Liu WH (2005) Determination of lead in water samples by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry after cloud point extraction. Talanta 67:992–996
Comitre ALD, Reis BF (2005) Automatic flow procedure based on multicommutation exploiting liquid–liquid extraction for spectrophotometric lead determination in plant material. Talanta 65:846–852
del Sole R, Scardino A, Lazzoi MR, Mergola L, Scorrano S, Vasapollo G (2013) A molecularly imprinted polymer for the determination of neopterin. Microchim Acta 180:1401–1409
Ebrahimzadeh H, Behbahani M, Yamini Y, Adlnasab L, Asgharinezhad AA (2013) Optimization of Cu (II)-ion imprinted nanoparticles for trace monitoring of copper in water and fish samples using a Box-Behnken design. React Funct Polym 73:23–29
Ensafi AA, Shiraz AZ (2008) On-line separation and preconcentration of lead(II) by solid-phase extraction using activated carbon loaded with xylenol orange and its determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 150:554–559
Esen C, Andaç M, Bereli N, Say RI, Henden E, Denizli A (2009) Highly selective ion-imprinted particles for solid-phase extraction of Pb2+ ions. Mat Sci Eng C 29:2464–2470
Fritz JS (1999) Analytical solid-phase extraction. Wiley-VCH, New York
Junping W, Mingfei P, Guozhen F, Shuo W (2009) Preparation of a novel molecularly imprinted polymer by a sol-gel process for on-line solid-phase extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography to detect trace enrofloxacin in fish and chicken samples. Microchim Acta 166:295–302
Korn MG, de Andrade JB, de Jesus DS, Lemos VA, Bandeira MLSF, dos Santos WNL, Bezerra MA, Amorim FAC, Souza AS, Ferreira SLC (2006) Separation and preconcentration procedures for the determination of lead using spectrometric techniques: a review. Talanta 69:16–24
Li P, Rong F, Yuan C (2003) Morphologies and binding characteristics of molecular imprinted polymers prepared by precipitation polymerization. Polym Int 52:1799–1806
Liang P, Sang HB (2008) Determination of trace lead in biological and water samples with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction preconcentration. Anal Biochem 380:21–25
Liu Y, Liu Z, Wang Y, Dai J, Gao J, Xie J, Yan Y (2010) A surface ion-imprinted mesoporous sorbent for separation and determination of Pb(II) ion by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchim Acta 172:309–317
Nabid MR, Sedghi R, Bagheri A, Behbahani M, Taghizadeh M, Oskooie HA, Heravi MM (2012) Preparation and application of poly(2-amino thiophenol)/MWCNTs nanocomposite for adsorption and separation of cadmium and lead ions via solid phase extraction. J Hazard Mater 203–204:93–100
Nagihan M, Karaaslan B, Senkal F, Cengiz E, Yaman M (2010) Novel polymeric resin for solid phase extraction and determination of lead in waters. Clean Soil Air Water 38(11):1047–1054
Otero-Romaní J, Moreda-Piñeiro A, Bermejo-Barrera P, Martin-Esteban A (2009) Inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry/mass spectrometry for the determination of Cu Ni, Pb and Zn in seawater after ionic imprinted polymer based solid phase extraction. Talanta 79:723–729
Soylak M, Narin I (2005) An On-Line Preconcentration System For Cadmium Determination In Environmental Samples By Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Chem Anal 50:705–715
Tamayo FG, Casillas JL, Martin-Esteban A (2003) Lanthanide sensitized chemiluminescence determination of grepafloxacin in tablets and human urine. Anal Chim Acta 482:165–173
Turiel E, Martin-Esteban (2004) A molecularly imprinted polymers: towards highly selective stationary phases in liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Anal Bioanal Chem 378:1876–1886
Tuzen M, Parlar K, Soylak M (2005a) Enrichment/separation of cadmium(II) and lead(II) in environmental samples by solid phase extraction. J Hazard Mater 121:79–87
Tuzen M, Soylak M, Elci L (2005b) Multi-element pre-concentration of heavy metal ions by solid phase extraction on Chromosorb 108. Anal Chim Acta 548:101–108
Wagner HP (1995) Determination of lead in beer using Zeeman background corrected graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. J Am Soc Brew Chem 53:141–144
Wang J, Cormack PAG, Sherrington DC, Khoshdel E (2003) Monodisperse, molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres prepared by precipitation polymerization for affinity separation applications. Angew Chem 115:5494–5496
World Health Organization, Health Criteria and Other Supporting Information, World Health Organization, Geneva, 1996
Zhong XW, Deng F, Wang YH, Luo XB (2013) A molecularly imprinted polymer for solid phase extraction of allantoin. Microchim Acta 180:1453–1460
Conflict of Interest
Mohammad Behbahani declares that he has no conflict of interest. Parmoon Ghareh Hassanlou declares that he has no conflict of interest. Mostafa M. Amini declares that he has no conflict of interest. Hamid Reza Moazami declares that he has no conflict of interest. Hamid Sadeghi Abandansari declares that he has no conflict of interest. Akbar Bagheri declares that he has no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Behbahani, M., Hassanlou, P.G., Amini, M.M. et al. Selective Solid-Phase Extraction and Trace Monitoring of Lead Ions in Food and Water Samples Using New Lead-Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles. Food Anal. Methods 8, 558–568 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-9924-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-9924-5