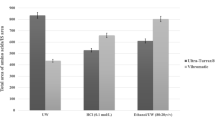
Abstract
A new method has been developed to determine resveratrol and piceid isomers in bee pollen using liquid chromatography (LC) coupled to electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (ESI-MS). An efficient extraction procedure has also been proposed (average analyte recoveries were between 89 and 96 %); this involved a cleaning step with hexane, a solid–liquid extraction using a mixture of ethanol and water (80:20, v/v), and a concentration step in a rotary evaporator. The separation of all the compounds was achieved using a C18 column (150 × 4.6 mm) and a mobile phase composed of 1 % (v/v) formic acid in water and acetonitrile at a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min. The method was fully validated in terms of selectivity, limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ), linearity, precision, and accuracy. The LOD and LOQ values ranged from 10 to 25 and 35 to 80 μg/kg, respectively. Finally, the proposed method was applied to analyze bee pollen samples from different origins.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballard TS, Mallikarjunan P, Zhou K, O’Keefe S (2010) Microwave-assisted extraction of phenolic antioxidant compounds from peanut skins. Food Chem 120:1185–1192
Cacho JI, Campillo N, Viñas P, Hernández-Córdoba M (2013) Stir bar sorptive extraction with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the determination of resveratrol, piceatannol and oxyresveratrol isomers in wine. J Chromatogr A 1315:21–27
Casas L, Mantell C, Rodríguez M, Martínez de la Ossa EJ, Roldán A, De Ory I, Caro I, Blandino A (2010) Extraction of resveratrol from the pomace of Palomino fino grapes by supercritical carbon dioxide. J Food Eng 96:304–308
Costa C, Lodesani M, Maistrello L (2010) Effect of thymol and resveratrol administered with candy or syrup on the development of Nosema ceranae and on the longevity of honeybees (Apis mellifera L.) in laboratory conditions. Apidologie 41:141–150
Counet C, Callemien D, Collin S (2006) Chocolate and cocoa: new sources of trans-resveratrol and trans-piceid. Food Chem 98:649–657
Cvejic JM, Djekic SV, Petrovic AV, Atanackovic MT, Jovic SM, Brceski ID, Gojkovic-Bukarica LC (2010) Determination of trans- and cis-resveratrol in Serbian commercial wines. J Chromatogr Sci 38:229–234
Dias F de S, Silva MF, David JM (2013) Determination of quercetin, gallic acid, resveratrol, catechin and malvidin in Brazilian wines elaborated in the vale do São Francisco using liquid-liquid extraction assisted by ultrasound and GC-MS. Food Anal Methods 6:963–968
Di Lecce G, Arranz S, Jáuregui O, Tresserra-Rimbau A, Quifer-Rada P, Lamuela-Raventós RM (2014) Phenolic profiling of the skin, pulp and seeds of Albariño grapes using hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight and triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry. Food Chem 145:874–882
Fernández-Mar MI, Mateos R, García-Parrilla MC, Puertas B, Cantos-Villar E (2012) Bioactive compounds in wine: resveratrol, hydroxytyrosol and melatonin: a review. Food Chem 130:797–813
Franquet-Griell H, Checa A, Núñez O, Saurina J, Hernández-Cassou Puignou L (2012) Determination of polyphenols in Spanish wines by capillary zone electrophoresis. Application to wine characterization by using chemometrics. J Agric Food Chem 60:8340–8349
Grippi F, Crosta L, Aiello G, Tolomeo M, Oliveri F, Gebbia N, Curione A (2008) Determination of stilbenes in Sicilian pistachio by high-performance liquid chromatographic diode array (HPLC-DAD/FLD) and evaluation of eventually mycotoxin contamination. Food Chem 107:483–488
Hashim SNNS, Schwarz LJ, Boysen RI, Yang Y, Danylec B, Hearn MTW (2013) Rapid solid-phase extraction and analysis of resveratrol and other polyphenols in red wine. J Chromatogr A 1313:284–290
International Conference on Harmonization (2005) ICH Topic Q2 (R1), Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology. http://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Quality/Q2_R1/Step4/Q2_R1__Guideline.pdf. Accessed 05.11.2014
Jaitz L, Siegl K, Eder R, Rak G, Abranko L, Koellensperger G, Hann S (2010) LC–MS/MS analysis of phenols for classification of red wine according to geographic origin, grape variety and vintage. Food Chem 122:366–372
Ji M, Li Q, Ji H, Lou H (2014) Investigation of the distribution and season regularity of resveratrol in Vitis amurensis via HPLC–DAD–MS/MS. Food Chem 142:61–65
Kačániová K, Rovná K, Arpášová H, Hleba L, Petrová J, Haščík P, Čuboň J, Pavelková A, Chlebo R, Bobková A, Stričik M (2013) The effects of bee pollen extracts on the broiler chicken’s gastrointestinal microflora. Res Vet Sci 95:34–37
Kong QJ, Ren XY, Hu N, Sun CR, Pan YJ (2011) Identification of isomers of resveratrol dimer and their analogues from wine grapes by HPLC/MSn and HPLC/DAD-UV. Food Chem 127:727–734
Leiro JM, Varela M, Piazzon MC, Arranz JA, Noya M, Lamas J (2010) The anti-inflammatory activity of the polyphenol resveratrol may be partially related to inhibition of tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Immunol 47:1114–1120
Liu C, Wang L, Wang J, Wu B, Liu W, Fan P, Liang Z, Li S (2013) Resveratrol in Vitis berry skins and leaves: their extraction and analysis by HPLC. Food Chem 136:643–649
Maistrello L, Lodesani M, Costa C, Leonardi F, Marani G, Caldon M, Mutinelli F, Granato A (2008) Screening of natural compounds for the control of Nosema disease in honeybees (Apis mellifera). Apidologie 39:436–445
Montsko G, Pour Nikfardjam MS, Szabo Z, Boddi K, Lorand T, Ohmacht R, Mark L (2008) Determination of products derived from trans-resveratrol UV photoisomerisation by means of HPLC–APCI-MS. J Photoch Photobio A 196:44–50
Moss R, Mao Q, Taylor D, Saucier C (2013) Investigation of monomeric and oligomeric wine stilbenoids in red wine by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Sp 27:1815–1827
Nicoletti I, De Rossi A, Giovinazzo G, Corradini D (2007) Identification and quantification of stilbenes in fruits of transgenic tomato plants (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) by reversed phase hplc with photodiode array and mass spectrometry detection. J Agric Food Chem 55:3304–3311
Piñeiro Z, Palma M, Barroso CG (2006) Determination of trans-resveratrol in grapes by pressurised liquid extraction and fast high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1110:61–65
Piñeiro Z, Guerrero RR, Fernández-Marin MI, Cantos-Villar E, Palma M (2013) Ultrasound-assisted extraction of stilbenoids from grape stems. J Agric Food Chem 61:12549–12556
Porrini MP, Fernández NJ, Garrido PM, Gende LB, Medici SK, Eguaras MJ (2011) In vivo evaluation of antiparasitic activity of plant extracts on Nosema ceranae (Microsporidia). Apidologie 42:700–707
Rascón B, Hubbard BP, Sinclair DA, Amdam GV (2012) The lifespan extension effects of resveratrol are conserved in the honey bee and may be driven by a mechanism related to caloric restriction. Aging 4:499–508
Rodríguez-Cabo T, Rodríguez I, López P, Ramil M, Cela R (2014) Investigation of liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry performance for identification and determination of hydroxylated stilbene antioxidants in wine. J Chromatogr A 1337:162–170
Shukitt-Hale B, Carey A, Simon L, Mark DA, Joseph JA (2006) Effects of Concord grape juice on cognitive and motor deficits in aging. Nutrition 22:295–302
Soto ME, Bernal J, Martín MT, Higes M, Bernal JL, Nozal MJ (2012) Liquid chromatographic determination of resveratrol and piceid isomers in honey. Food Anal Methods 5:162–171
Thompson M, Ellison SL, Wood R (2002) Harmonized guidelines for single laboratory validation of methods of analysis (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem 74:835–855
Viñas P, Campillo N, Hernández-Pérez M, Hernández-Córdoba M (2008) A comparison of solid-phase microextraction and stir bar sorptive extraction coupled to liquid chromatography for the rapid analysis of resveratrol isomers in wines, musts and fruit juices. Anal Chim Acta 611:119–125
Weng C-J, Wu C-F, Huang H-W, Wu C-H, Ho C-T, Yen G-C (2010) Evaluation of anti-invasion effect of resveratrol and related methoxy analogues on human hepatocarcinoma cells. J Agric Food Chem 58:2886–2894
Acknowledgments
Authors gratefully acknowledge funding (Project RTA2012-00076-CO2-02). Authors wish to thank the CAR of Marchamalo (Guadalajara, Spain) for supplying the blank pollen samples. A. M. Ares would like to thank the Spanish Ministry “Educación, Cultura y Deporte” for her Ph.D grant, while M.E. Soto thanks the MAEC-AECID for her grant. In addition, authors thank David Rixham (White Rose English School, Valladolid, Spain) for performing the English revision.
Conflict of Interest
Ana M. Ares declares that she has no conflict of interest.
María E. Soto declares that she has no conflict of interest.
María J. Nozal declares that she has no conflict of interest.
José L. Bernal declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Mariano Higes declares that he has no conflict of interest.
José Bernal declares that he has no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ares, A.M., Soto, M.E., Nozal, M.J. et al. Determination of Resveratrol and Piceid Isomers in Bee Pollen by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 8, 1565–1575 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-0048-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-0048-8