Abstract
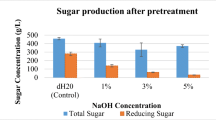
The aim of the present work was to enable valorization of glucan and xylan in corncob using a mild alkaline pretreatment route and lower the alkaline and water consumptions by spent liquor recycle process. Alkaline pretreatment at 80 °C, 2 h, 2% NaOH was proposed to recover glucan and xylan of corncob. For decreasing the alkaline and water consumptions in pretreatment process, spent liquor recycle process was carried out. Six batch spent liquor recycle pretreatment did not decrease the pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencies, and the consumptions of alkaline and wastewater would be saved by 22.5 and 63.1%, respectively. The pulp could be well converted to glucose and xylose with a low loading of enzymes. With 2% substrate loading, 15 FPU g−1 solid enzyme loading and 72-h incubation, the enzymatic glycan and xylan conversion ratios could reach about 95 and 98%, respectively. A maximal sugar concentration of 170.2 g l−1 was obtained with a yield of 0.54 g g−1 corncob. The sugar from enzymatic hydrolysis was used as substrate for 2,3-butanediol production. Under an optimized condition, a maximal 2,3-butanediol concentration of 52.5 g l−1 was obtained with a yield of 0.42 g g−1 sugar (84.8% of the theoretical yield) and a productivity of 0.88 g l−1 h−1 after 60-h fed-batch fermentation. This study opened up a promising route for high value application for glucan and xylan at the same time.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Voloch M, Jansen NB, Ladisch MR, Tsao GT, Narayan R, Rodwell VW (1985) 2, 3-Butanediol. In: Oxford, Pergamon/Elsevier, p 933–947
Syu MJ (2001) Biological production of 2, 3-butanediol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55:10–18
Kim SJ, Seo SO, Park YC, Jin YS, Seo JH (2014) Production of 2,3-butanediol from xylose by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biotechnol 192:376–382
Xin F, Basu A, Weng MC, Yang K, He J (2015) Production of 2, 3-butanediol from sucrose by a Klebsiella species. Bioenerg Res 9:15–22
Cho S, Kim T, Woo HM, Kim Y, Lee J, Um Y (2015) High production of 2,3-butanediol from biodiesel-derived crude glycerol by metabolically engineered Klebsiella oxytoca M1. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:1–12
Li LX, Chen C, Li K, Wang Y, Gao C, Ma CQ, Xu P (2015) Efficient simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of inulin to 2,3-butanediol by thermophilic Bacillus licheniformis ATCC 14580. Appl Environ Microb 80:6458–6464
Yang TW, Rao ZM, Zhang X, Xu MJ, Xu ZH, Yang ST (2015) Economic conversion of spirit-based distillers’ grain to 2,3-butanediol by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Process Biochem 50:20–23
Bozell JJ, Astner A, Baker D, Biannic B, Cedeno D, Elder T, Hosseinaei O, Delbeck L, Kim JW, O’Lenick CJ, Young T (2014) Integrating separation and conversion-conversion of biorefinery process streams to biobased chemicals and fuels. Bioenerg Res 7:856–866
Haveren JV, Scott EL, Sanders J (2008) Bulk chemicals from biomass. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin 2:41–57
Lee SJ, Lee JH, Yang X, Kim SB, Lee JH, Yoo HY, Park C, Kim SW (2015) Phenolic compounds: strong inhibitors derived from lignocellulosic hydrolysate for 2, 3-butanediol production by Enterobacter aerogenes. Biotechnol J 10:1920–1928
Sun Y, Cheng J (2002) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresour Technol 83:1–11
Cai BY, Ge JP, Lin HZ, Cheng KK, Ping WX (2012) Statistical optimization of dilute sulfuric acid pretreatment of corncob for xylose recovery and ethanol production. Biomass Bioenergy 36:250–257
Liu K, Lin XH, Yue J, Li XZ, Fang X, Zhu MT, Lin JQ, Qu YB (2010) High concentration ethanol production from corncob residues by fed-batch strategy. Bioresour Technol 101:4952–4958
Yang M, Li W, Liu B, Li Q, Xing J (2010) High-concentration sugars production from corn Stover based on combined pretreatments and fed-batch process. Bioresour Technol 101:4884–4888
Cheng KK, Wu J, Lin ZN, Zhang JA (2014) Aerobic and sequential anaerobic fermentation to produce xylitol and ethanol using non-detoxified acid pretreated corncob. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:1–9
Kim JS, Lee YY, Kim TH (2016) A review on alkaline pretreatment technology for bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 199:42–48
Guragain YN, Bastola KP, Madl RL, Vadlani PV (2016) Novel biomass pretreatment using alkaline organic solvents: a green approach for biomass fractionation and 2, 3-butanediol production. Bioenerg Res 9:643–655
Ghose TK (1987) Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure Appl Chem 59:257–268
Zheng ZM, Cheng KK, Hu QL, Liu HJ, Guo NN, Liu DH (2008) Effect of culture conditions on 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde detoxification in 1, 3-propanediol fermentation by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochem Eng J 39:305–310
Ragauskas AJ, Beckham GT, Biddy MJ, Chandra R, Chen F, Davis MF, Davison BH, Dixon RA, Gilna P, Keller M, Langan P, Naskar AK, Saddler JN, Tschaplinski TJ, Tuskan GA, Wyman CE (2014) Lignin valorization: improving lignin processing in the biorefinery. Science 344:1246843
Rawat R, Kumbhar B, Tewari L (2013) Optimization of alkali pretreatment for bioconversion of poplar (Populus deltoides) biomass into fermentable sugars using response surface methodology. Ind Crop Prod 44:220–226
Ji XJ, Nie ZK, Huang H, Ren LJ, Peng C, Ouyang PK (2011) Elimination of carbon catabolite repression in Klebsiella oxytoca for efficient 2, 3-butanediol production from glucose-xylose mixtures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:1119–1125
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, H., Cheng, K., Ge, J. et al. Corncob Mild Alkaline Pretreatment for High 2,3-Butanediol Production by Spent Liquor Recycle Process. Bioenerg. Res. 10, 566–574 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-017-9822-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-017-9822-y