Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to evaluate the carotid intima media thickness (IMT) in patients with thyrotoxicosis who received radioactive iodine (RAI) treatment.
Methods
This study was planned to be conducted with two different groups of people. There were 87 patients in the patient group and 98 controls. Participants were evaluated for atherosclerosis risk factors. Mean carotid IMT was measured from three consecutive traces at the common carotid artery bifurcation.
Results
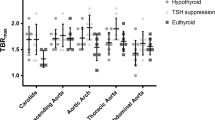
The mean carotid IMT was 0.81 ± 0.20 in patient group and this was higher than the controls (0.68 ± 0.19) (p < 0.01). IM thickening was positively correlated with the applied RAI dose levels in the treatment group (p = 0.029). In patients with only HT, the data of the two groups showed a significant difference, with the average IMT being higher in the patient group than that of the control group (p: 0.011).
Conclusion
RAI used in the treatment of thyrotoxicosis increases the IMT of carotid artery independent of age and sex. This treatment yields better results with higher doses, and this effect is more marked in patients with HT. Hence, we believe that it is necessary to calculate the dose properly for hyperthyroid cases in which treatment with RAI is planned. In particular, the patients with HT need to be treated with the minimum possible dose. Further, carotid arteries should be evaluated with US following RAI treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lambert V, Thierens H, Monsieurs M, Roncancio C, Laurent C. Translocation frequencies measured in patients one year after radioactive iodine therapy for thyrotoxicosis. Int J Radiat Biol. 2001;77:679–85.
Lee SL. Radioactive iodine therapy. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2012;19:420–8.
Moon JA, Yoo CH, Kim MH, Lee SM, Oh YJ, Ryu YH, et al. Knowledge, self-efficacy and perceived barriers on the low-iodine diet among thyroid cancer patients preparing for radioactive iodine therapy. Clin Nutr Res. 2012;1:13–22.
Cundiff JG, Portugal L, Sarne DH. Parathyroid adenoma after radioactive iodine therapy for multinodular goiter. Am J Otolaryngol. 2001;22:374–5.
Panareo S, Rossi R, Fabbri S, De Paola G, Candini GC, Feggi L, et al. A practical method for the estimation of therapeutic activity in the treatment of Graves’ hyperthyroidism. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;55:576–85.
Traino AC, Grosso M, Mariani G. Possibility of limiting the un-justified irradiation in (131) I therapy of Graves disease: a thyroid mass-reduction based method for the optimum activity calculation. Phys Med. 2010;26:71–9.
Dorn R, Kopp J, Vogt H, Heidenreich P, Carroll RG, Gulec SA. Dosimetry-guided radioactive iodine treatment in patients with metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer: largest safe dose using a risk-adapted approach. J Nucl Med. 2003;44:451–6.
Berg GE, Michanek AM, Holmberg EC, Fink M. Iodine-131 treatment of hyperthyroidism: significance of effective half-life measurements. J Nucl Med. 1996;37:228–32.
Huang TL, Hsu HC, Chen HC, Lin HC, Chien CY, Fang FM, et al. Long-term effects on carotid intima-media thickness after radiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiat Oncol. 2013;8:1–6.
Carmody BJ, Arora S, Avena R, Curry KM, Simpkins J, Cosby K, et al. Accelerated carotid artery disease after high-dose head and neck radiotherapy: is there a role for routine carotid duplex surveillance? J Vasc Surg. 1999;30:1045–51.
So NM, Lam WW, Chook P, Woo KS, Liu KH, Leung SF, et al. Carotid intima-media thickness in patients with head and neck irradiation for the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Radiol. 2002;57:600–3.
Sürücü E, Bekiş R, Şengöz T, Demir Y, Çelik AO, Orbay Ö, et al. The effect of radioiodine on the intima media thickness of the carotid artery. Mol Imaging Radionucle Ther. 2013;22:85–9.
Kablak-Ziembicka A, Tracz W, Przewlocki T, Pieniazek P, Sokolowski A, Konieczynska M. Association of increased carotid intima-media thickness with the extent of coronary artery disease. Heart. 2004;90:1286–90.
Bots ML, Hoes AW, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman A, Grobbee DE. Common carotid intima-media thickness and risk of stroke and myocardial infarction: the Rotterdam Study. Circulation. 1997;96:1432–7.
Lorenz MW, Markus HS, Bots ML, Rosvall M, Sitzer M. Prediction of clinical cardiovascular events with carotid intima-media thickness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation. 2007;115:459–67.
Sibal L, Agarwal SC, Home PD. Carotid intima-media thickness as a surrogate marker of cardiovascular disease in diabetes. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2011;19:23–34.
Sato M, Ogawa T, Sugimoto H, Otsuka K, Nitta K. Relation of carotid intima—media thickness and silent cerebral infarction to cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in chronic hemodialysis patients. Intern Med. 2012;51:2111–7.
Hayase T, Ayaori M, Sato H, Tanaka N, Ohashi K, Uto-Kondo H, et al. Impact of low-and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels on carotid intima-media thickness differs by smoking status in middle-aged men. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2012;19:664–72.
Lee EJ, Kim HJ, Bae JM, Kim JC, Han HJ, Park CS, et al. Relevance of common carotid intima-media thickness and carotid plaque as risk factors for ischemic stroke in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28:916–9.
Iglesias del Sol A, Bots ML, Grobbee DE, Hofman A, Witteman JC. Carotid intima-media thickness at different sites: relation to incident myocardial infarction; The Rotterdam Study. Eur Heart J. 2002;23:934–40.
Luo X, Yang Y, Cao T, Li Z. Differences in left and right carotid intima-media thickness and the associated risk factors. Clin Radiol. 2011;66:393–8.
Allahabadia A, Daykin J, Sheppard MC, Gough SC, Franklyn JA. Radioiodine treatment of hyperthyroidism-prognostic factors for outcome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:3611–7.
Franklyn JA. The management of hyperthyroidism. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:1731–8.
Enyi EMJ, Omotayo OK, Enyi EJ, Solomon AK, Eniojukan FJ. Effectiveness of fixed dose radioactive iodine (RAI) for the treatment of hyperthyroidism: experience of a teaching hospital in South West Nigeria. Mol Imaging Radionucl Ther. 2013;22:36–41.
Weetman AP. Radioiodine treatment for benign thyroid diseases. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2007;66:757–64.
Seto K, Yamagata K, Uchida F, Yanagawa T, Onizawa K, Bukawa H. Radiation-induced carotid artery stenosis in a patient with carcinoma of the oral floor. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2013;2013:379039.
Li CS, Schminke U, Tan TY. Extracranial carotid artery disease in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients with post-irradiationischemic stroke. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2010;112:682–6.
Zhao W, Robbins ME. Inflammation and chronic oxidative stress in radiation-induced late normal tissue injury: therapeutic implications. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16:130–43.
Fonkalsrud EW, Sanchez M, Zerubavel R, Mahoney A. Serial changes in arterial structure following radiation therapy. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1977;145:395–400.
O’Leary DH, Polak JF, Kronmal RA, Manolio TA, Burke GL, Wolfson SK Jr. Carotid-artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older adults. Cardiovascular Health study Collaborative Research Group. N Engl J Med. 1999;7:14–22.
Nagasaki T, Inaba M, Henmi Y, Kumeda Y, Ueda M, Tahara H, et al. Change in von Willebrand factor and carotid intima-media thickness in hypothyroid patients with normal thyroid function after levothyroxine replacement therapy. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;150:125–31.
Gao N, Zhang W, Zhang YZ, Yang Q, Chen SH. Carotid intima-media thickness in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism: a meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis. 2013;227:18–25.
Bilir C, Gökosmanoglu F, Caliskan M, Cinemre H, Akdemir R. Regression of the carotid intima media thickness by propylthiouracil therapy in graves’ hyperthyroidism. Am J Med Sci. 2012;343:273–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şanal, B., Işık, İ., Korkmaz, M. et al. Effect of radioactive iodine therapy on carotid intima media thickness in patients with hyperthyroidism. Ann Nucl Med 30, 75–80 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-015-1033-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-015-1033-z