Abstract
Objective
Myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) systems using a multifocal collimator can reduce scan time substantially compared with conventional MPI systems. In this study, we evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of multifocal collimator SPECT/CT in coronary artery disease (CAD) detection by comparing it with coronary artery angiography (CAG).
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 50 consecutive patients who had undergone CAG and stress 201Tl MPI multifocal collimator SPECT/CT within a 3-month period. A summed difference score (SDS) was calculated for each vascular territory from the MPI images. On CAG, a stenotic coronary artery was defined as one with luminal narrowing of ≥75 % with quantitative coronary angiography software.
Results
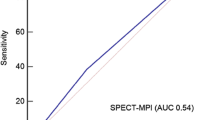
We analyzed the diagnostic accuracy of coronary artery stenosis detection using the definition that a coronary artery territory was ischemic when the SDS per vessel was ≥2. We generated receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves to evaluate the usefulness of SDS per vascular territory to find coronary artery stenoses. The area under the ROC curve was 0.86 and cut-off value was 2. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and accuracy to detect stenoses were 85, 83, 66, 94 and 84 %, respectively.
Conclusions
We confirmed the high accuracy of imaging with multifocal collimator SPECT/CT for detection of angiographically significant CAD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajaram R, Bhattacharya M, Ding X, Malmin R, Rempel TD, Vija AH, et al. Tomographic performance characteristics of the IQ SPECT system. IEEE nuclear science symposium conference record. 2011;2451–6.
Vija AH, Malmin R, Yahil A, Zeintl J, Bhattacharya M, Rempel TD, et al. A method for improving the efficiency of myocardial perfusion imaging using conventional SPECT and SPECT/CT imaging systems. IEEE nuclear science symposium and medical imaging conference record. 2010; 3433–7.
Caobelli F, Pizzocaro C, Paghera B, Guerra UP. Evaluation of patients with coronary artery disease. IQ-SPECT protocol in myocardial perfusion imaging: preliminary results. Nuklearmedizin. 2013;52:178–85.
Horiguchi Y, Ueda T, Shiomori T, Kanna M, Matsushita H, Kawaminami T, et al. Validation of a short-scan-time imaging protocol for thallium-201 myocardial SPECT with a multifocal collimator. Ann Nucl Med. 2014;28:707–15.
Nakata T, Watanabe S, Matsuo H, Hosokawa R, Kasai T. Risk management guidelines for the routine clinical use of stress myocardial perfusion imaging. Shinzoukakuigaku. 2008;9:6–10 (in Japanese).
Cerqueria MD, Weissman NJ, Dilsizian V, Jacobs AK, Kaul S, Laskey WK, et al. Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomographic imaging of the heart: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Cardiac Imaging Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology of the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2002;105:539–42.
Cohen J. Weighted kappa: nominal scale agreement with provision for scaled disagreement or partial credit. Psychol Bull. 1968;70:213–20.
Ozaki Y, Keane D, Herrman JP, et al. Coronary arteriography for quantitative analysis: an experimental and clinical comparison of cinefilm and video recordings. Am Heart J. 1995;129:471–5.
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33:159–74.
Tamaki N, Morita K. SPECT in cardiology. Q J Nucl Med. 2005;49:193–203.
Cuocolo A, Acampa W, Imbriaco M, De Luca N, Iovino GL, Salvatore M. The many ways to myocardial perfusion imaging. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;49:4–18.
Nakajima K, Matsuo S, Kawano M, Matsumoto N, Hashimoto J, Yoshinaga K, et al. The validity of multi-center common normal database for identifying myocardial ischemia: Japanese Society of Nuclear Medicine working group database. Ann Nucl Med. 2010;24:99–105.
Allman KC, Berry J, Sucharski LA, Stafford KA, Petry NA, Wysor W, et al. Determination of extent and location of coronary artery disease in patients without prior myocardial infarction by thallium-201 tomography with pharmacologic stress. J Nucl Med. 1992;33:2067–73.
Förster S, Rieber J, Ubleis C, Weiss M, Bartenstein P, Cumming P, et al. Tc-99 m sestamibi single photon emission computed tomography for guiding percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with multivessel disease: a comparison with quantitative coronary angiography and fraction flow reserve. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010;26:203–13.
Tonino PA, De Bruyne B, Pijls NH, Siebert U, Ikeno F, van’t Veer M, et al. Fractional flow reserve versus angiography for guiding percutaneous coronary intervention. N Engl J Med 2009;15:213–224.
Fiechter M, Ghadri JR, Kuest SM, Pazhenkottil AP, Wolfrum M, Nkoulou RN, et al. Nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging with a novel cadmium–zinc–telluride detector SPECT/CT device: first validation versus invasive coronary angiography. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;38:2025–30.
Nakazato R, Berman DS, Hayes SW, Fish M, Padgett R, Xu Y, et al. Myocardial perfusion imaging with a solid-state camera: simulation of a very low dose imaging protocol. J Nucl Med. 2013;54:373–9.
Conflict of interest
We have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogino, Y., Horiguchi, Y., Ueda, T. et al. A myocardial perfusion imaging system using a multifocal collimator for detecting coronary artery disease: validation with invasive coronary angiography. Ann Nucl Med 29, 366–370 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-015-0955-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-015-0955-9