Abstract
Objective
In a diagnostic context, determination of absorbed dose is required before the introduction of a new radiopharmaceutical to the market to obtain marketing authorization from the relevant agencies. In this work, the absorbed dose of [67 Ga]-ethylenecysteamine cysteine [(67 Ga)ECC] to human organs was determined by using distribution data for rats.
Methods
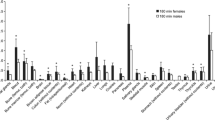
For biodistribution data, the animals were sacrificed by CO2 asphyxiation at selected times after injection (0.5, 2 and 48 h, n = 3 for each time interval), then the tissue (blood, heart, lung, brain, intestine, feces, skin, stomach, kidneys, liver, muscle and bone) were removed. The absorbed dose was determined by Medical Internal Radiation Dose (MIRD) method after calculating cumulated activities in each organ.
Results
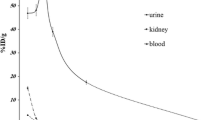
Our prediction shows that a 185-MBq injection of 67Ga-ECC into the humans might result in an estimated absorbed dose of 0.029 mGy in the whole body. The highest absorbed doses are observed in the spleen and liver with 33.766 and 16.847 mGy, respectively.
Conclusion
The results show that this radiopharmaceutical can be a good SPECT tracer since it can be produced easily and also the absorbed dose in each organ is less than permitted absorbed dose.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stabin MG, Tagesson M, Thomas SR, Ljungberg M, Strand SE. Radiation dosimetry in nuclear medicine. Appl Radiat Isotopes : including data, instrumentation and methods for use in agriculture, industry and medicine. 1999;50:73–87.
Eberlein U, Broer JH, Vandevoorde C, Santos P, Bardies M, Bacher K, et al. Biokinetics and dosimetry of commonly used radiopharmaceuticals in diagnostic nuclear medicine—a review. Eur J Nucl Med Mol. 2011;I(38):2269–81.
Stabin MG. MIRDOSE: personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med: official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 1996;37:538–46.
Loevinger R, Budinger TF, Watson EE. MIRD primer for absorbed dose calculations. New York: Society of Nuclear Medicine; 1988.
Sparks RB, Aydogan B. Comparison of the effectiveness of some common animal data scaling techniques in estimating human radiation dose. In Sixth International Radiopharmaceutical Dosimetry Symposium Oak Ridge, Oak Ridge Associated Universities, 1996; 705–16.
Lahooti A, Shanehsazzadeh S, Oghabian MA, Allen BJ. Assessment of human effective absorbed dose of Tc-99 m-USPIO based on biodistribution rat data. J Labelled Compd Rad. USA: Wiley; 2013. p. S258.
Stabin MG. The importance of patient-specific dose calculations in nuclear medicine. Nucl Eng Technol. 2008;40:527.
Lederer CM, Shirley VS, Browne E, Shihab-Eldin AA. Table of isotopes. New York: Wiley; 1978. p. 67.
Mariani G, Bodei L, Adelstein SJ, Kassis AI. Emerging roles for radiometabolic therapy of tumors based on Auger electron emission. J Nucl Med. 2000;41:1519–21.
Mez-Tejedor GGG, Fuss MC. Radiation Damage in Biomolecular Systems. USA: Springer; 2012.
Firestone RB, Shirley VS, Baglin CM, Chu SF, Zipkin J. Table of Isotopes, vol. II. New York: Willey; 1996.
Cutler CS, Giron MC, Reichert DE, Snyder AZ, Herrero P, Anderson CJ, et al. Evaluation of gallium-68 tris(2-mercaptobenzyl)amine: a complex with brain and myocardial uptake. Nucl Med Biol. 1999;26:305–16.
Tsang BW, Mathias CJ, Green MA. A gallium-68 radiopharmaceutical that is retained in myocardium: 68 Ga [(4, 6-MeO2sal) 2BAPEN]. J Nucl Med: official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 1993;34:1127.
Jalilian A, Shanehsazzadeh S, Akhlaghi M, Garoosi J, Rajabifar S, Tavakoli M. Preparation and evaluation of [67 Ga]-DTPA-β-1-24-corticotrophin in normal rats. Radiochim Acta. 2008;96:435–9.
Shanehsazzadeh S, Jalilian AR, Sadeghi HR, Allahverdi M. Determination of human absorbed dose of 67GA-DTPA-ACTH based on distribution data in rats. Radiat Prot Dosim. 2009;134:79–86.
Jalilian A, Shanehsazzadeh S, Akhlaghi M, Garousi J, Rajabifar S, Tavakoli M. Preparation and biodistribution of [67 Ga]-DTPA-gonadorelin in normal rats. J Radioanal Nucl Ch. 2008;278:123–9.
Shanehsazzadeh S, Jalilian A. Development of [67ga]-Dtpa-Gonadorelin in Normal Rats. J Labelled Compd Rad. 2009;52(Suppl 1):S326.
Shanehsazzadeh S, Lahooti A, Sadeghi HR, Jalilian AR. Estimation of human effective absorbed dose of 67 Ga–cDTPA–gonadorelin based on biodistribution rat data. Nucl Med Commun. 2011;32:37–43.
Shanehsazzadeh S, Oghabian MA, Lahooti A, Abdollahi M, Haeri SA, Amanlou M, et al. Estimated background doses of [67 Ga]-DTPA-USPIO in normal Balb/c mice as a potential therapeutic agent for liver and spleen cancers. Nucl Med Commun. 2013;34:915–25.
Jalilian A, Yousefnia H, Zolghadri S, Khoshdel M, Bolourinovin F, Rahiminejad A. Development of radiogallium–ethylenecysteamine cysteine complex as a possible renal imaging agent. J Radioanal Nucl Ch. 2010;284:49–54.
Shanehsazzadeh S, Oghabian MA, Lahooti A, Allen BJ. Development of ultra small super paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles labeled with Gallium 67 as a dual modality probe. J Labelled Compd Rad. USA: Wiley; 2013. p. S236.
Council B. Guidelines on the use of living animals in scientific investigations. Biological Council 1987.
Jalilian A, Shanehsazzadeh S, Akhlaghi M, Kamali-dehghan M, Moradkhani S. Development of [111In]-DTPA-buserelin for GnRH receptor studies. Radiochim Acta. 2010;98:113–9.
Shanehsazzadeh S, Oghabian MA, Daha FJ, Amanlou M, Allen BJ. Biodistribution of ultra small superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in BALB mice. J Radioanal Nucl Ch. 2013;295:1517–23.
Sadeghzadeh M, Shanehsazzadeh S, Lahooti A. Assessment of the effective absorbed dose of 4-benzyl-1-(3-[125I]-iodobenzylsulfonyl) piperidine in humans on the basis of biodistribution data of rats. Nucl Med Commun. 2014;. doi:10.1097/MNM.0000000000000210.
Jalilian AR, Shanesazzadeh S, Rowshanfarzad P, Bolourinovin F, Majdabadi A. Biodistribution study of [< sup > 61 </sup > Cu] pyruvaldehyde-bis (N-4-methylthiosemicarbazone) in normal rats as a PET tracer. Nucl Sci Tech. 2008;19:159–64.
Lahooti A, Shanehsazzadeh S, Jalilian AR, Tavakoli MB. Assessment of effective absorbed dose of 111In-DTPA-Buserelin in human on the basis of biodistribution rat data. Radiat Prot Dosim. 2013;154:1–8.
Moghaddam AK, Jalilian AR, Hayati V, Shanehsazzadeh S, Dodangeh A. Evaluation And Calculation of Human absorbed dose of (201) Tl(III)-DTPA-HIgG based on biodistribution data in rats. J Labelled Compd Rad. USA: Wiley; 2011. p. S347.
Moghaddam AK, Jalilian AR, Hayati V, Shanehsazzadeh S. Determination of human absorbed dose of 201Tl (III)-DTPA-HIgG based on biodistribution data in rats. Radiat Prot Dosim. 2010;141:269–74.
Bevelacqua J. Internal dosimetry primer. Radiat Prot Manage. 2005;22:7.
Icrp Radiation dose to patients from radiopharmaceuticals. Addendum 3 to ICRP Publication 53. ICRP Publication 106. Approved by the Commission in October 2007. Ann ICRP. 2008; 38:1–197.
Snyder W, Ford M, Warner G, Watson S. S″ absorbed dose per unit cumulated activity for selected radionuclides and organs. MIRD Pamphlet No. 11. New York: Society of Nuclear Medicine; 1975.
Vallabhajosula S, Kuji I, Hamacher KA, Konishi S, Kostakoglu L, Kothari PA, et al. Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution of 111In- and 177Lu-Labeled J591 Antibody Specific for Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen: Prediction of 90Y-J591 Radiation Dosimetry Based on 111In or 177Lu? J Nucl Med. 2005;46:634–41.
Food and Drug Administration. Title 21 CFR 361.1, Radioactive Drugs for Certain Research Uses. In 4-1-01 ed; National Archives and Records Administration, Washington, 2001; p 300–305.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Nuclear Science and Technology Research Institute (NSTRI) and Tehran University of Medical Sciences. The authors would like to express their deep gratitude to all technicians who support this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shanehsazzadeh, S., Yousefnia, H., Lahooti, A. et al. Assessment of human effective absorbed dose of 67 Ga–ECC based on biodistribution rat data. Ann Nucl Med 29, 118–124 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-014-0917-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-014-0917-7