Abstract
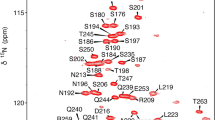
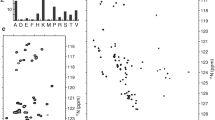
The phosphorylation state of the RNA polymerase II C-terminal repeat domain (CTD) regulates progression through the mRNA biogenesis cycle. Termination of transcription and recycling of RNA polymerase II is promoted by an interaction between the general transcription factor IIF (TFIIF) and the TFIIF-associating CTD phosphatase (FCP1). The acidic C-terminal region of FCP1 is disordered in the free state, but adopts an α-helical conformation upon binding to the heavy chain of TFIIF. Here we report 1H, 13C, and 15N resonance assignments for the intrinsically disordered unbound form of human C-terminal FCP1 (residues 879–961). The use of recently developed 13C direct detected “protonless” NMR experiments allowed the nearly complete assignment of FCP1 reported here and is likely to be a generally effective strategy for the chemical shift assignment of disordered proteins.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archambault J, Pan GH, Dahmus GK, Cartier M, Marshall N, Zhang S, Dahmus ME, Greenblatt J (1998) FCP1, the RAP74-interacting subunit of a human protein phosphatase that dephosphorylates the carboxyl-terminal domain of RNA polymerase IIO. J Biol Chem 273:27593–27601. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.42.27593
Bermel W, Bertini I, Felli IC, Lee YM, Luchinat C, Pierattelli R (2006a) Protonless NMR experiments for sequence-specific assignment of backbone nuclei in unfolded proteins. J Am Chem Soc 128:3918–3919. doi:10.1021/ja0582206
Bermel W, Bertini I, Felli IC, Piccioli M, Pierattelli R (2006b) C-13-detected protonless NMR spectroscopy of proteins in solution. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 48:25–45. doi:10.1016/j.pnmrs.2005.09.002
Csizmok V, Felli IC, Tompa P, Banci L, Bertini I (2008) Structural and dynamic characterization of intrinsically disordered human securin by NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 130:16873–16879. doi:10.1021/ja805510b
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A (1995) Nmrpipe—a multidimensional spectral processing system based on unix pipes. J Biomol NMR 6:277–293. doi:10.1007/BF00197809
Goddard T, Kneller D (2006) SPARKY 3.113
Kamada K, Roeder RG, Burley SK (2003) Molecular mechanism of recruitment of TFIIF-associating RNA polymerase C-terminal domain phosphatase (FCP1) by transcription factor IIF. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2296–2299. doi:10.1073/pnas.262798199
Meinhart A, Kamenski T, Hoeppner S, Baumli S, Cramer P (2005) A structural perspective of CTD function. Genes Dev 19:1401–1415. doi:10.1101/gad.1318105
Nguyen BD, Abbott KL, Potempa K, Kobort MS, Archambault J, Greenblatt J, Legault P, Omichinski JG (2003a) NMR structure of a complex containing the TFIIF subunit RAP74 and the RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal domain phosphatase FCP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5688–5693. doi:10.1073/pnas.1031524100
Nguyen BD, Chen HT, Kobor MS, Greenblatt J, Legault P, Omichinski JG (2003b) Solution structure of the carboxyl-terminal domain of RAP74 and NMR characterization of the FCPI-binding sites of RAP74 and human TFIIB. Biochemistry 42:1460–1469. doi:10.1021/bi0265473
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by start-up funds from the Pennsylvania State University to SAS. We are grateful to Alan Benesi for assistance with the NMR spectrometers.
Ethical Compliance
The experiments performed comply with the current laws of the United States.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Showalter, S.A. NMR assignment of the intrinsically disordered C-terminal region of Homo sapiens FCP1 in the unbound state. Biomol NMR Assign 3, 179–181 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-009-9169-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-009-9169-1