Abstract
Objective
To describe the feasibility, safety, efficacy, and complication profile of primary hypofractionated gamma knife radiosurgery (GKRS), and practical nuances of performing the same in pediatric patients.
Methods
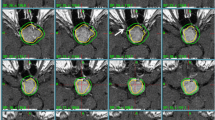
Three pediatric patients (age range 17–65 mo) underwent primary hypofractionated GKRS in 2–3 consecutive days with interfraction interval of 24 h. All patients had precocious puberty and were on GnRH analogue. Frame based GKRS done with 8.1–9.2 Gy radiation per fraction at 50% isodose in 2–3 fractions targeting the entire hamartoma volume. The mean target volume was 5.67 cc (4.45–7.39 cc). The authors followed these patients for clinical and endocrinological assessment at every 6 mo interval while the repeat MRI done at 6 mo and then annually. The seizure outcome analysis was done using Engel scale.
Results
At a mean follow up of 27 mo (24–30 mo), 2 patients became Engel class 3 while one achieved Engel class 1 control. 2 patients showed halted pubertal growth with no additional hormonal aberration. 2 patients showed significant volumetric reduction (48% and 32%) and patchy necrosis inside the hypothalamic hamartoma (HH). There was no deficit in visual function, memory and cognition. One patient showed reduction in aggressiveness.
Conclusion
Giant HH are exceptionally difficult neurological diseases. Primary hypofractionated GKRS may be an alternative approach as mono/multitherapy with promising results and minimal complication.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paillas JE, Roger J, Toga M, et al. Hamartoma of the hypothalamus. Clinical, radiological and histological study. Results of excision. Rev Neurol (Paris). 1969;120:177–94.
Weissenberger A, Dell M, Liow K, et al. Aggression and psychiatric comorbidity in children with hypothalamic hamartomas and their unaffected siblings. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2001;40:696–703.
Nguyen D, Singh S, Zaatreh M, et al. Hypothalamic hamartomas: seven cases and review of the literature. Epilepsy Behav. 2003;4:246–58.
Tassinari CA, Riguzzi P, Rizzi R, et al. Gelastic seizures. In: Tuxhorn I, Holthausen H, editors. Paediatric Epilepsy Syndromes and their Surgical Management. London: John Libbey. 1997;429–46.
Munari C, Kahane P, Francione S, et al. Role of the hypothalamic hamartoma in the genesis of gelastic fits (a video-stereo-EEG study). Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1995;95:154–60.
Kuzniecky R, Guthrie B, Mountz J, et al. Hypothalamic hamartomas and gelastc seizures: evidence for subcortical seizure generation by ictal SPECT and cerebral stimulation. Epilepsia. 1995;36(Suppl 3):s266.
Kerrigan JF, Ng YT, Chung S, Rekate HL. The hypothalamic hamartoma: a model of subcortical epileptogenesis and encephalopathy. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2005;12:119–31.
Kameyama S, Masuda H, Murakami H. Ictogenesis and symptomatogenesis of gelastic seizures in hypothalamic hamartoma: an ictal SPECT study. Epilepsia. 2010;51:2270–9.
Scholly J, Staack AM, Kahane P, et al. Hypothalamic hamartoma: epileptogenesis beyond the lesion? Epilepsia. 2017;58(Suppl. 2):32–40.
Prigatano GP, Wethe JV, Gray JA, et al. Intellectual functioning in presurgical patients with hypothalamic hamartoma and refractory epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2008;13:149–55.
Frattali CM, Liow K, Craig GH, et al. Cognitive deficits in children with gelastic seizures and hypothalamic hamartoma. Neurology. 2001;57:43–6.
Wagner K, Jennifer W, Schulze-Bonhage A, et al. Cognition in epilepsy patients with hypothalamic hamartomas. Epilepsia. 2017;58(Suppl. 2):85–93.
Ng YT, Rekate HL, Prenger EC, et al. Transcallosal resection of hypothalamic hamartoma for intractable epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2006;47:1192–202.
Ng YT, Rekate HL, Prenger EC, et al. Endoscopic resection of hypothalamic hamartomas for refractory symptomatic epilepsy. Neurology. 2008;70:1543–8.
Wait S, Abla AA, Killory BD, et al. Surgical approaches to hypothalamic hamartomas. Neurosurg Focus. 2011;30(2):E2.
Drees C, Chapman K, Prenger E, et al. Seizure outcome and complications following hypothalamic hamartoma treatment in adults: endoscopic, open, and gamma knife procedures. J Neurosurg. 2012;117(2):255–61.
Regis J, Cross JH, Kerrigan JF. Achieving a cure for hypothalamic hamartomas: a Sisyphean quest? Epilepsia. 2017;58(Suppl. 2):7–11.
Díaz-Martínez JA, Arenas-Ruiz JA, Quezada-Bautista AA, et al. Hypothalamic hamartomas: a review. JSM Pediatr Neurol. 2017;1(1):1005.
Abla AA, Shetter AG, Chang SW, et al. Gamma knife surgery for hypothalamic hamartomas and epilepsy: patient selection and outcomes. J Neurosurg. 2010;113(Suppl):207–14.
Regis J, Scavarda D, Tamura M, et al. Epilepsy related to hypothalamic hamartomas: surgical management with special reference to gamma knife surgery. Childs Nerv Syst. 2006;22:881–95.
Regis J, Scavarda D, Tamura M, et al. Gamma knife surgery for epilepsy related to hypothalamic hamartomas. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2007;14:73–9.
Mathieu D, Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Flickinger J, Lunsford LD. Gamma knife radiosurgery for refractory epilepsy caused by hypothalamic hamartomas. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2006;84:82–7.
Mathieu D, Deacon C, Pinard CA, Kenny B, Duval J. Gamma knife surgery for hypothalamic hamartomas causing refractory epilepsy: preliminary results from a prospective observational study. J Neurosurg. 2010;113(Suppl):215–21.
Regis J, Lagmari M, Carron R, et al. Safety and efficacy of gamma knife radiosurgery in hypothalamic hamartomas with severe epilepsies: a prospective trial in 48 patients and review of the literature. Epilepsia. 2017;58(Suppl. 2):60–71.
Delalande O, Fohlen M. Disconnecting surgical treatment of hypothalamic hamartoma in children and adults with refractory epilepsy and proposal of a new classification. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2003;43:61–8.
Mukherjee KK, Kumar N, Tripathi M, et al. Dose fractionated gamma knife radiosurgery for large arteriovenous malformations on daily or alternate day schedule outside the linear quadratic model: proof of concept and early results. A substitute to volume fractionation. Neurol India. 2017;65(4):826–35.
Tripathi M, Rekhapalli R, Batish A, et al. Safety and efficacy of primary multisession dose fractionated gamma knife radiosurgery for jugular paragangliomas. World Neurosurg. 2019 Jul 16.
Engel J Jr, Van Neaa PC, Rasmussen TB, Oejmann LM: Outcome with respect to epileptic seizures. In: Engel J Jr, editor. Surgical Treatment of the Epilepsies, 2 ed. 1993. p. 609–21.
Kumar R, Yadav J, Sahu JK, Tripathi M, Ahuja C, Dayal D. Episodes of prolonged “trance-like state” in an infant with hypothalamic hamartoma. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2019;24:55–9.
Mittal S, Mittal M, Montes JL, et al. Hypothalamic hamartomas. Part 2. Surgical considerations and outcome. Neurosurg Focus. 2013;34(6):E7.
Fohlen M, Lellouch A, Delalande O. Hypothalamic hamartoma with refractory epilepsy: surgical procedures and results in 18 patients. Epileptic Disord. 2003;5:267–73.
Palmini A, Paglioli-Neto E, Montes J, Farmer JP. The treatment of patients with hypothalamic hamartomas, epilepsy and behavioural abnormalities: facts and hypotheses. Epileptic Disord. 2003;5:249–55.
Rosenfeld JV, Feiz-Erfan I. Hypothalamic hamartoma treatment: surgical resection with the transcallosal approach. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2007;14:88–98.
Stabell KE, Bakke SJ, Egge A. Cognitive and neurological sequelae after stereoendoscopic disconnection of a hypothalamic hamartoma. A case study. Epilepsy Behav. 2012;24:274–8.
Castinetti F, Brue T, Morange I, Carron R, Régis J. Gamma knife radiosurgery for hypothalamic hamartoma preserves endocrine functions. Epilepsia. 2017;58(Suppl. 2):72–6.
Jung H, Neumaier Probst E, Hauffa BP, et al. Association of morphological characteristics with precocious puberty and/or gelastic seizures in hypothalamic hamartoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:4590–5.
Kameyama S, Shirozu H, Masuda H, et al. MRI-guided stereotactic radiofrequency thermocoagulation for 100 hypothalamic hamartomas. J Neurosurg. 2015;124(5):1503–12.
Tandon V, Sarat Chandra P, Doddamani RS, et al. Stereotactic radiofrequency thermocoagulation of hypothalamic hamartoma using robotic guidance (ROSA) coregistered with O-arm guidance preliminary technical note. World Neurosurg. 2018;112:267–74.
Du VX, Gandhi SV, Rekate HL, Mehta AD. Laser interstitial thermal therapy: a first line treatment for seizures due to hypothalamic hamartoma? Epilepsia. 2017;58(Suppl 2):77–84.
Wilfong A, Curry DJ. Hypothalamic hamartomas: optimal approach to clinical evaluation and diagnosis. Epilepsia. 2013;54:5.
Schulze-Bonhage A, Homberg V, Trippel M, et al. Interstitial radiosurgery in the treatment of gelastic epilepsy. Neurology. 2008;71:277–82.
Wolf A, Naylor K, Tam M, et al. Risk of radiation-associated intracranial malignancy after stereotactic radiosurgery: a retrospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2019;2(1):159–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MT and PM: Concept, patient management, radiosurgery, manuscript writing, review, critical evaluation, submission; NS and JKS: Patient management, critical evaluation of manuscript; RK: Patient management, critical evaluation of manuscript, endocrinological management; NK: Radiotherapy, patient management; CKA: Radiology support, patient management; PK, RK and AB: Patient management, literature review; SM: Literature review and administration support. NS will act as guarantor for this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Equal first authorship to Manjul Tripathi and Prashant Maskara
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 21 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathi, M., Maskara, P., Sankhyan, N. et al. Safety and Efficacy of Primary Hypofractionated Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Giant Hypothalamic Hamartoma. Indian J Pediatr 88, 1086–1091 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-020-03637-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-020-03637-w