Abstract
Objective
To identify areas of deficiencies and gaps in child protection services in Northern Sri Lanka. Also, to help in recommending strategies, programmes of interventions for addressing issues of child abuse and advice the legal system.
Methods
A retrospective study was done to determine the socio-demographic details, type of abuse, clinical profile, relationship of the perpetrator and nature of abuse among children admitted to a tertiary care centre from 2009 through 2014, a period after cessation of a 60-y conflict. Data were obtained from hospital based records and records maintained at the district probation office.
Results
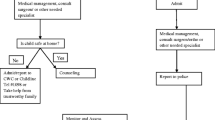
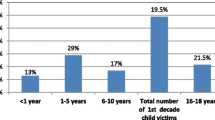
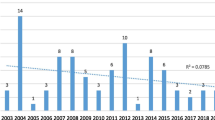
Seven hundred twenty cases were referred to the tertiary care centre with abuse. Majority of the children were from the Jaffna district, the northern city of the war affected area and mean age of the children affected was 14.5 ± 2.6 y. Females were affected more than the males and 352 children were seen following sexual abuse. The clinical examination showed penetrative injury in 15 %. The perpetrator was known in 70 % of the situations and the victim was coerced into a relationship for abuse. Attempted suicide was seen in significant numbers during the immediate post war period and school dropout and delinquent behaviour was seen in later years.
Conclusions
The problem of child abuse is considerable in this region and there is an urgent need to strengthen the services offered to the victims. Urgent steps are needed to safeguard these children, especially in the war affected areas.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldsone E. The effect of war on children. Child Abuse Negl. 1996;20:809–19.
World Report on Violence and Health. Chapter 3: child abuse and neglect by parents and other caregivers. Available at: http://www.who.int/violence_injury_prevention/violence/global_campaign/en/chap3. Accessed 28 Dec 2012.
Report of the Consultation on Child Abuse Prevention, 29–31 March 1999. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1999. (document WHO/HSC/PVI/99.1). Available at: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/1999/aaa00302.pdf. Accessed on 22 November, 2009.
Radford L, Corral S, Bradley C, et al. Child maltreatment in the family. In: Radford L, Corral S, Bradley C, et al, editors. Child Abuse and Neglect in the UK Today. London: National Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Children; 2009. p. 45–56.
Theodore AD, Runyan DK. A medical research agenda for child maltreatment: negotiating the next steps. Pediatrics. 1999;104:168–77.
Colomboge SM, Dassanayake PB, Waidyaratna DL. A study on child abuse in Anuradhapura, Colombo South and Ratnapura. Available at: http://www.unicef.org/srilanka/2012_SL_PUB_Study_on_CA__in.pdf. Accessed on 30 November 2014.
UK statistics: Copyright © 2014 NSPCC - All rights reserved. National Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Children. Available at: www.nspcc.org.uk. Accessed on 30th November 2014.
Harlow C. U.S. Department of Justice, Office of Justice Programs. (1999). Prior abuse reported by inmates and probationers (NCJ 172879). Available at: http://bjs.ojp.usdoj.gov/content/pub/pdf/parip.pdf. Accessed on 12th October 2014.
de Jong R, Alink L, Bijleveld C, et al. Transition to adulthood of child sexual abuse victims. In: Van Hasselt VB, editor. Aggression and Violent Behavior. Vol 24. Florida, USA: Elsevier; 2015. p. 175–87.
Straus MA. Corporal Punishment and Primary Prevention of Physical Abuse. Child Abuse Neglect. 2000;24:1109–14.
Acknowledgments
Technical support, administrative and Dr A Annieston at the Department of Paediatrics, University of Jaffna, Sri Lanka.
Contributions
MGS: Data collection, analysis and writing; SSR: Writing and correction of manuscript; KV and SM: Data collection. MGS will act as guarantor for the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Source of Funding
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sathiadas, M.G., Mayoorathy, S., Varuni, K. et al. Child Abuse in Northern Sri Lanka. Indian J Pediatr 84, 128–133 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-016-2193-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-016-2193-0