Abstract
Objective
To compare efficacy and safety of chloral hydrate (CH), chloral hydrate and promethazine (CH + P) and chloral hydrate and hydroxyzine (CH + H) in electroencephalography (EEG) sedation.
Methods
In a parallel single-blinded randomized clinical trial, ninety 1–7 y-old uncooperative kids who were referred to Pediatric Neurology Clinic of Shahid Sadoughi University, Yazd, Iran from April through August 2012, were randomly assigned to receive 40 mg/kg of chloral hydrate or 40 mg/kg of chloral hydrate and 1 mg/kg of promethazine or 40 mg/kg of chloral hydrate and 2 mg/kg of hydroxyzine. The primary endpoint was efficacy in sufficient sedation (obtaining four Ramsay sedation score) and successful completion of EEG. Secondary endpoint was clinical adverse events.
Results
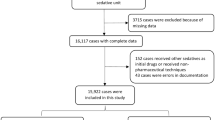
Thirty nine girls (43.3 %) and 51 boys (56.7 %) with mean age of 3.34 ± 1.47 y were assessed. Sufficient sedation and completion of EEG were achieved in 70 % (N = 21) of chloral hydrate group, in 83.3 % (N = 25) of CH + H group and in 96.7 % (N = 29) of CH + P group (p = 0.02). Mild clinical adverse events including vomiting [16.7 % (N = 5) in CH, 6.7 % (N = 2) in CH + P, 6.7 % (N = 2) in CH + H], agitation in 3.3 % of CH + P (N = 1) group and mild transient hypotension in 3.3 % of CH + H (N = 1) group occurred. Safety of these three sedation regimens was not statistically significant different (p = 0.14).
Conclusions
Combination of chloral hydrate—antihistamines can be used as the most effective and safe sedation regimen in drug induced sleep electroencephalography of kids.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jagoda A, Gupta K. The emergency department evaluation of the adult patient who presents with a first-time seizure. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2011;29:41–9.
Sahyoun C, Krauss B. Clinical implications of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of procedural sedation agents in children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2012;24:225–32.
Ashrafi MR, Mohammadi M, Tafarroji J, Shabanian R, Salamati P, Zamani GR. Melatonin versus chloral hydrate for recording sleep EEG. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2010;14:235–8.
Razieh F, Sharam J, Motahhareh G, Sedighah AK, Mohammad-Hosein J. Efficacy of chloral hydrate and promethazine for sedation during electroencephalography in children; A randomised clinical trial. Iran J Pediatr. 2013;23:27–31.
Nishida M, Sood S, Asano E. In-vivo animation of midazolam-induced electrocorticographic changes in humans. J Neurol Sci. 2009;287:151–8.
Mason KP, O’Mahony E, Zurakowski D, Libenson MH. Effects of dexmedetomidine sedation on the EEG in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2009;19:1175–83.
Olson DM, Sheehan MG, Thompson W, Hall PT, Hahn J. Sedation of children for electroencephalograms. Pediatrics. 2001;108:163–5.
Cortellazzi P, Lamperti M, Minati L, Falcone C, Pantaleoni C, Caldiroli D. Sedation of neurologically impaired children undergoing MRI: A sequential approach. Paediatr Anaesth. 2007;17:630–6.
Haselkorn T, Whittemore AS, Udaltsova N, Friedman GD. Short-term chloral hydrate administration and cancer in humans. Drug Saf. 2006;29:67–77.
Costa LR, Costa PS, Brasileiro SV, Bendo CB, Viegas CM, Paiva SM. Post-discharge adverse events following pediatric sedation with high doses of oral medication. J Pediatr. 2012;160:807–13.
Sander J, Shamdeen MG, Gottschling S, Gortner L, Gräber S, Meyer S. Melatonin does not influence sleep deprivation electroencephalogram recordings in children. Eur J Pediatr. 2012;171:675–9.
da Costa LR, da Costa PS, Lima AR. A randomized double-blinded trial of chloral hydrate with or without hydroxyzine versus placebo for pediatric dental sedation. Braz Dent J. 2007;18:334–40.
Patanwala AE, Amini R, Hays DP, Rosen P. Antiemetic therapy for nausea and vomiting in the emergency department. J Emerg Med. 2010;39:330–6.
Adolph O, Köster S, Georgieff M, Georgieff EM, Moulig W, Föhr KJ. Promethazine inhibits NMDA-induced currents - new pharmacological aspects of an old drug. Neuropharmacology. 2012;63:280–91.
American Academy of Pediatrics; American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry, Coté CJ, Wilson S, Work Group on Sedation. Guidelines for monitoring and management of pediatric patients during and after sedation for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures: An update. Pediatrics. 2006;118:2587–602.
Ramsay MA, Savege TM, Simpson BR, Goodwin R. Controlled sedation with alphaxalone-alphadolone. Br Med J. 1974;2:656–9.
Britton JW, Kosa SC. The clinical value of chloral hydrate in the routine electroencephalogram. Epilepsy Res. 2010;88:215–20.
Ashrafi MR, Azizi Malamiri R, Zamani GR, Mohammadi M, Hosseini F. Sleep inducing for EEG recording in children: A comparison between oral midazolam and chloral hydrate. Iran J Child Neurol. 2013;7:15–9.
Loewy J, Hallan C, Friedman E, Martinez C. Sleep/sedation in children undergoing EEG testing: A comparison of chloral hydrate and music therapy. Am J Electroneurodiagnostic Technol. 2006;46:343–55.
Aksu R, Kumandas S, Akin A, Bicer C, Gümüş H, Güler G, et al. The comparison of the effects of dexmedetomidine and midazolam sedation on electroencephalography in pediatric patients with febrile convulsion. Paediatr Anaesth. 2011;21:373–8.
Mehta UC, Patel I, Castello FV. EEG sedation for children with autism. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2004;25:102–4.
Torres-Pérez J, Tapia-García I, Rosales-Berber MA, Hernández-Sierra JF, Pozos-Guillén AJ. Comparison of three conscious sedation regimens for pediatric dental patients. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2007;31:183–6.
Wilson S, Easton J, Lamb K, Orchardson R, Casamassimo P. A retrospective study of chloral hydrate, meperidine, hydroxyzine, and midazolam regimens used to sedate children for dental care. Pediatr Dent. 2000;22:107–12.
Avalos-Arenas V, Moyao-García D, Nava-Ocampo AA, Zayas-Carranza RE, Fragoso-Ríos R. Is chloral hydrate/hydroxyzine a good option for paediatric dental outpatient sedation? Curr Med Res Opin. 1998;14:219–26.
Roach CL, Husain N, Zabinsky J, Welch E, Garg R. Moderate sedation for echocardiography of preschoolers. Pediatr Cardiol. 2010;31:469–73.
Fávero ML, Ponce FA, Pio MR, Tabith Jr A, Carvalho e Silva FL. Chloral hydrate to study auditory brainstem response. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;76:433–6.
Heistein LC, Ramaciotti C, Scott WA, Coursey M, Sheeran PW, Lemler MS. Chloral hydrate sedation for pediatric echocardiography: Physiologic responses, adverse events, and risk factors. Pediatrics. 2006;117:e434–41.
Fallah R, Nakhaei MH, Behdad S, Moghaddam RN, Shamszadeh A. Oral chloral hydrate and intranasal midazolam for sedation during computerized tomography. Indian Pediatr. 2013;50:233–5.
Avlonitou E, Balatsouras DG, Margaritis E, Giannakopoulos P, Douniadakis D, Tsakanikos M. Use of chloral hydrate as a sedative for auditory brainstem response testing in a pediatric population. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;75:760–3.
Coskun S, Yuksel H, Onag A. Chloralhydrate in children undergoing echocardiography. Indian J Pediatr. 2001;68:319–22.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Professor Nasrollah Bashardoost for data analyzing help.
Contributions
RF: Writing the manuscript; AA and AS: Gathering the data; SAK: Editing the manuscript. RF will act as guarantor for this paper.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Role of Funding Source
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fallah, R., Alaei, A., Akhavan Karbasi, S. et al. Chloral Hydrate, Chloral Hydrate - Promethazine and Chloral Hydrate -Hydroxyzine Efficacy in Electroencephalography Sedation. Indian J Pediatr 81, 541–546 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-013-1298-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-013-1298-y