Abstract
Purpose
In the present study we compared three different Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) treatment delivery techniques in terms of treatment time (TT) and their relation with intrafraction variation (IFV). Besides that, we analyzed if different clinical factors could have an influence on IFV. Finally, we appreciated the soundness of our margins.
Materials and methods
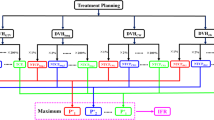
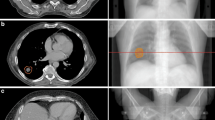
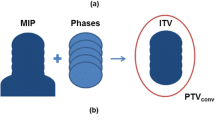
Forty-five patients undergoing SBRT for stage I lung cancer or lung metastases up to 5 cm were included in the study. All underwent 4DCT scan to create an internal target volume (ITV) and a 5 mm margin was added to establish the planning target volume (PTV). Cone-beam CTs (CBCTs) were acquired before and after each treatment to quantify the IFV. Three different treatment delivery techniques were employed: fixed fields (FF), dynamically collimated arcs (AA) or a combination of both (FA). We studied if TT was different among these modalities of SBRT and whether TT and IFV were correlated. Clinical data related to patients and tumors were recorded as potential influential factors over the IFV.
Results
A total of 52 lesions and 147 fractions were analyzed. Mean IFV for x-, y- and z-axis were 1 ± 1.16 mm, 1.29 ± 1.38 mm and 1.17 ± 1.08 mm, respectively. Displacements were encompassed by the 5 mm margin in 96.1 % of fractions. TT was significantly longer in FF therapy (24.76 ± 5.4 min), when compared with AA (15.30 ± 3.68 min) or FA (17.79 ± 3.52 min) (p < 0.001). Unexpectedly, IFV did not change significantly between them (p = 0.471). Age (p = 0.003) and left vs. right location (p = 0.005) were related to 3D shift ≥2 mm. In the multivariate analysis only age showed a significant impact on the IFV (OR = 1.07, p = 0.007).
Conclusions
The choice of AA, FF or FA does not impact on IFV although FF treatment takes significantly longer treatment time. Our immobilization device offers enough accuracy and the 5 mm margin may be considered acceptable as it accounts for more than 95 % of tumor shifts. Age is the only clinical factor that influenced IFV significantly in our analysis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGarry RC, Papiez L, Williams M, Whitford T, Timmerman RD. Stereotactic body radiation therapy of early-stage non-small cell lung carcinoma: phase I study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;63(4):1010–5.
Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J, Michalski J, Straube W, Bradley J, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA. 2010;303(11):1070–6.
Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Fujino M, Gomi K, et al. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (HypoFXSRT) for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: updated results of 257 patients in a Japanese multi-institutional study. J Thorac Oncol. 2007;2(7 Suppl 3):S94–100.
Grills IS, Mangona VS, Welsh R, Chmielewski G, McInerney E, Martin S, et al. Outcomes after stereotactic lung radiotherapy or wedge resection for stage I nonsmall-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(6):928–35.
Fakiris AJ, McGarry RC, Yiannoutsos CT, Papiez L, Williams M, Henderson MA, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early-stage non-small-cell lung carcinoma: four-year results of a prospective phase II study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;75(3):677–82.
Chang JY, Senan S, Paul MA, Mehran RJ, Louie AV, Balter P, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus lobectomy for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: a pooled analysis of two randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(6):630–7.
Siva S, Mac Manus M, Ball D. Stereotactic radiotherapy for pulmonary oligometastases a systematic review. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5(7):1091–9.
Wolthaus JW, Sonke JJ, van Herk M, Belderbos JS, Rossi MM, Lebesque JV, et al. Comparison of different strategies to use four-dimensional computed tomography in treatment planning for lung cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70(4):1229–38.
Uematsu M, Sonderegger M, Shioda A, Tahara K, Fukui T, Hama Y, et al. Daily positioning accuracy of frameless stereotactic radiation therapy with a fusion of computed tomography and linear accelerator (focal) unit: evaluation of z-axis with a z-marker. Radiother Oncol. 1999;50:337–9.
Grills IS, Hugo G, Kestin LL, Galerani AP, Chao KK, Wloch J, et al. Image-guided radiotherapy via daily online cone-beam CT substantially reduces margin requirements for stereotactic lung radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70(4):1045–56.
Purdie TG, Bissonnette JP, Franks K, Bezjak A, Payne D, Sie F, et al. Cone-beam computed tomography for on-line image guidance of lung stereotactic radiotherapy: localization, verification, and intrafraction tumor position. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;68(1):243–52.
Rauschenbach BM, Mackowiak L, Malhotra HK. A dosimetric comparison of three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy, volumetric-modulated arc therapy, and dynamic conformal arc therapy in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer using stereotactic body radiotherapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2014;15(5):4898.
Han K, Cheung P, Basran PS, Poon I, Yeung L, Lochray F. A comparison of two immobilization systems for stereotactic body radiation therapy of lung tumors. Radiother Oncol. 2010;95(1):103–8.
Lagerwaard FJ, Haasbeek CJ, Smit EF, Slotman BJ, Senan S. Outcomes of risk-adapted fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70(3):685–92.
Hurkmans CW, Cuijpers JP, Widder J, van der Heide UA, Schuring D, Senan S. Recommendations for implementing stereotactic radiotherapy in peripheral stage IA non-small cell lung cancer: report from the Quality Assurance Working Party of the randomised phase III ROSEL study. Radiat Oncol. 2009;4:1.
Jensen HR, Hansen O, Hjelm-Hansen M, Brink C, et al. Inter- and intrafractional movement of the tumour in extracranial stereotactic radiotherapy of NSCLC. Acta Oncol. 2008;47:1432–7.
Sonke JJ, Rossi M, Wolthaus J, van Herk M, Damen E, Belderbos J. Frameless stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer using fourdimensional cone beam CT guidance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;74(2):567–74.
Boggs DH, Feigenberg S, Walter R, Wissing D, Patel B, Wu T, et al. Stereotactic radiotherapy using tomotherapy for early-stage non-small cell lung carcinoma: analysis of intrafraction tumour motion. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2014;58(6):706–13.
Siva S, Devereux T, Kron T, Gill S, Macmanus M, Bressel M, et al. Vacuum immobilisation reduces tumour excursion and minimises intrafraction error in a cohort study of stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy for pulmonary metastases. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2014;58(2):244–52.
Baba F, Shibamoto Y, Tomita N, Ikeya-Hashizume C, Oda K, Ayakawa S, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for stage I lung cancer and small lung metastasis: evaluation of an immobilization system for suppression of respiratory tumor movement and preliminary results. Radiat Oncol. 2009;4:15.
Shah C, Grills IS, Kestin LL, McGrath S, Ye H, Martin SK, et al. Intrafraction variation of mean tumor position during image-guided hypofractionated stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;82(5):1636–41.
Shah C, Kestin LL, Hope AJ, Bissonnette JP, Guckenberger M, Xiao Y, et al. Target margins for image-guided lung SBRT: assessment of target position intrafraction and correction residuals. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2013;3(1):67–73.
Guckenberger M, Meyer J, Wilbert J, Richter A, Baier K, Mueller G, et al. Intra-fractional uncertainties in cone-beam CT based image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) of pulmonary tumors. Radiother Oncol. 2007;83(1):57–64.
Worm ES, Hansen AT, Petersen JB, Muren LP, Præstegaard LH, Høyer M. Inter- and intrafractional localisation errors in cone-beam CT guided stereotactic radiation therapy of tumours in the liver and lung. Acta Oncol. 2010;49:1177–83.
Dahele M, Verbakel W, Cuijpers J, Slotman B, Senan S. An analysis of patient positioning during stereotactic lung radiotherapy performed without rigid external immobilization. Radiother Oncol. 2012;104(1):28–32.
Li W, Purdie TG, Taremi M, Fung S, Brade A, Cho BC, et al. Effect of immobilization and performance status on intrafraction motion for stereotactic lung radiotherapy: analysis of 133 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81(5):1568–75.
Liu HW, Khan R, Nugent Z, Krobutschek K, Dunscombe P, Lau H. Factors influencing intrafractional target shifts in lung stereotactic body radiation therapy. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2014;4(1):e45–51.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rico, M., Martínez, E., Pellejero, S. et al. Influence of different treatment techniques and clinical factors over the intrafraction variation on lung stereotactic body radiotherapy. Clin Transl Oncol 18, 1011–1018 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-015-1475-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-015-1475-8