Abstract
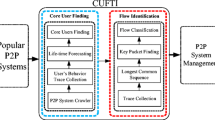
As P2P dominates Internet traffic in recent years, ISPs are striving to balance between providing the basic networking services for P2P users and properly managing network bandwidth usage. That is, ISPs are required to provide proper bandwidth for each P2P user to get every file to fulfill their provision for communications, while they have to control bandwidth consumption for efficient usage. However, current P2P traffic management strategies are unable to satisfy both requirements. In this paper, our goal is to design a simple and effective scheme for ISPs to moderate the tradeoff. It is achieved by proposing a file-aware P2P traffic classification method that can identify files and the associated flows. The file-level information can lead to more efficient and flexible management strategies on a per-file basis. We offer two alternatives: constraining the per-file bandwidth consumption and the number of per-file concurrent flows. Finally, a real-life trace is measured using our file-aware method from the perspectives of peers and files. The results indicate that ISPs can gain enough opportunities to flexibly choose proper traffic manage parameters according to actual demands.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aceto G, Dainotti A, de Donato W, Pescape A (2010) PortLoad: taking the best of two worlds in traffic classification. In: Proc. INFOCOM workshops, San Diego, CA, USA
BlueCoat (2011) Blue coat packetShaper. http://www.bluecoat.com/products/packetshaper. Accessed 3 Sep 2011
Canini M, Li W, Moore A, Bolla R (2009) GTVS: boosting the collection of application traffic ground truth. In: Proc. 1st international workshop on traffic monitoring and analysis, Aachen, Germany
Cisco (2005) Managing Peer-to-Peer traffic with cisco service control technology. http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/ps7045/ps6129/ps6133/ps6150/prod_white_paper0900aecd8023500d.html. Accessed 3 Sep 2011
Cohen B (2004) The bitTorrent protocol specification. http://www.bittorrent.org/beps/bep_0003.html. Accessed 3 Sep 2011
Dischinger M, Marcon M, Guha S, Gummadi K, Mahajan R, Saroiu S (2010) Glasnost: enabling end users to detect traffic differentiation. In: Proc. USENIX NSDI, San Jose, California, USA
Erman J, Mahanti A, Arlitt M (2007a) Byte me: a case for byte accuracy in traffic classification. In: Proc. SIGCOMM MineNet workshop, San Diego, CA, USA
Erman J, Mahanti A, Arlitt M, Williamson C (2007b) Identifying and discriminating between web and Peer-to-Peer traffic in the network core. In: Proc. ACM WWW, Banff, Alberta, Canada
F5 (2007) Bandwidth management for Peer-to-Peer applications. http://www.f5.com/pdf/white-papers/rateshaping-wp.pdf. Accessed 3 Sep 2011
Gallagher B, Iliofotou M, Eliassi-Rad T, Faloutsos M (2010) Link homophily in the application layer and its usage in traffic classification. In: Proc. IEEE INFOCOM, San Diego, CA, USA
Haffner P, Sen S, Spatscheck O, Wang D (2005) ACAS: automated construction of application signatures. In: Proc. SIGCOMM MineNet workshops, Philadelphia, PA, USA
Iliofotou M, Faloutsos M, Mitzenmacher M (2009) Exploiting dynamicity in graph-based traffic analysis: techniques and applications. In: Proc. ACM CoNEXT, Rome, Italy
Karagiannis T, Papagiannaki K, Faloutsos M (2005) BLINC: multilevel traffic classification in the dark. In: Proc. ACM SIGCOMM, Philadelphia, PA, USA
Kim H, Claffy K, Fomenkov M, Barman D, Faloutsos M, Lee K (2008) Internet traffic classification demystified: myths, caveats, and the best practices. In: Proc. ACM CoNEXT, Madrid, Spain
Kulbak Y, Bickson D (2005) The eMule protocol specification. http://www.cs.huji.ac.il/labs/danss/p2p/resources/emule.pdf. Accessed 3 Sep 2011
Kumar S, Turner J, Crowley P (2008) Peacock hashing: deterministic and updatable hashing for high performance networking. In: Proc. IEEE INFOCOM, Phoenix, AZ, USA
LimeWire (2008) Gnutella protocol specification. http://wiki.limewire.org/index.php?title=GDF. Accessed 3 Sep 2011
Ma J, Levchenko K, Kreibich C, Savage S, Voelker G (2006) Unexpected means of protocol inference. In: Proc. SIGCOMM IMC, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Mohammadi M, Raahemi B, Akbari A, Moeinzadeh H, Nasersharif B (2011) Genetic-based minimum classification error mapping for accurate identifying Peer-to-Peer applications in the internet traffic. Expert Syst Appl 38(6):6417–6423
Moore A, Papagiannaki K (2005) Toward the accurate identification of network applications. In: Proc. passive and active network measurement, Boston, USA
Nam G, Patankar P, Kesidis G, Das C, Seren C (2009) Mass purging of stale tcp flows in per-flow monitoring systems. In: Proc. IEEE ICCCN, San Franciso, CA, USA
Nguyen T, Armitage G (2008) A survey of techniques for internet traffic classification using machine learning. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 10(4):56–76
Qi Y, Xu B, He F, Yang B, Yu J, Li J (2007) Towards high-performance flow-level packet processing on multi-core network processors. In: Proc. ACM ANCS, Orlando, Florida, USA
Raahemi B, Mumtaz A (2010) Classification of Peer-to-Peer traffic using a two-stage window-based classifier with fast decision tree and ip layer attributes. International Journal of Data Warehousing and Mining (IJDWM) 6(3):28–42
Raahemi B, Hayajneh A, Rabinovitch P (2007) Peer-to-Peer ip traffic classification using decision tree and ip layer attributes. International Journal of Business Data Communications and Networking (IJBDCN) 3(4):60–74
Raahemi B, Zhong W, Liu J (2009) Exploiting unlabeled data to improve Peer-to-Peer traffic classification using incremental tri-training method. Peer-to-Peer Netw Appl 2(2):87–97
Ramakrishna M, Fu E, Bahcekapili E (1994) A performance study of hashing functions for hardware applications. In: Proc. ICCI, Peterborough, Ontario, Canada
Sandvine (2008) Sandvine white paper. http://www.sandvine.com. Accessed 3 Sep 2011
Schulze H, Mochalski K (2010) Internet study 2008/2009. http://www.ipoque.com/resources/internet-studies/internet-study-2008_2009. Accessed 3 Sep 2011
Sen S, Spatscheck O, Wang D (2004) Accurate, scalable in-network identification of P2P traffic using application signatures. In: Proc. ACM WWW, New York, USA
Song H, Dharmapurikar S, Turner J, Lockwood J (2005) Fast hash table lookup using extended bloom filter: an aid to network processing. In: Proc. ACM SIGCOMM, Philadelphia, PA, USA
Xu J, Singhal M (2002) Cost-effective flow table designs for high-speed routers: architecture and performance evaluation. IEEE Trans Comput 51(9):1089–1099
Ye M, Wu J, Xu K, Chiu D (2009) Identify P2P traffic by inspecting data transfer behaviour. In: Proc. IFIP NETWORKING, Aachen, Germany
Zhou Z, Song T (2011) File-aware P2P traffic classification. In: Proc. IEEE GLOBECOM workshops, Houston, Texas, USA
Zhou Z, Song T, Wenliang F (2012) RocketTC: a high throughput traffic classification architecture. In: Proc. IEEE ICNC, Maui, Hawaii, USA
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61272510, 60803002), Beijing Key Discipline Program. We thank Dr. Zhaoyi Wei for his help and valuable suggestions. Thanks also to the editors and reviewers for their insightful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, T., Zhou, Z. File-aware P2P traffic classification: An aid to network management. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 6, 325–339 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-012-0172-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-012-0172-4