Abstract
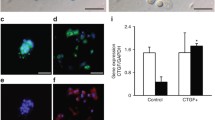
ErbB4 receptor and thyroid transcription factor (TTF)-1 are important modulators of fetal alveolar type II (ATII) cell development and injury. ErbB4 is an upstream regulator of TTF-1, promoting its expression in MLE-12 cells, an ATII cell line. Both proteins are known to promote surfactant protein-B gene (SftpB) and protein (SP-B) expression, but their feedback interactions on each other are not known. We hypothesized that TTF-1 expression has a feedback effect on ErbB4 expression in an in-vitro model of isolated mouse ATII cells. We tested this hypothesis by analyzing the effects of overexpressing HER4 and Nkx2.1, the genes of ErbB4 and TTF-1 on TTF-1 and ErbB4 protein expression, respectively, as well as SP-B protein expression in primary fetal mouse lung ATII cells. Transient ErbB4 protein overexpression upregulated TTF-1 protein expression in primary fetal ATII cells, similarly to results previously shown in MLE-12 cells. Transient TTF-1 protein overexpression down regulated ErbB4 protein expression in both cell types. TTF-1 protein was upregulated in primary transgenic ErbB4-depleted adult ATII cells, however SP-B protein expression in these adult transgenic ATII cells was not affected by the absence of ErbB4. The observation that TTF-1 is upregulated in fetal ATII cells by ErbB4 overexpression and also in ErbB4-deleted adult ATII cells suggests additional factors interact with ErbB4 to regulate TTF-1 levels. We conclude that the interdependency of TTF-1 and ErbB4 is important for surfactant protein levels. The interactive regulation of ErbB4 and TTF-1 needs further elucidation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATII cells:
-
Alveolar type II cells
- BPD:
-
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- RDS:
-
Respiratory distress syndrome of the neonate
- ErbB4:
-
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase
- HER4 :
-
Human ErbB4 encoding gene
- TTF-1:
-
Thyroid transscription factor 1
- Nkx2.1 :
-
TTF-1 encoding gene
- SP-B:
-
Surfactant protein B
- SftpB :
-
SP-B encoding gene
- 4ICD:
-
ErbB4 intracellular domain
- MLE-12:
-
Mouse lung epithelium 12 cell line
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- E:
-
Embryonic day
- HBSS:
-
Hank’s buffered salt solution
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline solution
- HER4heart(−/−):
-
Homozygote ErbB4 negative transgene
- HER4heart(+/-):
-
Heterozygote transgene
- EGFP:
-
Enhanced green fluorescent protein
- HITES:
-
Hydrocortisone, insulin, transferrin, estrogen and selenium
- BCA:
-
Bicinchoninic acid
References
Beam KS (2014) A systematic review of randomized controlled trials for the prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in infants. J Perinatol 34(9):705–710
Berghmans T (2006) Prognostic role of thyroid transcription factor-1 in stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 52(2):219–224
Bingle CD (1997) Thyroid transcription factor-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 29(12):1471–1473
Boggaram V (2009) Thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1/Nkx2.1/TITF1) gene regulation in the lung. Clin Sci (Lond) 116(1):27–35
Bose CL (2008) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia and inflammatory biomarkers in the premature neonate. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 93(6):F455–F461
Brasch F, Johnen G, Winn-Brasch A, Guttentag SH, Schmiedl A, Kapp N, Suzuki Y, Müller KM, Richter J, Hawgood S, Ochs M (2004) Surfactant protein B in type II pneumocytes and intra-alveolar surfactant forms of human lungs. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 30(4):449–458
Carpenter RH (2002) Reaching out: cortical mechanisms of directed action. Curr Biol 12(15):R517–R519
Chi X, Garnier G, Hawgood S, Colten HR (1998) Identification of a novel alternatively spliced mRNA of murine pulmonary surfactant protein B. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 19(1):107–113
Corti M (1996) Isolation and primary culture of murine alveolar type II cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 14(4):309–315
Dammann CE (2003) Role of neuregulin-1 beta in the developing lung. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167(12):1711–1716
Das A (2011) Thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) gene: identification of ZBP-89, Sp1, and TTF-1 sites in the promoter and regulation by TNF-alpha in lung epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 301(4):L427–L440
DeFelice M (2003) TTF-1 phosphorylation is required for peripheral lung morphogenesis, perinatal survival, and tissue-specific gene expression. J Biol Chem 278(37):35574–35583
Devriendt K (1998) Deletion of thyroid transcription factor-1 gene in an infant with neonatal thyroid dysfunction and respiratory failure. N Engl J Med 338(18):1317–1318
Dey Hazra RO (2011) Age-Dependent In Vitro mouse lung type II cell behavior. E-PAS 2011:3825.200
Fiaturi N (2014) Dissociated presenilin-1 and TACE processing of ErbB4 in lung alveolar type II cell differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1843(4):797–805
Frerking I (2001) Pulmonary surfactant: functions, abnormalities and therapeutic options. Intensive Care Med 27(11):1699–1717
Gassmann M (1995) Aberrant neural and cardiac development in mice lacking the ErbB4 neuregulin receptor. Nature 378(6555):390–394
Gullick WJ (2003) c-erbB-4/HER4: friend or foe? J Pathol 200(3):279–281
Hamdan H (1998) Structure of the human Nkx2.1 gene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1396(3):336–348
Hamm A (2002) Efficient transfection method for primary cells. Tissue Eng 8(2):235–245
Hoeing K (2011) Presenilin-1 processing of ErbB4 in fetal type II cells is necessary for control of fetal lung maturation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813(3):480–491
Jobe AH (1993) Beneficial effects of the combined use of prenatal corticosteroids and postnatal surfactant on preterm infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol 168(2):508–513
Jonckheere N (2010) The mouse Muc5b mucin gene is transcriptionally regulated by thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) and GATA-6 transcription factors. FEBS J 278(2):282–294
Kair LR (2012) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Rev 33(6):255–263, quiz 263–4
Kao WW (1977) Proline analogue removes fibroblasts from cultured mixed cell populations. Nature 266(5597):63–64
Keller-Wood ME (1984) Corticosteroid inhibition of ACTH secretion. Endocr Rev 5(1):1–24
Kwei KA (2008) Genomic profiling identifies TITF1 as a lineage-specific oncogene amplified in lung cancer. Oncogene 27(25):3635–3640
Lee HJ (2002) Presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase-like intramembrane cleavage of ErbB4. J Biol Chem 277(8):6318–6323
Li C (2000) Two functionally distinct forms of NKX2.1 protein are expressed in the pulmonary epithelium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 270(2):462–468
Liu W (2007) The ErbB4 receptor in fetal rat lung fibroblasts and epithelial type II cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1772(7):737–747
Liu W (2010) ErbB4 regulates the timely progression of late fetal lung development. Biochim Biophys Acta 1803(7):832–839
Marsh LM (2009) Surface expression of CD74 by type II alveolar epithelial cells: a potential mechanism for macrophage migration inhibitory factor-induced epithelial repair. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 296(3):L442–L452
Minoo P (1995) TTF-1 regulates lung epithelial morphogenesis. Dev Biol 172(2):694–698
Moldvay J (2004) The role of TTF-1 in differentiating primary and metastatic lung adenocarcinomas. Pathol Oncol Res 10(2):85–88
Northway WH Jr (1967) Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane disease. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med 276(7):357–368
Perez-Gil J (2008) Structure of pulmonary surfactant membranes and films: the role of proteins and lipid-protein interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778(7–8):1676–1695
Purevdorj E (2008) ErbB4 deletion leads to changes in lung function and structure similar to bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294(3):L516–L522
Saugstad OD (2003) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia-oxidative stress and antioxidants. Semin Neonatol 8(1):39–49
Shupnik MA (1989) Molecular biology of thyrotropin. Endocr Rev 10(4):459–475
Stahlman MT (1996) Expression of thyroid transcription factor-1(TTF-1) in fetal and neonatal human lung. J Histochem Cytochem 44(7):673–678
Takahashi Y (2010) Thyroid transcription factor-1 influences the early phase of compensatory lung growth in adult mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 181(12):1397–1406
Tanaka H (2007) Lineage-specific dependency of lung adenocarcinomas on the lung development regulator TTF-1. Cancer Res 67(13):6007–6011
Tidcombe H (2003) Neural and mammary gland defects in ErbB4 knockout mice genetically rescued from embryonic lethality. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(14):8281–8286
Warshamana GS (2001) TNF-alpha, PDGF, and TGF-beta(1) expression by primary mouse bronchiolar-alveolar epithelial and mesenchymal cells: tnf-alpha induces TGF-beta(1). Exp Mol Pathol 71(1):13–33
Whitsett JA (2015) Alveolar development and disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol
Wikenheiser KA (1993) Production of immortalized distal respiratory epithelial cell lines from surfactant protein C/simian virus 40 large tumor antigen transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90(23):11029–11033
Williams CC (2004) The ERBB4/HER4 receptor tyrosine kinase regulates gene expression by functioning as a STAT5A nuclear chaperone. J Cell Biol 167(3):469–478
Zhou B (2008) Foxp2 inhibits Nkx2.1-mediated transcription of SP-C via interactions with the Nkx2.1 homeodomain. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 38(6):750–758
Zscheppang K (2011) Neuregulin receptor ErbB4 functions as a transcriptional cofactor for the expression of surfactant protein B in the fetal lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 45(4):761–767
Zscheppang K (2013) ErbB4 is an upstream regulator of TTF-1 fetal mouse lung type II cell development in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833(12):2690–2702
Zu YF (2012) Thyroid transcription factor 1 represses the expression of Ki-67 and induces apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep 28(5):1544–1550
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. M. Gassmann and C. Birchmeier for providing the HER4heart mouse line. The studies were funded by NIH NHLBI R01 HL085648, HL037930, and Hannover Medical School.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Authors’ contributions
Elger Marten - experimental design, data generation and analysis, manuscript preparation; Heber Nielsen - experimental design, manuscript preparation; Christiane Dammann - experimental design, manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Figure 1
HER4heart transgenic mice are rescued from their lethal cardiac defect by the α-myosin heavy chain (MHC) promotor resulting in ErbB4 gene expression exclusively in the heart. (A) This cardiac rescue construct (upper blot) was detected by PCR in all mice containing at least one ErbB4-mutated allele. The mutated allele itself was detected at 320 bp and the wild type allele at 150 bp (lower blot). Representative samples of heterozygous (+/−), homozygous wild type (+/+) and homozygous ErbB4 mutated (−/−) mice are shown. (B) Representative Western blots of lung fibroblast homogenates of heterozygous (−/+) and homozygous (−/−) transgenic HER4heart mice confirmed that there is no pulmonary ErbB4 protein expression in ErbB4 −/− animals. β-actin reprobing was used to control for protein loading. (GIF 87 kb)
Supplemental Figure 2
Transfection efficiency in MLE-12 cells (A) and primary fetal ATII cells (B). Fluorescence-labeled EGFP constructs were used to identify transfection cells. The transfection efficiency was about 30–40 % in MLE-12 cells and about 20 % in primary fetal ATII cells. DAPI staining was used to identify total cell numbers. (GIF 46 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marten, E., Nielsen, H.C. & Dammann, C.E.L. Interdependent TTF1 - ErbB4 interactions are critical for surfactant protein-B homeostasis in primary mouse lung alveolar type II cells. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 9, 207–215 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-015-0299-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-015-0299-1